This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor II Nguyen Binh - Department of General Surgery - Vinmec Ha Long International Hospital. Doctor Nguyen Binh has more than 20 years of experience in the field of anesthesia and resuscitation.Endotracheal anesthesia is a technique used in laparoscopic cholecystectomy to control the patient's breathing during and after surgery.
1. What is endotracheal anesthesia?
In laparoscopic cholecystectomy, general anesthesia with endotracheal intubation, also known as endotracheal anesthesia, is used to control the patient's breathing during and after surgery. .2. What preparation is required for endotracheal anesthesia for laparoscopic cholecystectomy?
To perform endotracheal anesthesia for laparoscopic cholecystectomy, it is necessary to have the following means, machinery, equipment, and medications:The system includes an anesthetic machine (with breathing), oxygen hand squeezer, monitor vital function indicators (such as arterial blood pressure, breathing rate, temperature, ECG, EtCO2, SpO2), suction machine, defibrillator, ... endotracheal tube sizes to place, lights laryngoscope, mask, straw, oropharyngeal cannula, squeeze balloon, soft mandrin, Magill pliers. Salbutamol and Lidocaine 10% spray. Other means of supporting endotracheal anesthesia in case of difficult intubation: laryngeal mask, Cook tube, flexible bronchoscope, mouth opening pliers, tracheostomy kit, ...
3. Endotracheal anesthesia procedure laparoscopic cholecystectomy
Before performing surgery, patients need to be examined under anesthesia to promptly detect and prevent possible risks, as well as evaluate difficult intubation status.
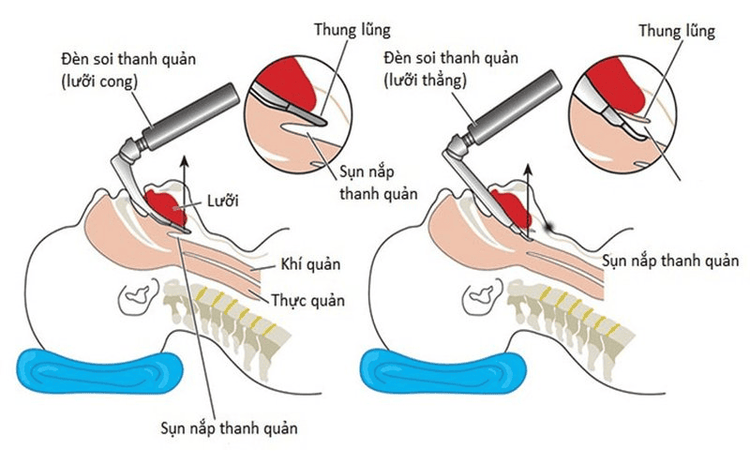
Step 1: Put the patient in a supine position, at least 5 minutes before induction of anesthesia, give 100% oxygen with the dose 3 - 6 liters/min. Install machines to monitor and set up transmission lines. If necessary, the patient can be given sedatives from the night before surgery. Step 2: Initiation of anesthesia begins with intravenous injection (drugs: etomidate, propofol, ketamine, ...), analgesics (fentanyl, sufentanil, ...), using muscle relaxants (rocuronium, succinylcholine, .. .). It is necessary to ensure conditions for endotracheal intubation in laparoscopic cholecystectomy (patients sleep deeply, muscles relax enough). Step 3: Perform oral intubation. The technique of oral intubation is performed as follows: (1) Open the patient's mouth, insert the laryngoscope into the right side of the mouth, move the tongue to the left side of the mouth, insert the light deeply, and combine Use the right hand to press the cricoid cartilage to find the lid and glottis; (2) Perform rapid induction of anesthesia and perform the Sellick maneuver when the stomach is full (as soon as the patient loses consciousness, press the cricoid cartilage 20 - 30 kg until the intubation process is complete); (3) The next step in endotracheal anesthesia is to gently insert the endotracheal tube through the glottis, when the endotracheal tube balloon passes through the vocal cords about 2-3 cm, it stops; (4) Gently withdraw the laryngoscope; (5) Intubation of endotracheal balloon; (6) Listen to the lungs, see the EtCO2 index to check that the endotracheal tube is in place; (7) Use adhesive tape to fix the endotracheal tube. In case, if it is necessary to avoid biting the endotracheal tube, the cannula can be placed into the patient's mouth. Step 4: The next step in endoscopic cholecystectomy anesthesia is to maintain anesthesia with anesthetics (intravenous or vapor), analgesia, muscle relaxants (if needed), and control breathing of the patient by machine.
4. Monitoring during endotracheal anesthesia laparoscopic cholecystectomy
During endotracheal anesthesia for laparoscopic cholecystectomy, the following signs and indicators should be monitored:Depth of anesthesia: Monitor blood pressure, heart rate, blood pressure, sweating status , tears, BIS, MAC, Entropy (if any) ... Vital signs: Monitor blood pressure, heart rate, body temperature, EtCO2, SpO2 indicators. Monitor in case of wrong position of endotracheal tube, or blocked, folded tube. At the end of endotracheal anesthesia, the following criteria should be met before extubation:
The patient is awake and can follow orders. Breathe spontaneously, breathe evenly, breathing rate is within normal limits. Blood pressure and pulse are stable. Body temperature over 35 degrees Celsius. Raise head >5 seconds, TOF index >0.9 (if any). The patient had no complications from anesthesia and surgery.
5. Management of complications after endotracheal anesthesia laparoscopic cholecystectomy
During endotracheal anesthesia, laparoscopic cholecystectomy may occur some complications that need to be treated as follows:Gastric reflux airway: When digestive juices are detected in the oral cavity and airway, immediately drain the fluid, place the patient in a low position and tilt the head to the side. Rapidly intubate the endotracheal tube and remove all fluid from the airway. Monitor patients for lung infections after surgery. Hemodynamic disturbances: Depending on the cause and symptoms such as arrhythmia, increase or decrease in blood pressure, ... will be treated appropriately. Difficult intubation in anesthesia laparoscopic cholecystectomy: Switch to difficult intubation procedure or proceed to another method of anesthesia. Misplaced endotracheal tube into the stomach: Re-intubate the endotracheal tube when misplaced with symptoms of auscultation of the lungs without alveolar murmurs, no measurement of EtCO2. Constriction of the larynx, trachea, bronchi: Complications during endotracheal anesthesia can cause difficulty or inability to ventilate, at this time there will be a hissing sound or a muted lung. For management, it is necessary to provide adequate oxygen, and at the same time give sleeping pills and muscle relaxants, bronchodilators and corticosteroids to ensure ventilation. In case of respiratory failure, difficult intubation procedure should be applied. Trauma in endotracheal intubation: Depending on the injury such as tooth fracture, bleeding, foreign body in the airway, ... will be treated appropriately. Respiratory complications: Find and treat the cause, ensure ventilation and provide 100% oxygen when endotracheal anesthesia causes respiratory complications such as endotracheal tube being folded, retracted or pushed deep into one lung. , open or collapsed respiratory system, oxygen is exhausted, the effect of soda is gone, causing hypoxia. Complications after extubation: Depending on the cause, choose appropriate management when symptoms appear after extubation such as respiratory failure, hoarseness, sore throat, laryngospasm, gas trachea, bronchi, laryngotracheal and tracheal stenosis, upper respiratory tract infection. Endotracheal anesthesia laparoscopic cholecystectomy oral endotracheal intubation. During and after anesthesia, surgery needs to be monitored and promptly treated for possible complications.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.