This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Nguyen Xuan Tinh - Anesthesiologist - Resuscitation - Department of General Surgery - Vinmec Phu Quoc International General Hospital. Doctor Nguyen Xuan Tinh has more than 18 years of experience studying and working in the field of Anesthesia - Resuscitation.Goiter surgery is an effective method in the treatment of goiter. When surgery is indicated, the patient will be given endotracheal anesthesia to ensure a smooth treatment process and improve the success rate.
1. An overview of goiter
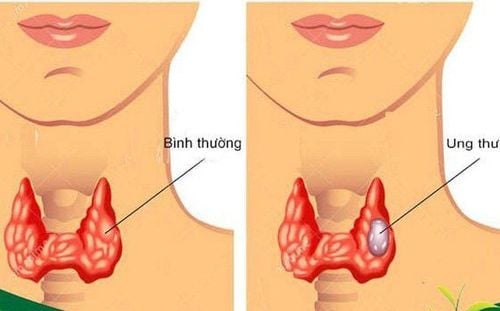
Goiter is a common disease in the thyroid gland, more common in women than in men, with the basic manifestation of the patient's neck area being protruded due to the influence of thyroid size. There are 5 types of goiter:Simple goiter Toxic thyroid goiter Benign thyroiditis Thyroiditis with goiter Thyroid cancer. The most common cause of goiter is iodine deficiency. In addition, the risk of disease will increase if using synthetic antithyroid drugs, contrast agents... inhibiting the thyroid's ability to synthesize hormones; congenital factors; smoking, thyroiditis, hormonal changes,...
Symptoms of goiter patients are enlarged thyroid gland, difficulty swallowing, difficulty breathing when lying down, or nervousness, excessive sweating, decreased Weight loss, frequent stress, dry skin, impaired memory, frequent constipation or feeling cold,... Treatment methods for goiter include: Periodic follow-up (clinical examination and glandular ultrasound) thyroid), medical treatment (using drugs to return thyroid hormone to a normal state), thyroid radiation therapy (using radioactive iodine to reduce the size of the thyroid gland) and thyroid surgery (removal of a thyroid gland). part or all of the thyroid gland).
2. Endotracheal anesthesia for goiter surgery
Endotracheal anesthesia is a technique of general anesthesia, endotracheal intubation for the purpose of controlling breathing for patients during surgery and postoperative resuscitation.Patients undergoing goiter surgery are assigned anesthesia. This technique is relatively contraindicated if the patient does not agree to the treatment, the place of operation does not have enough anesthesia and resuscitation facilities, or the operator is not proficient in the technique.
2.1 Anesthesia preparation Personnel to perform: Anesthesiology specialist doctors and nurses; Technical facilities: Anesthesia machine system with breathing, life function monitor, defibrillator, hand squeeze oxygen source, suction machine, laryngoscope, endotracheal tube of all sizes, mask, suction tube , squeezing ball, canul, Magill forceps, soft mandrin, Salbutamol spray, Lidocaine 10% spray, means of preventing difficult intubation; Patients: Are examined for anesthesia before surgery (to detect and prevent the risk of complications); be explained about the procedure, benefits and risks; evaluated difficult intubation; sedation may be used the night before surgery if necessary; Medical records: Complete according to regulations.

Step 2: General procedure: Put the patient in supine position, breathe 100% oxygen with flow rate 3 - 6 liters/minute at least 5 minutes before induction of anesthesia. Simultaneously, install a monitor, establish an effective line, and give pre-anesthesia if necessary.
Step 3: Initiating anesthesia: Give the patient sleeping pills (including intravenous anesthetics, volatile anesthetics), pain relievers and muscle relaxants if needed. Conditions for endotracheal intubation are satisfied when the patient is in deep sleep and has adequate muscle relaxation.
Step 4: Intubation: Choose 1 of 2 following techniques:
Intubation of the nasal passage:
Select the side of the nasogastric tube and perform nasal vasoconstrictor drops; Choose an endotracheal tube that is smaller in size than an oral tube. Then, insert the tube lubricated with Lidocaine grease through the nostril; Open the patient's mouth, insert the laryngoscope into the mouth, coordinate the manipulation to find the epiglottis and glottis; In favorable circumstances, gently insert the endotracheal tube through the glottis, stopping if the balloon of the tube passes about 2 - 3 cm across the vocal cords. Then, use Magill pliers to guide the end of the endotracheal tube into the correct glottis hole, coordinate pushing the tube in from the outside in difficult cases. Then, remove the laryngoscope, inflate the endotracheal balloon, listen to the lungs and rely on EtCO2 results to check the exact position of the endotracheal tube; fix the endotracheal tube with adhesive tape; In case of difficult intubation, the difficult intubation procedure is applied. Oral endotracheal intubation:
Open the patient's mouth, insert the laryngoscope into the mouth, coordinate manipulation to find the epiglottis and glottis; Rapid induction of anesthesia and a Sellick maneuver (if the patient's stomach is full); Pass the endotracheal tube gently through the glottis and stop when the balloon is about 2 - 3 cm past the vocal cords; Gently withdraw the laryngoscope, inflate the endotracheal balloon; Check the position of the endotracheal tube through auscultation and EtCO2 results; Fix the tube with adhesive tape, place the cannula in the mouth to prevent the patient from biting the endotracheal tube if necessary. Step 5: Maintain anesthesia with volatile anesthetics or intravenous anesthetics, analgesics and muscle relaxants (if necessary). At the same time, control the patient's breathing with a machine or hand squeeze.
Step 6: Monitor the depth of anesthesia based on sweating, blood pressure, heart rate, lacrimation. At the same time, monitor vital signs (heart rate, body temperature, blood pressure, SpO2 and EtCO2); prevent the endotracheal tube from being misplaced or folded or blocked.
Step 7: Criteria for extubation: The patient is awake and can follow the doctor's request; Raise the head for more than 5 seconds, breathe spontaneously, the respiratory rate is within normal limits, the body temperature is above 35°C, the pulse and blood pressure are stable, there are no complications from anesthesia or surgery.
2.3 Risk of complications and management Hemodynamic disorders: The patient may have hypotension or hypertension, arrhythmia. The treatment will depend on the cause and symptoms, strictly adhere to the standard treatment regimen; Reflux of gastric juice into the airway: Manifested by the presence of digestive juices in the oral cavity and airways of the patient. The appropriate intervention is to drain the fluid, place the patient's head low and tilt the head to the side; Place the endotracheal tube quickly and clear the airway. Next, monitor and prevent lung infection after goiter surgery; Complications due to intubation: Including failure to put the endotracheal tube, wrong placement of the tube into the stomach, laryngospasm - tracheobronchospasm, trauma when intubation,... The management will depend on causes and symptoms of damage; Respiratory complications: Including folding, retraction, tube pushed deep into 1 lung, out of oxygen source, hypoxia, hypercapnia,... Should be intervened by ensuring ventilation, providing 100% oxygen to the patient and find out the cause for appropriate treatment; Complications after extubation: Sore throat, hoarseness, respiratory failure, laryngotracheal-bronchospasm, laryngotracheal stenosis, upper respiratory tract inflammation,... The management will depend on the symptoms. symptoms and causes, strictly followed the standard protocol.

Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
SEE MOREGoiter: When to operate? Common symptoms warning thyroid disease Surgery to treat thyroid cancer