This is an automatically translated article.
Children with ductus arteriosus are prone to bronchitis, pneumonia, physical retardation, and malnutrition. Endoscopic ductal clamping is a safe and effective method for the treatment of ductal artery disease.
1. What problems does the ductus arteriosus cause for the child?
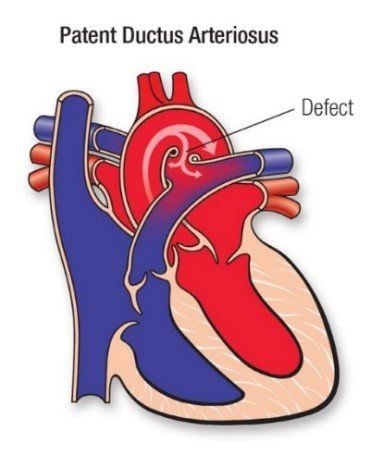
During fetal development, a ductus arteriosus exists for communication between the aorta and pulmonary artery.After the baby is born, the ductus arteriosus will have to be closed. However, in some children, this ductus arteriosus still exists, causing left-right shunts, overloading the pulmonary circulation, left atrium and left ventricle leading to pulmonary hypertension, respiratory symptoms such as: Fatigue, dyspnea, pulmonary artery dilation, left atrium, left ventricle dilation, diastolic blood pressure drop.
In these cases, the patient will have surgery to close the ductus arteriosus and prevent and treat complications.

Ống động mạch không đóng gây ra nhiều biến chứng xấu cho trẻ
2. Endoscopic thoracoscopic surgery with ductal clamping
2.1. Indications Patients are diagnosed with ductal artery disease and accompanied by one or more of the following symptoms: large ducts (over 4mm), shortness of breath, pneumonia, growth retardation, structural changes of heart chambers, heart valves , endocarditis. The diameter of the ductus arteriosus should not exceed the diameter of the clip (8-9mm). 2.2 Contraindications Relative contraindications for cases.
Fixed pulmonary hypertension Heart failure, severe liver and kidney failure Complicated congenital heart disease Progressive infection Chest deformity, left pleural thickening due to trauma or pathology.

Phẫu thuật chống chỉ định với đối tượng mắc bệnh lý tim bẩm sinh phức tạp
2.3 Procedure Posture: Patient lying on his side should be slightly prone 20-30 degrees from the table. Let small children lie horizontally and older children lie vertically on the table. The surgeon stands at the patient's feet and the assistant stands to the left of the surgeon, the monitor is placed at the patient's head. Anesthesia ventilation 1 lung Place 4 Trocar Inflatable pressure 6-8mmHg, flow rate 1 liter/min. Move the superior lobe of the lung into the ductus arteriosus. Open the pleura along the anterior border of the aorta from below the duct to the origin of the subclavian artery. Pull the pleural flap with the X nerve and the recurrent nerve inward, dissecting to clearly see the recurrent nerve. Exposing the ductus arteriosus, dissecting the superior and inferior slits between the aorta and the ductus arteriosus; Dissect the posterior aspect of the ductus arteriosus until the surgical needle can be inserted through the posterior surface of the ductus arteriosus to the angle between the ductus arteriosus and the aorta above the ductus. Next, insert a segment of vicryl 2.0 suture through the posterior surface into the inferior cleft of the ductus arteriosus with the aorta; Raise the thread to pull the ductus arteriosus forward. Then, insert the clip-carrying pliers into the thorax, pass through the ductus arteriosus and clip the ductus arteriosus with 1 or 2 clips Withdraw 3 Trocart for the instrument, suture the skin incision Squeeze the balloon to inflate the lung Withdraw Trocart for the bronchoscope , suture skin incision
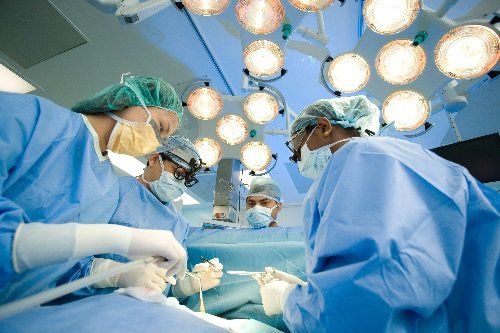
Tiến hành mổ nội soi lồng ngực kẹp ống động mạch
2.4.Monitoring after surgery Monitor pulse, blood pressure, breathing rate. When the patient returns to the recovery room: Take a lung scan. Monitor for signs of bleeding, pneumothorax. Follow-up of incisions Check echocardiogram before hospital discharge After 6 months, ultrasound 1 time to assess cardiac rehabilitation after surgery 2.5. Management of complications Hemothorax-pneumothorax: medical treatment, pleural drainage or re-operation depending on the severity.
Atelectasis: Bronchoscopy to aspirate sputum, re-operate. Heart failure: Cardiac treatment, resuscitation. Infection: Change dressing, culture microbiology then treat according to antibiotic chart. Residual tube: Medical treatment or re-surgery. Nerve damage: Medical treatment. Any questions that need to be answered by a specialist doctor as well as if you want to be examined and treated at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide or register online. online HERE.