This is an automatically translated article.
Endoscopic nasopharyngeal fibrocystectomy is one of the advanced methods in the treatment of nasopharyngeal fibroids. Currently, this is a common disease in puberty, causing facial deformities in patients and the cause is still unknown.1. What is nasopharyngeal angioma?
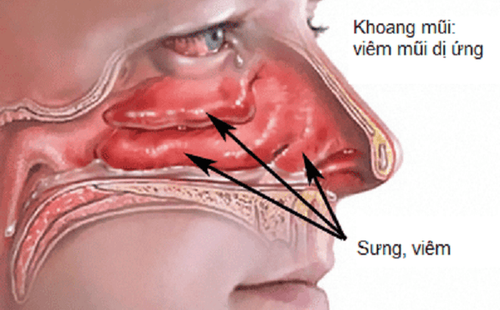
Nasopharyngeal fibroma is a benign tumor with the nature of an accumulation of vascular fibers. However, this tumor has the ability to spread quickly and destroy bone, even spreading to the intracranial cavity, endangering the patient's life if not treated promptly.Nasopharyngeal fibroids are a common disease in puberty from 15 to 25 years old, common in men. To date, the pathogenesis is still not clear, but many studies indicate that this tumor formation may be related to the hormonal changes during puberty.
2. Learn the surgery to cut nasopharynx fibroids
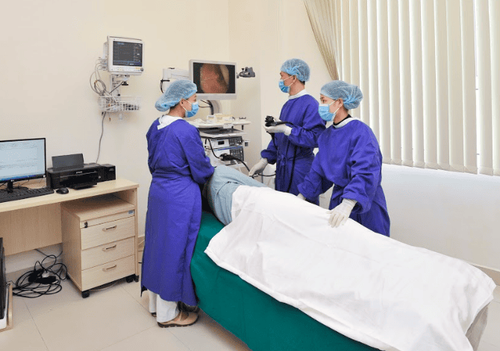
Nasopharyngeal angioplasty is a treatment method that uses endoscopy in combination with surgical instruments and nasopharynx microsurgery to dissect and remove the tumor through the natural route in the nasal cavity.This surgery will be performed by an ENT specialist with extensive training in head and neck tumor surgery - ENT.
3. In which case is cutting nasopharyngeal fibroid indicated?
Phẫu thuật mổ nội soi cắt u xơ vòm mũi họng được chỉ định trong các trường hợp bệnh nhân có u xơ mạch vòm mũi họng ở giai đoạn I và giai đoạn II
Tumor is localized in the posterior nasal cavity, maxillary sinus, nasopharynx and sphenoid fossa. No tumor has spread to the lower fossa of the temples, the base of the skull, the eye sockets... Nasopharyngeal fibroid surgery has no absolute contraindications.
4. How is surgery performed to remove nasopharynx fibroids?
Preparation Doctors will check the patient's medical record before anesthesia, and the patient will have angiography and digital embolization to reduce the risk of bleeding during surgery. Besides, the patient is also checked more about body temperature, vascular disease, blood pressure,...Techniques used in surgery for nasopharyngeal angiofibromas. Then 1: endoscopy to check for lesions. and perform vasoconstriction by numbing wick impregnated with oxymetazolin, naphazolin or lidocaine, xylocaine 3%. After about 3-5 minutes, withdraw the anesthetic wick and inject 2% lidocaine to numb the area of the hook process, the medial coil, along the septum and the position of the outlet of the posterior palatal sphenoid artery. Stage 2: endoscopically cut the middle or the middle tail depending on the volume, size and extent of tumor spread. Use a blunt-tipped probe to probe, assess, and predict tumor volume, adhesion, bleeding potential, and structures to be removed. Stage 3: widen the maxillary sinus opening and partially resect the inner and posterior wall of the maxillary sinus. Stage 4: using bipolar electrocoagulation to coagulate the veins of the tumor's attachment legs from top to bottom, front to back, and from outside to inside. Note that this is a bleeding step, so the doctor performing it must be able to handle the possible risks. During electrocoagulation, the attachment legs of the tumor are gradually separated from the tumor. After this process, use tongue pressure to check and gently remove the tumor along the oropharynx. Stage 5: examine the surgical cavity, hemostasis by bipolar electrocoagulation and other techniques. Stage 6: evaluate the amount of blood lost, the time of surgery and the prognosis of possible complications, from which to plan the follow-up. End of surgery. Follow-up after surgery to remove nasopharyngeal fibroids. Patients after surgery will still be sedated due to the effects of drugs. The patient will regain consciousness within a few hours and the breathing tube will be removed once the patient is fully awake and there is no longer bleeding.
After about 48 hours, the doctors will remove the nasal wick and take gelaspon if any. In addition, the patient will be monitored for bleeding, infection, swelling, etc. to have a suitable remedy.
When the incision is completely safe and bleeding is stopped, the patient will be discharged from the hospital (usually about 7 days after surgery).
5. Possible complications when performing surgery to cut nasopharyngeal fibroids
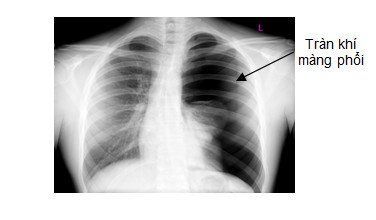
Tràn khí màng phổi là một trong số những tai biến có thể gặp trong gây mê
Other complications Ocular artery occlusion. Cerebrospinal fluid leak. Orbital hematoma... Laparoscopic surgery to cut nasopharyngeal fibroids is a complex microsurgery that requires high expertise and good skill from the performer.
Vinmec International General Hospital examines and treats common nasopharyngitis diseases, head and neck tumors, congenital malformations of the ear, nose and throat area with the most optimal internal and surgical methods for patients, both children and adults. Coming to Vinmec International General Hospital, patients will receive a direct, dedicated and professional examination from a team of qualified and experienced medical staff.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE
See more:
Throat cancer: Causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment of Nasal Polyps: Causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment Nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment