This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Dong Xuan Ha - Gastroenterologist - Department of Medical Examination and Internal Medicine - Vinmec Ha Long International Hospital.The gastroscopy will help doctors observe the gastric endoscopy image in a clear and detailed way and accurately assess the extent of the disease to predict the possibility of treatment.
1. What is gastritis?
Gastritis is a condition that causes inflammation and ulcers on the lining of the stomach. The cause of these injuries is because the last protective lining of the stomach is severely eroded, exposing the underlying tissue layer, causing inflammation leading to stomach ulcers. The disease can cause gastrointestinal bleeding if the ulcer is large and bleeds. If the patient does not detect gastrointestinal bleeding complications for timely treatment, it may die from blood loss.The main causes of gastritis are:
Helicobacter pylori: HP is a bacteria that, after penetration, will develop in the mucous layer of the stomach lining. They secrete toxins that make the mucosa less resistant to acid, causing chronic gastritis that progresses to ulcers or gastric cancer. Excessive use of pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs: Pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs, when used for a long time, will have side effects that increase acid secretion, inhibit the protective substances of the stomach lining causing pain and lead to inflammation. stomach and stomach ulcers. Excessive stress: Stress, fear, or anger can cause gastric juice to increase, causing serious damage to the protective lining of the stomach, leading to gastritis. Eating and living in moderation: Eating and living in moderation such as: eating too late, sleeping too late, getting up too early, ... leading to the contraction of the stomach is affected, causing gastric juice. The stomach increases secretion, so the protective layer of the mucosa is seriously damaged, which will eventually lead to gastritis and stomach ulcers. Some other causes of gastritis such as autoimmune diseases, chemicals, frequent drinking, smoking, ...

Abdominal pain in the epigastrium: This is the main sign of the disease. This symptom will appear during fasting or at night. The pain is dull or persistent with a burning sensation in the epigastrium. Frequent burping: People with gastritis often burp, burp, burp, belch, nausea, vomiting and have an uncomfortable feeling in the stomach. Digestive disorders: The patient has bloating, slow digestion, diarrhea or maybe constipation due to unstable digestion.

2. Gastroscopy to diagnose gastritis
The gastroscopy will help the doctor observe the gastric endoscopy image clearly and in detail and accurately assess the extent of the disease to predict the possibility of treatment.2.1. What is gastroscopy? Gastroscopy is a procedure that uses a flexible endoscope to view the esophagus, duodenum, duodenum, and stomach. This method is relatively safe. Possible complications such as mucosal scratches, infection, bleeding, tearing are due to the patient's non-cooperation. Those who have the following symptoms should go for a gastroscopy:
Indigestion, heartburn, belching, heartburn. Epigastric pain, nausea or vomiting, bloating, slow digestion. Pass black stools. People who treat diseases related to the digestive system. Some special cases such as difficulty swallowing, choking, prolonged cough with no known cause, weight loss, anemia...
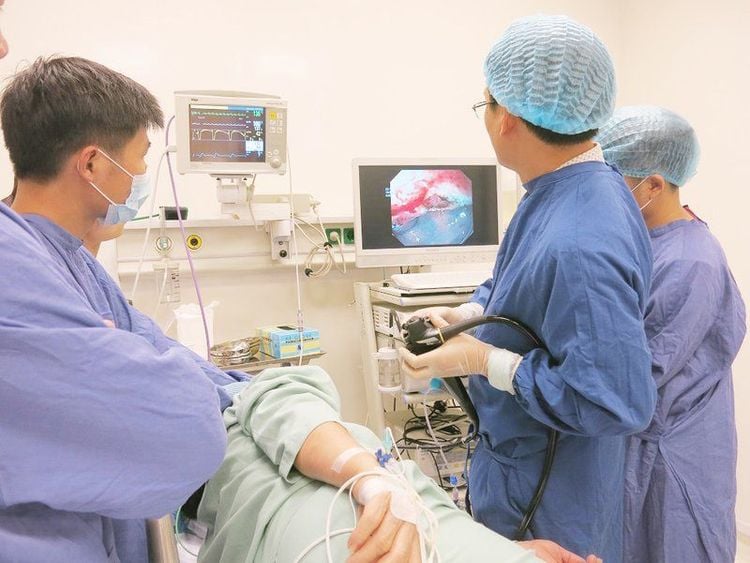
When conducting endoscopy, endoscopic images of the stomach are normal when the mucosa is soft, smooth, and pink; the body mucosa on the large curvature runs longitudinally, <5mm in width, disappears when inflated; Blood vessels in the gastric aneurysm can be observed.
Endoscopic signs of gastritis are diagnosed when:
Edema: The gastric mucosa is raised, slightly pale, white in color, possibly accompanied by secretions. Congestive: The mucosal area has black or red blood. Increased secretions: This condition is common in acute gastritis; there is a lot of mucus. Mucous membrane: Frictional mucosa; Hemorrhagic spots appear on light impact. Flat and convex: There is slippage in the mucosa (usually in the antrum or body); gastroscopy showed pseudomembranous fundus, congested margins; At the same time, there are high bulges. Mucosal atrophy: The mucosal area is thin, the mucosal folds of the body are atrophied. Intestinal metaplasia: Nodular raised lesion, may also have small plaques. Mainly found in the antrum. Endoscopic signs of gastritis are also diagnosed when bleeding in the wall, prominent blood vessels with granulomas, ...

MORE:
How long should I fast before a gastroscopy? What is colorectal cancer screening? Diet for patients with peptic ulcer disease
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.