This is an automatically translated article.
Currently, there are different treatments for endometriosis, including medication and surgery. Although surgery is considered the most effective method of treatment, however, doctors recommend that patients should prioritize the use of drugs first.
1. What is endometriosis?
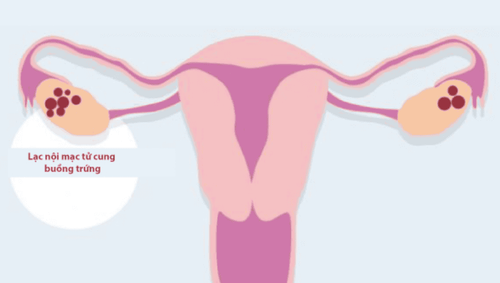
Endometriosis occurs when the endometrial tissue does not work as it should. During the menstrual cycle, instead of exiting the body with menstrual blood, these tissues back up and accumulate in other locations outside the uterus, such as the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and urinary tract. This condition can cause internal bleeding, inflammation and the formation of scar tissue making it difficult for you to get pregnant.
2. Symptoms of endometriosis
When you have endometriosis, the patient may face the following symptoms:
Severe abdominal pain during menstruation Low back pain Pelvic pain Pain that increases over time and has no signs signs of relief Pain during and after sex Abdominal pain before or during menstruation Pain when urinating or defecating Vaginal bleeding after sex Bloody stools or urine Menstrual disorders, irregular periods Body fatigue Constipation, flatulence, diarrhea, nausea Can't get pregnant

Đau bụng vùng chậu cảnh báo bệnh lý phụ khoa ở phụ nữ
These are common signs of endometriosis, symptoms can range from mild to severe, depending on the location and extent of growth of the “stray” tissue in the uterus. body. Although endometriosis is a benign disease, it still causes pain and discomfort for women in the "red light" days. If these symptoms are not controlled and treated early, they can lead to more serious complications, even leading to infertility. Therefore, when there are any signs of endometriosis, you should proactively see your doctor as soon as possible to get a diagnosis and find the appropriate treatment.
3. Causes of endometriosis
Endometriosis can be caused by many different factors, including:
Reflux: This is the most common cause of endometriosis. Endothelial cells are regurgitated into the body and adhere to the pelvic cavity. Abnormal immune system: Makes it difficult for the body to recognize and eliminate abnormal endometriosis tissue. Having a history of surgery: Scars left after surgery like a hysterectomy or a cesarean section can cause endometrial cells to stick to it and lead to endometriosis. uterine lining. The hormones estrogen and progesterone that work abnormally in the body is also one of the main causes of endometriosis. Inherited from family members, such as grandmothers, mothers, sisters, and younger sisters. toxic chemicals, especially dioxins. Early menstruation Abnormal shape and size of uterus

Yếu tố di truyền là nguyên nhân gây ra lạc nội mạc tử cung
4. Non-surgical endometriosis treatment options
Treatments for endometriosis will be selected based on each person's medical condition. The overall goal of treatment is to control and eliminate endometriosis, while helping to preserve fertility for the patient.
Experts often recommend that patients choose to treat endometriosis with drugs first, if this treatment is not effective, then switch to surgery. Here are some non-operative treatment options for endometriosis:
4.1 Pain medication If you have only mild symptoms, your doctor may prescribe pain medication. Pain relievers include:
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: including diclophenac, ibuprofen, or meloxicam. Antipyretic, analgesic: eg aspirin, paracetamol. Opioid pain relievers: include tramadol, hydrocodone, or fentanyl.
These pain relievers can be used alone or in combination to increase the effectiveness of treatment, helping patients control pain caused by endometriosis.
4.2 Hormone therapy Hormone therapy helps relieve symptoms of pain or heavy menstrual bleeding caused by endometriosis. The most common hormone therapies include:
Birth control pills, patches or rings: A combination of estrogen and progestin, or progestin only. The drug is given as an injection or in pill form. GnRH agonists: if pain cannot be controlled with NSAIDS or hormone therapy, your doctor may prescribe an active ingredient similar to gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH). This drug causes the ovaries to stop producing estrogen, which in turn causes endometriosis tissue to shrink. According to statistics, more than 80% of women after using this treatment have significantly reduced pain conditions, including cases of severe pain. Danazol (Danocrine): This drug works to block hormone release and ovulation, and increase the body's immune system. If the mother becomes pregnant while taking danazol, it may cause the baby girl to develop male characteristics. Aromatase inhibitors: Help the body limit the production of estrogen. These inhibitors are often used in combination with oral contraceptives when other treatments for endometriosis have not been effective.

Người bệnh nên đến gặp bác sĩ để được tư vấn về cách điều trị lạc nội mạc tử cung
5. Side effects of using drugs to treat endometriosis
Although pain relievers are very helpful in treating endometriosis, they can bring unwanted side effects to the patient. Specifically:
Causes stomach ulcers or high blood pressure if using pain relievers for a long time Causes drowsiness, nausea, dizziness, even respiratory failure when using opioid pain relievers . Birth control pills can cause symptoms such as headaches, breast tenderness, irregular bleeding, weight gain, or mood swings. Vaginal dryness, decreased sex drive, decreased bone density, or insomnia have been reported with the use of GnRH agonists. Edema, acne, or appearance of male characteristics such as dense, deep voice when using danazol. Causes osteoporosis if aromatase inhibitors are used for a long time. To limit the occurrence of the above side effects, you should use the drug exactly as prescribed by the doctor, absolutely do not arbitrarily use the drug.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Article reference source: Webmd.com