This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor II Nguyen Quoc Viet - Interventional Cardiologist - Department of Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Danang International HospitalElectrocardiogram is a very popular method of monitoring the electrical activity of the heart today, almost every medical facility uses it as a diagnostic standard for cardiovascular diseases. So what is an electrocardiogram test, what is the result of a normal electrocardiogram?
1. What is an electrocardiogram?
Electrocardiogram (ECG - Electrocardiogram) is a graph that records the changes of electric current in the human heart per unit time. The heart's rhythmic contraction is controlled by an electrical conduction system of the heart muscle. Although the electrical current of the heart is small, only a thousandth of a volt, it can be detected through electrodes placed on the patient's arms, legs, chest and transferred to an electrical recorder. Here, the current will be amplified and recorded on graph paper, also known as an electrocardiogram.
The heart works thanks to the impulses transmitted through the autonomic nervous system, first at the sinus node, the impulses are transmitted to the atrial muscle to depolarize the atria, then the impulses will be transmitted through the atrioventricular node, through the bundle of His. into the ventricles to depolarize the ventricles.
Trắc nghiệm: Huyết áp của bạn có đang thực sự tốt?
Huyết áp cao hay thấp đều ảnh hưởng đến tình trạng sức khỏe con người. Để biết tình trạng huyết áp của bạn có thực sự tốt không, hãy làm bài trắc nghiệm sau đây để đánh giá.Electrocardiogram measurement does not cause harm to people's health due to its relatively low cost and is considered a basic and routine test in medical examination and treatment. An electrocardiogram is not a measurement of the blood flow (flow) in the heart.
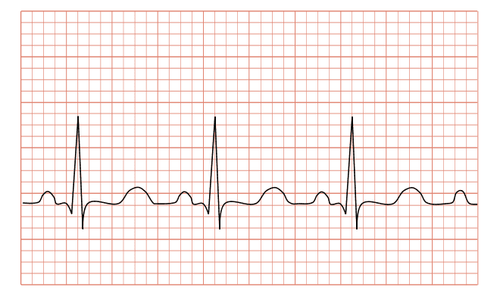
2. When is an electrocardiogram indicated?
EKG is indicated for: the elderly (high cardiovascular risk), hypertension, dyslipidemia (dyslipidemia), diabetes mellitus (diabetes), smoking, angina attacks , palpitations, shortness of breath, history of syncope or emergency hospital admission for any reason. In addition, the indications for electrocardiogram measurement include:Perform preoperative electrocardiogram. Electrocardiogram to monitor treatment. An electrocardiogram is a routine screening test in people over 40 years of age. There are many cardiovascular diseases that are discovered by chance through an electrocardiogram test, even if the patient has no symptoms of chest pain, palpitations or shortness of breath...

3. Basic electrocardiogram analysis
How to view basic ECG results as follows:
3.1. P wave characteristics Best seen in D2, V1 Possibly biphasic in V1 Wide < 3 small cells (< 12 ms) High < 2.5 small cells (< 2.5 mV) Positive in D1, D2, aVL, aVF , V3, V4, V5, V6. Sound in aVR. Changes in D3, aVL, V1, V2. 3.2. PR segment (PQ): 12 – 20 ms Duration 0.12 – 0.20s. Long: First degree AV block Short: pre-excitation syndrome
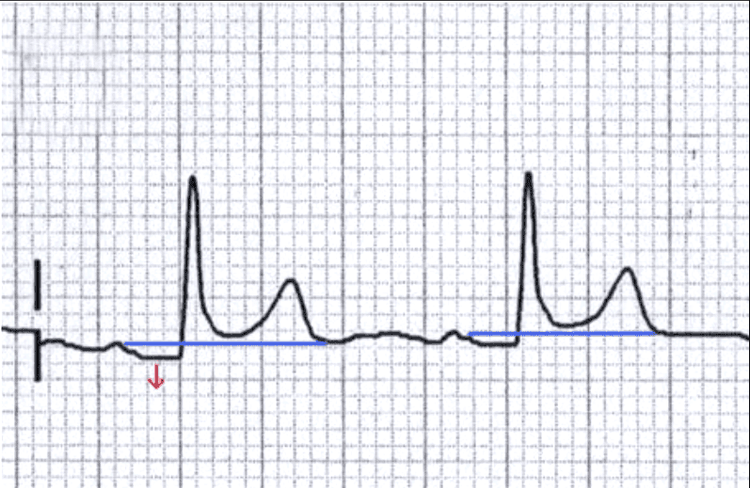
3.3. Features of QRS complex Width no more than 12 ms (3 small cells) Duration < 0.10 s. Sokolow = (SV1 + RV5) < 35mm. R/S < 1 in V1, V2; R/S > 1 in V5, V6. In the right precordial lead (V1): S >> R In the left precordial lead (V5,6): no more than 25 mm high In the left lead there may be Q waves due to depolarization of the interventricular septum but: no depth more than 2mm and not more than 1mm wide. 3.4. QRS abnormality Too wide: branching block; branch, extrasystolic rhythm... Too high: ventricular hypertrophy Right ventricular thickening: right axis (>110 degrees); R >>S at V1, V2; Deep S in V5-6 Left ventricular thickening: left axis (< 0 degrees); R is high at V5.6 (>= 25mm); S deep in V1-2; Sokolow-Lyon index (SV1 + RV5 or RV6) >= 35mm.
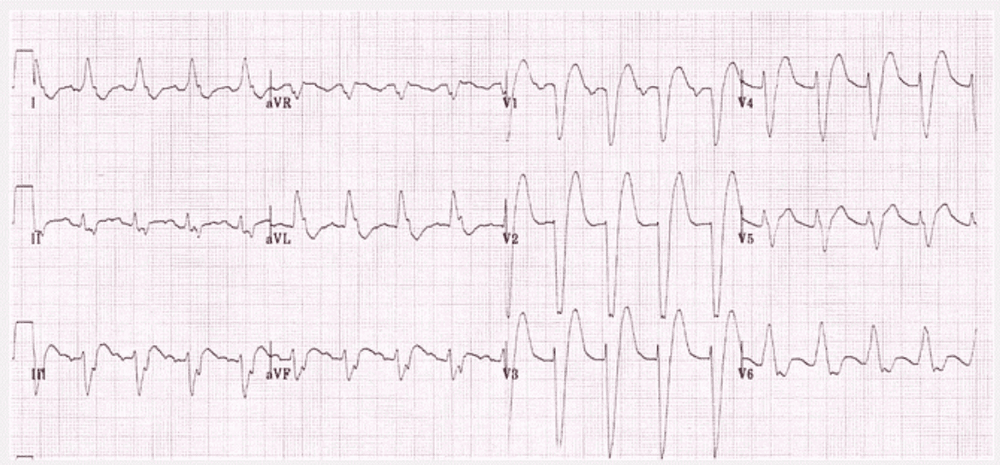
3.5. Q wave Normal: formed by depolarization of the interventricular septum from left to right; <1mm wide; < 2mm deep. Pathology: Cardiac muscle cells die (necrosis) -> depolarize from the inside to the outside of the heart surface at the site of necrosis -> Q wave pathology in the contrast area. 3.6. ST-segment normal ST segment is isoelectric Changes associated with new myocardial injury or pericarditis; ventricular hypertrophy; digoxin may be elevated; depression... Different shapes, different positions allow diagnosis. 3.7. T-wave Asymmetrical: gentle ascending slope, steeper descending slope Round top. Positive at D1, D2, aVL, V2, V3, V4, V5, V6. Sound in aVR. Changes in D3, aVF, V1. Usually in the same direction QRS Highest in V3-V4 There is no standard for limiting altitude.
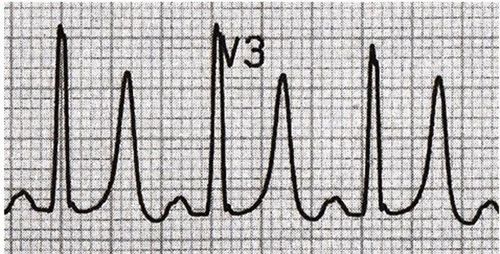
3.8. Abnormal T Due to coronary artery disease Ventricular hypertrophy Digoxin bundle branch block... 3.9. QT interval QT: 0.35 – 0.45 ms Values showing ECG results include: heart rate, rate, PR (Q) segment and conduction problem, ECG axis QRS, wave description P, describe QRS complex, describe ST and T segments, describe arrhythmia if present. Finally, the results of the electrocardiogram are given.
Vinmec International General Hospital has applied electrocardiogram technique in examination and diagnosis of many cardiovascular diseases. Electrocardiogram testing at Vinmec International General Hospital is carried out methodically and in accordance with standard procedures by a team of highly skilled doctors and nurses, with modern standard machinery for accurate results, contributing to plays an important role in determining the disease and the stage of the disease.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.