This is an automatically translated article.
Article by Doctor Pham Anh Tuan - Vinmec Institute of Stem Cell and Gene TechnologyMutation in the EGFR gene, also known as Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor, is considered as the epidermal growth factor receptor, this is the type of mutation that is often seen in people with lung cancer. Recent statistics show that up to 50% of Asians with lung cancer have mutations in the EGFR gene. Besides the racial factor; EGFR mutations also occur with a high rate of lung cancer patients who are female, non-smokers and whose histology is adenocarcinoma.
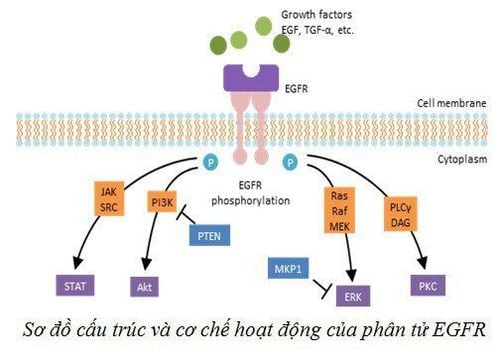
EGFR (epithelial growth factor receptor) is located on the surface of some common cell types and can also be found in certain types of cancer cells at high concentrations to help Cancer grows and divides aggressively.
Blocking EGFR can limit cancer cell proliferation, so some drugs inhibit tyrosine kinase (this enzyme attaches a phosphate moiety to the amino acid tyrosine, a protein on the receptor, then phosphorylation occurs) turn on/off certain functions of receptors and cellular processes) have been used in cancer therapy and are known as EGFR inhibitors (EGFR/EGFR tyrosine inhibitors). However, up to 60% of non-small cell lung cancer patients develop an EGFR T790M mutation that renders tyrosine kinase inhibitors ineffective. Patients carrying this mutation usually respond well to 3rd generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors, but there are some risks (safety as well as cost) when confirming this mutation through tissue biopsy. ~37,000 USD) and is often not feasible.
For liquid biopsies using cfDNA can be considered noninvasive but has low sensitivity due to too few copies in the circulation. Therefore, the authors have developed and validated a new method to overcome the quantitative/concentration limitations of this mutation in detection by the simultaneous combination: capture and thorough exploration. Exosome RNA/DNA and cfDNA (extracted from plasma of non-small cell lung cancer patients) in the same highly sensitive quantitative PCR assay for the specific allele (EGFR exon 20).
The study was conducted on 201 biological samples from 102 NSCLC patients positive for the T790M mutation and negative samples were obtained from biologically confirmed patients or tumor-free donors.
As we know, mutations can occur in both RNA and DNA, however conventional liquid secretion can only probe cfDNA. With this new method, the authors can deal with all mutation sources to ensure high sensitivity mutation confirmation. Identification of the T790M mutation is particularly difficult in patients with confirmed disease (M0/M1a or M1b). More recently, methods such as droplet PCR were able to detect 18% of the T790M mutation, or 51% with the cobas EGFR Mutation Test v2 (Roche, FDA-approved test), or 27% when performed with BEAMing, compared with the new method of the authors, the sensitivity was much higher (88% for M0/M1a and 94% for M1b, Table 1.B). For patients with intrathoracic or undetermined lung cancer, this new method has a sensitivity of up to 92% and a specificity of 89% (Table 1.A).
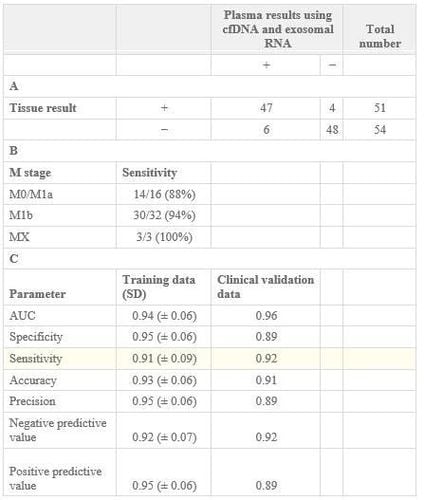
Bảng 1. Đánh giá hiệu quả phương pháp
Since exosomes serve as a storehouse of cells and cfDNA is released from dead or apoptotic cells, the simultaneous detection of nucleic acids in exosomes and cfDNA will help us analyze two other biological processes. tumor cells and may detect resistance mutations developing earlier. This avoids the need for biopsies to identify the T790M mutation in lung cancer patients.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
ReferencesKenneth W. Witwer et al., Standardization of sample collection, isolation and analysis methods in extracellular vesicle research, May 2013, Journal of extracellular vesicles,. Pin Li et al., Progress in exosome isolation techniques, Jan 2017, Theranostics Journal. Ning Wang et al., Circulating exosomes contain protein biomarker of metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer, Mar 2018, Cancer Science. Yan-Zi Sun et al., Extracellular Vesicles: A new perspective in tumor therapy, Apr 2018, Hindawi BioMed Research International Journal. Elena Castellanos-Rizaldos et al., Exosome-Based Detection of EGFR T790M in Plasma from Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients, June 2018, Clinical Cancer Research Journal, 24.12