This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Master, Doctor Mai Vien Phuong - Department of Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General HospitalThe formation of liver fibrosis and progression to cirrhosis is a complex mechanism that interacts between the formation of the fibrous matrix and its degradation. Currently, studies on the efficacy and safety of anti-cirrhotic drugs caused by viral hepatitis have achieved certain achievements.
1. Liver disease caused by hepatitis B virus
Chronic hepatitis B (CHB) defined as persistence of Australian antigen for more than 6 months) is a major cause of the worldwide development of cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Over the past 3 decades, hepatitis B virus (HBV) infections in the United States have decreased by 82%, although the likelihood of the virus progressing to chronic infection and subsequently cirrhosis continues to have profound health effects. long-term health. Several studies have shown that through the inhibition of viral deoxyribonucleic acid, modern medicine can achieve histological response.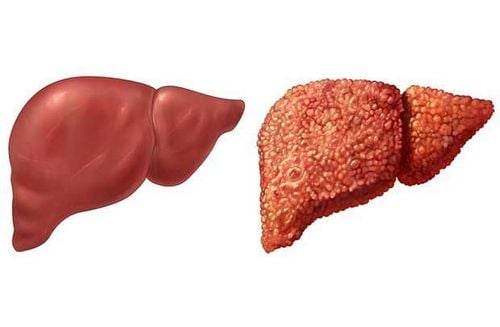
These improvements were more common in responders, defined as undetected seroconversion of the HBeAg antigen to HBeAg, at completion of therapy than in nonresponders. One of the first oral antivirals, lamivudine, is a nucleoside analog that has also been shown to improve fibrosis in multiple studies through its antiviral effects.
In a 3-year study, lamivudine resulted in improvements in histological graded bridging liver fibrosis and cirrhosis in 63% and 73% of patients with YMDD [tyrosine (Y), methionine (M), aspartate) (D) and aspartate (D) amino acids] HBV variants, respectively. A similar study showed improvement in both bridging fibrosis and cirrhosis in both HBeAg-positive YMDD and non-YMDD patients. Long-term hepatitis B treatment with lamivudine (10 years) was associated with complete liver degeneration/cirrhosis or improved Ishak fibrosis score in 21% and 47% of patients tested, particularly due to loss of HBeAg and seroconversion together with a prolonged duration of treatment allow for improved histology and regeneration.
1.1 Role of Adefovir in Anti-Cirrhosis Adefovir is a reverse transcriptase inhibitor (nucleotide analog). Although not a direct anti-fibrotic drug, it acts as an antiviral agent that can reduce ongoing liver inflammation, which has clinical significance in preventing fibrosis, similar to other nucleos(t)Ide analogues. In a study conducted by Hadziyannis et al., Ishak fibrosis scores improved in 71% of patients treated with Adefovir dipivoxil for 240 weeks. Similar histological improvements were seen in a follow-up study, in which 60% of study participants showed improved fibrosis scores on follow-up biopsies.
1.2 Role of the drug Entecavir Entecavir (a nucleoside analog) has also shown benefits similar to an antiviral agent, with one study showing histological improvement (decreased Knodell necrotizing inflammation score and no worsened Knodell fibrosis score) in 96% of patients and improved Ishak fibrosis score in 88% of patients, including all 10 patients who had advanced fibrosis or cirrhosis prior to treatment initiation .
Similar findings were found in a Japanese study by Yokosuka et al., in which 57% of nucleoside-nave patients were treated with entecavir for 3 years showing improvement in fibrosis. chemical. A more recent prospective study analyzing 120 treatment-nave patients with CHB demonstrated both fibrosis regression in 54 patients (45%) and decreased hepatic stiffness [transient elastography ( TE)] in patients with fibrosis compared with those with no improvement in fibrosis after 78 weeks of entecavir treatment (-46.4% vs -28.6%, P<0.001).
1.3 Role of Tenofovir Tenofovir is a commonly used nucleotide analog that is an effective antiviral treatment for both human immunodeficiency virus-1 and HBV. Marcellin et al evaluated cirrhotic patients with baseline Ishak scores of 5 or 6 (96 patients), treated with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate. Histological improvement with resolution of cirrhosis (giảm1 stage reduction) was observed in 71 patients (74%) after completion of 5 years of treatment. It has been shown that in HBV patients treated with tenofovir or entecavir; all noninvasive scores [aspartate aminotransferase (AST)/alanine aminotransferase, AST index/platelet ratio, Fibrosis-4, erythrocyte volume to platelet width ratio] were significantly lower after during treatment at both 12 and 24 months.
2. Liver disease caused by hepatitis C virus
The advent of novel and extremely effective compounds in achieving sustained virological response is promising in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C (CHC) patients with fibrosis and cirrhosis. In a marker study that included patients with stage 2 or greater fibrosis at baseline, treatment with a combination of pegylated interferon alpha (IFN-α) and ribavirin resulted in an 82% reduction in fibrosis scores with some control showed normal/near-normal liver histology after 5 years of follow-up liver biopsy. In a similar prospective study of patients treated with an antiretroviral regimen (interferon monotherapy, IFN + ribavirin, or IFN + pegylated ribavirin), 88% demonstrated improved fibrosis scores improved using TE measurements.2.1 The Role of Next Generation Antiviral Agents Novel direct antiviral agents (DAAs) have greatly changed and revolutionized the treatment of CHC. In a multicenter observational study, DAA response was evaluated among 392 patients receiving DAA-based hepatitis C therapy. The results showed regression of TE (-32.4%) as well as reduction in Fibrosis-4 ratio (-29.1%) and AST/platelet index values (-60.9%), significantly different between the groups before and after treatment. Similar findings were reported in a recent study demonstrating 40% remission in fibrosis after DAA, using TE measurement. Regression of fibrosis was significantly more common in patients with early-stage fibrosis than in those with liver fibrosis F0-F1 (P < 0.001). Improvement in liver fibrosis was also observed with 12 weeks of sofosbuvir, which demonstrated enhanced improvement in liver fibrosis and liver stiffness measurement with FibroScan ® TE.

2.3 Role of Angiotensin II Angiotensin II, secreted by astrocytes, has been shown to promote fibrinogenesis by binding to the angiotensin II type 1 receptor and triggering intracellular responses different Janus kinase 2 mediated. In a small published clinical trial, patients with CHC and fibrosis were treated with losartan, an angiotensin II receptor antagonist, for 18 months.
Post-treatment biopsies of fourteen patients with ≥F2 fibrosis showed improved fibrosis rates in 50% of patients, along with a significant reduction in the expression of several proto-protozoal genes. The different angiotensin II receptor antagonists are discussed further later in this review.
Recent studies have demonstrated a reduction in the risk of fibrosis progression as well as a reduction in the development of cirrhosis with statin use in patients with CHC. Mechanisms that may permit a reduction in fibrosis progression include antiviral and immunomodulatory effects, reduction of portal hypertension by increasing nitric oxide formation in spores, and cytostatic inhibition. astrocytes through the regulation of certain transcription factors.

3. Conclusion
The formation of liver fibrosis and progression to cirrhosis is a complex mechanism that interacts between the formation of the fibrous matrix and its degradation. Scientists will not only continue to study the effectiveness of individual drugs, but should continue to develop combination therapies that target different points of the concurrent fibrosis chain. Potential benefits may also be explored using compounds that have been implicated in other forms of systemic fibrosis, as many of the pathways are shared across organ systems.To protect everyone's health, now, Vinmec International General Hospital provides customers with standard to advanced hepatobiliary screening packages to help diagnose cirrhosis in particular and hepatobiliary diseases. Generally speaking.
Vinmec is the leading prestigious and reliable address in the field of screening and treatment of hepatobiliary diseases, with the following outstanding advantages:
As one of the few hospitals across the country applying ultrasound Liver tissue recovery (also known as ARFI technique) to monitor liver disease, assess the degree of cirrhosis such as imaging, test kits from basic to advanced. With the state-of-the-art LOGIQ E9 ultrasound system, a powerful and flexible ultrasound imaging system that meets a wide range of general examination needs. New technology using Shear Wave: This is a technology that allows qualitative and quantitative measurement of the elastic energy of the parenchyma through a color-coded table along with the value of elastic levels in Kpa pressure units. A team of specialists and specialists with extensive experience and expertise helps the treatment process to be highly effective, shortening the treatment time. Professional, comprehensive examination and consultation service, civilized, polite, safe and sterilized medical examination space.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
ReferenceToosi AE. Liver Fibrosis: Causes and Methods of Assessment, A Review. Rom J Intern Med. 2015;53:304-314. [PubMed] [DOI] Hernandez-Gea V, Friedman SL. Pathogenesis of liver fibrosis. Annu Rev Pathol. 2011;6:425-456. [PubMed] [DOI] Kochanek KD, Murphy SL, Xu J, Arias E. Deaths: Final Data for 2017. Natl Vital Stat Rep. 2019;68:1-77. [PubMed] Konstantinos Damiris, Efficacy and safety of anti-hepatic fibrosis drugs, World J Gastroenterol. Nov 7, 2020; 26(41): 6304-6321