This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Le Nguyen Hong Tram - Gastroenterologist - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Nha Trang International Hospital
Esophageal diverticulum is a rare disease but will significantly reduce quality of life if complications occur. Patients with esophageal diverticulum need to recognize early signs for timely treatment.
1. Is esophageal diverticulum dangerous?
The esophagus is the part of the digestive system that carries food from the mouth to the stomach. The esophagus is tubular in shape, about 25cm long, bridged by muscle, not covered by serosa, and loosely attached to surrounding structures. The esophagus is divided into three main parts: the cervical esophagus, the thoracic esophagus, and the abdominal esophagus.Esophageal diverticulum is a rare clinical disease, the characteristic lesion of esophageal diverticulum is the existence of a pouch-like structure that protrudes beyond the normal limits of the esophagus. Esophageal diverticula usually occur at sites of junctions between the esophagus and other structures or at weak points in the esophageal wall. A diverticulum in the posterior wall of the pharynx, at the junction of the esophagus to the pharynx, or a Zenker's diverticulum is the most common. The main cause of diverticulum is high pressure inside the esophageal lumen due to narrowing of the lower segment or spasm of the cardiac muscle.
An esophageal diverticulum may be composed of all the structures of the esophageal tube such as mucosa, submucosa, and muscle or only the mucosa and submucosa of the esophagus.
Esophageal diverticulum is usually a benign, progressive disease that lasts for many years but causes many complications for patients. As the diverticulum increases in size, the diverticulum can put pressure on the trachea, surrounding nerves and blood vessels, causing respiratory and circulatory abnormalities. Food stagnation inside the diverticulum is a risk factor for inflammation from decaying food. Bronchitis and pneumonia can also be complications of esophageal diverticulum.
The existence of esophageal diverticula also interferes with esophageal motility during swallowing. Esophageal reflux due to diverticula is also common and reduces quality of life, often occurring at night or while lying down. Esophageal diverticula can also ulcerate, perforate, and bleed. Esophageal diverticulosis may also occur, although uncommon, less than 1% frequency.
2. Causes of esophageal diverticulum
Esophageal diverticulum can occur due to the following reasons:
Increased esophageal pressure due to esophageal stricture, esophageal spasm, esophageal tumor ... Enlarged lymph nodes due to inflammation, infection Deformity traction of the esophagus due to fibrous scars, sticky fibers from inflammatory organizations or after surgical interventions in the esophagus and surrounding area. Diaphragmatic hernia
3. Signs to recognize esophageal diverticulum
If the esophageal diverticulum is small, there are no clinical symptoms. Patients will live peacefully with esophageal diverticulum until the disease causes complications. Patients with esophageal diverticulum may present with the following clinical manifestations:
Dysphagia: This may be a clinical symptom of underlying causes of esophageal diverticulum such as esophageal stricture, esophageal stricture disorder. In addition, diverticula located in the cervical esophagus can also lead to difficulty swallowing because the diverticulum increases in size and presses on the lumen of the esophagus. Increased salivation, bad breath Cough and difficulty breathing if the diverticulum affects causing bronchitis, pneumonia. A dull feeling of pressure behind the breastbone if the diverticulum is large in the thoracic esophagus. Ợ gas, regurgitation of food. Physical exhaustion due to food not reaching the stomach for digestion.
4. Diagnosis of esophageal diverticulum
Diagnosis of esophageal diverticulum should be based on assessment of the patient's symptoms, clinical examination, and use of imaging modalities. The clinical symptoms of the disease are diverse but not really specific and easy to confuse with other diseases, so the main role in the diagnosis depends on imaging techniques.Some commonly selected clinical imaging methods include:
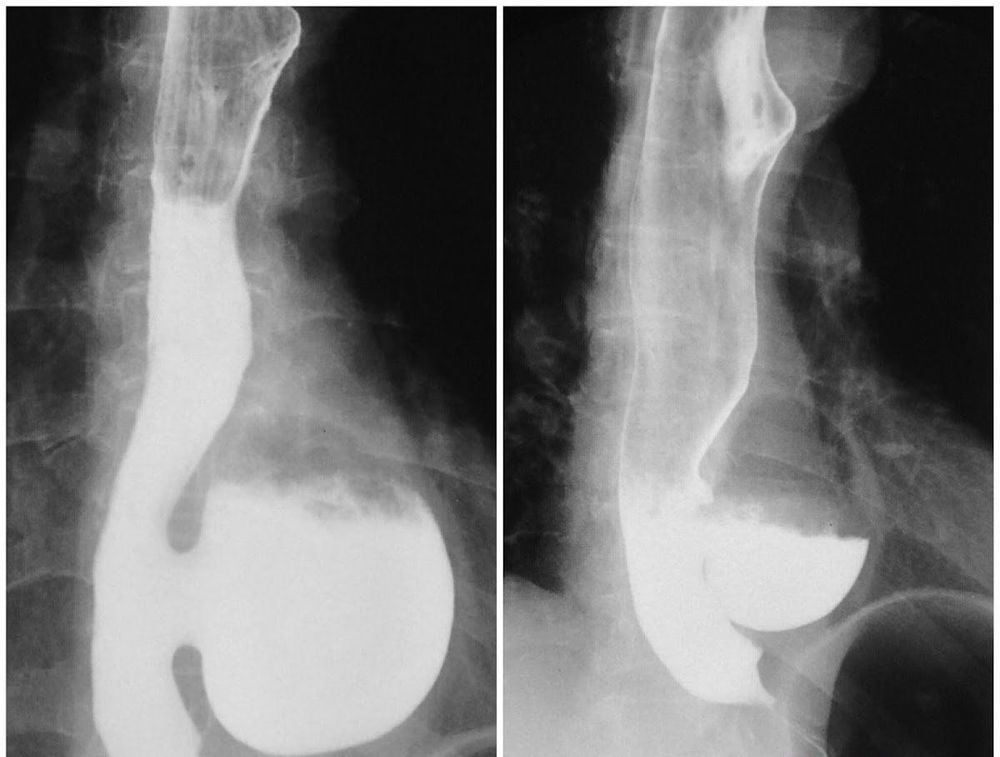
Esophageal X-ray with contrast: Detecting esophageal diverticulum as a continuous drug deposition with the esophageal wall. Gastroesophageal endoscopy: Observe the diverticulum image, size, food accumulation, other complications such as ulceration, bleeding and detect some causes of esophageal diverticulum formation. Esophageal endoscopy has both a diagnostic and therapeutic role.
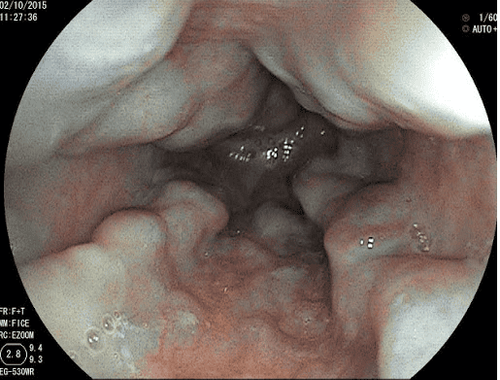
Computed tomography of the esophagus: Assesses esophageal diverticulum with features including shape, location, size and degree of compression of other nearby organs.
5. Should esophageal diverticulum be removed?
The choice of treatment methods for esophageal diverticulum is decided based on the characteristics of the diverticulum, clinical symptoms and the degree of impact on the patient's quality of life. If the diverticulum is small in size and does not show clinical signs, therapeutic interventions will not be necessary.
To limit the increase in diverticulum size and complications, patients should pay attention to lifestyle changes such as eating bland foods, chewing food thoroughly, drinking water after eating and not lying down immediately after eating. In cases where the diverticulum is large and causes troublesome complications, the esophageal diverticulum should be surgically removed or sutured. Laparoscopic surgery is often preferred over open surgery because of its low invasiveness, quick recovery time, and less pain for the patient. If the cause of esophageal diverticulum is detected, surgery to address the cause should be performed in combination to avoid recurrence and improve the patient's quality of life.
Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of modern facilities, medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in medical examination and treatment, patients can rest assured to visit examination and treatment at the Hospital.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.