This is an automatically translated article.
The article was consulted with Specialist II Chung Thi Mong Thuy - Pediatrician - Neonatologist - Department of Pediatrics - Neonatal, Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Essential newborn care has been popular in many countries for a long time and also has specific regulations. In 2016, the Ministry of Health issued a decision on professional procedures for essential maternal and newborn health care early during and after cesarean section. This process consists of 5 steps: right after birth, the baby is dried, warmed, waiting for the umbilical cord to stop beating, late clamping the umbilical cord, skin-to-skin contact, oxytocin injection for the mother, early breastfeeding in the first 60 minutes after birth. This essential care program brings a lot of benefits and benefits to mothers and babies.
1. The effectiveness of essential neonatal care
Early essential neonatal care is a simple, low-cost but highly effective care method for both mother and baby, reducing the rate of postpartum haemorrhage for the mother and reducing postpartum and neonatal infections. , significantly reducing neonatal mortality.Its methods include: active management of the third stage of labor and early breastfeeding.
2. Essential care methods for babies born by caesarean section
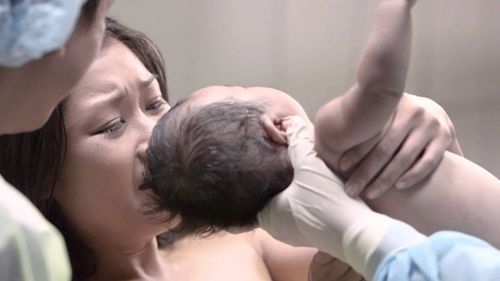
2.1. Giving the baby skin-to-skin contact with the mother Skin-to-skin contact soon after birth, the baby will be dried by medical staff quickly and comprehensively and placed in skin-to-skin contact on the chest mother, the time of skin-to-skin contact between mother and baby is at least 90 minutes.With skin-to-skin contact soon after birth, the baby will not have hypothermia, the baby will find the mother's breast sooner and the ability to breastfeed is healthier and better. The mother's psychology also reduces the anxiety due to being able to hold her own baby from the first moment of birth and the pain of having to give birth alone will lessen. With this method of skin-to-skin contact after cesarean section, this is a natural way to bond between mother and baby.

However, in case the mother gives birth by cesarean section with pregnancy risk such as the mother with hypertension, diabetes, medical disease, cardiovascular disease, infection, anesthesia... can be advised not to apply. Skin-to-skin approach in the care of infants after cesarean section. The reason is that the mother is tired, her health is not guaranteed to hold the baby in front of her chest well In this case, the mother and the baby will not perform skin-to-skin contact, but still maintain the mother's milk supply by sucking directly or by the mother. express breast milk every 3 hours.
Routine care after the baby has finished the first feed and has direct skin-to-skin contact for at least 90 minutes. Other routine care steps such as: weighing, measuring the baby's length and head circumference; wear identification rings, get a full body examination, inject vitamin K1 and prevent diseases as prescribed.
In case the infant cannot breathe or hiccups:
After drying the whole body and stimulating for about 30 seconds, but the baby still does not breathe or hiccups, it is necessary to clamp and cut the umbilical cord immediately, and give the baby to the resuscitation table to conduct neonatal resuscitation according to the protocol of neonatal resuscitation. If the baby can cry, has a stable breathing rate, and has ruddy skin, move the baby to lie down in skin-to-skin contact with the mother and take the next steps of care as in the case of a breathing infant. If the baby is whining, pale skin, it is necessary to transfer the child to the neonatal care unit or department for further monitoring. 2.2. Clamping and cutting the baby's umbilical cord is 1 hour late. Physiologically in newborns, in the first minute when the baby is born without cutting the umbilical cord, blood continues to pass from the placenta to the newborn through the umbilical cord about 80ml-100ml during the first minute of life. 3 minutes after birth. Cutting the umbilical cord late will help increase the baby's blood supply, which is a rich source of iron, helping babies prevent iron deficiency anemia in the first months of life.
If the umbilical cord is clamped after the umbilical blood vessels stop beating, a certain amount of blood from the placenta through the umbilical cord to the baby will help the baby born at term to prevent the risk of iron deficiency anemia in the first months, especially for newborns. Premature is not anemic while reducing the rate of cerebral hemorrhage due to decreased prothrombin.
However, it is necessary to clamp and cut the umbilical cord of the newborn 1 minute early in cases where the baby needs intensive resuscitation and respiratory support.

Therefore, to prevent bleeding after birth is the first measure in maternal and child care after cesarean section. Prophylaxis of bleeding is accomplished by active management of the third stage of labor with three main interventions: intramuscular oxytocin injection to the mother immediately after birth, controlled delivery of the placenta and perineal massage of the mother's uterus. every 15 minutes for the first 2 hours after birth.
2.4. Early breast-feeding Instruct the mother on the infant's infant demand for breast-feeding signs such as opening mouth, drooling, licking, sucking, crawling for the breast... at the same time, instructing the mother how to give The baby latches on to the breast properly.
It is necessary to breastfeed the baby early and exclusively breastfeed in the first hour after birth. Do not give the baby any other food besides breast milk. According to the recommendations of the World Health Organization (WHO), you should exclusively breastfeed your baby for the first 6 months and continue to breastfeed and supplement with other appropriate foods until 2 years of age. Or maybe longer depending on the case.
Exclusive breastfeeding for the first 6 months will strengthen the baby's immunity, can prevent death from diarrhea and acute respiratory infections in the first 3 months. At the same time, early breastfeeding can also stimulate the pituitary gland to increase the secretion of oxytocin in the mother, helping to better contract the uterus to prevent bleeding or the risk of bleeding in the mother after birth.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.