This is an automatically translated article.
Ear mastoid surgery is indicated in cases of ear-mastoid pathology requiring surgical intervention in order to clear the infection and thoroughly treat the disease.1.Massial mastoid surgery is a technique to drain the mastoid fossa in the case of mastoiditis to remove the necrotic tissue, leaving only the healthy tissue. case of chronic mastoiditis
Ear mastoid surgery includes simple mastoidectomy, partial mastoidectomy, total mastoidectomy, mastoidectomy in some special clinical forms
2 Surgical methods of mastoid ear 2.1. Simple mastectomy. Purpose: Drain the mastoid fossa by opening the mastoid cavern and the mastoid sinuses and ensuring that all lesions are removed. Indications: acute mastoiditis, subacute mastoiditis, mastoid otitis in children unresponsive to medical treatment.
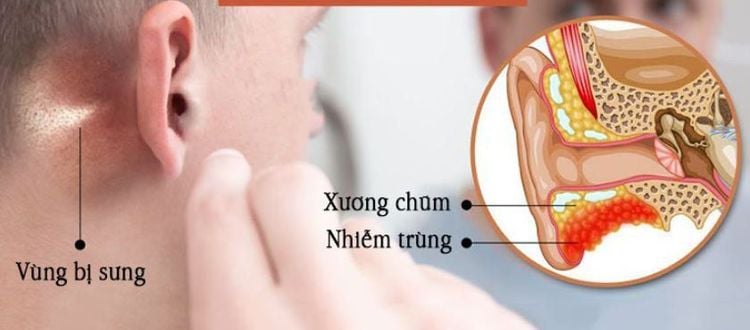
Trường hợp viêm xương chũm cấp tính cần được phẫu thuật mở khoét chũm đơn thuần
Surgical procedure. Preparation:
Patient lies supine with head on pillow facing opposite side. The surgeon stands on the side of the surgery, the assistant stands at the patient's head. After thoroughly disinfecting the surgical site, determine the position of the mastoid process. Steps to take:
Step 1: Make an incision behind the ear. Make an incision in the crease behind the ear or 2mm away from the groove. The incision is a curved line parallel to the groove behind the ear, going from the top down to the mastoid process. The shallow incision below makes a deep incision down to the bone. Step 2: Dissect the fascia to reveal mastoid bone, revealing Henle spine and posterior pituitary space. Behind exposed the stony bones, above to reveal the mastoid process. Step 3: Open the cymbal to open the cymbal. Punch abc breakout triangle. First find the opening of the pole at the apex of the triangle, and then expand the vertex by chiseling back towards the bottom of the triangle. If you go deep down to 10-13mm, you will see a planing pole. Check if the pole position is correct. Then use a small scraper to press against the door of the pole, widen the pole and pole to the outside and up. Step 4: Dredging the damaged cell groups. Dredging all groups of damaged cysts located around the striatum. Using a spatula and pliers, work your way down to the bottom bc of the breakout triangle in turn. Sometimes it is necessary to dredge down to the mastoid process based on the principle that only healthy organs can be kept. Step 5: Clean and tidy the incision. The incision walls must be smooth, not rough, and have no crevices in order to facilitate skin penetration. Pumping the surgical hole with isotonic saline, removing all bone fragments Step 6: Close the incision, sprinkle with antibiotic powder, place a drainage tube, sew 2 edges of the skin, and apply pressure to finish. 2.2. Partial mastoid hollowing surgery. Purpose: Open mastoid cavernous, mastoid sinus in the upper middle ear, cavernous catheter, for direct examination Indications: opening surgery to patch eardrum followed by partial mastoidectomy, case cholesteatoma has spread from the upper middle ear to the mastoid cavity.
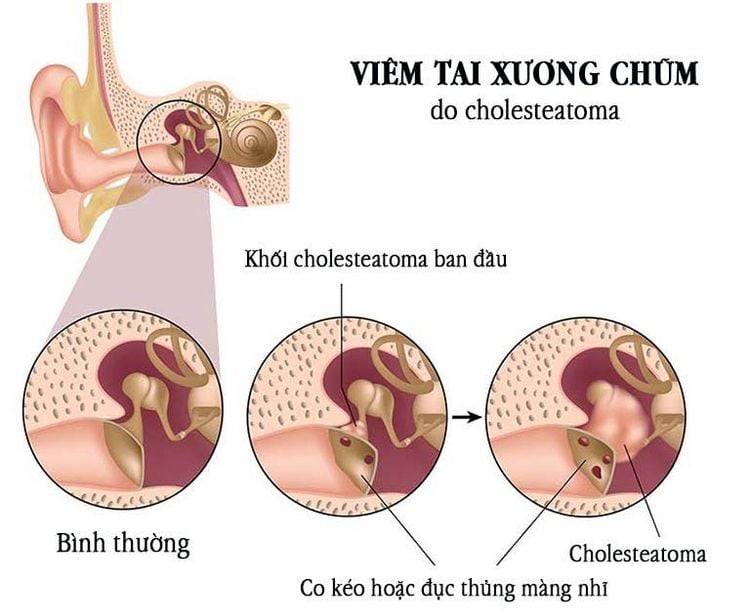
Hình ảnh mô tả trường hợp viêm tai xương chũm cholesteatoma
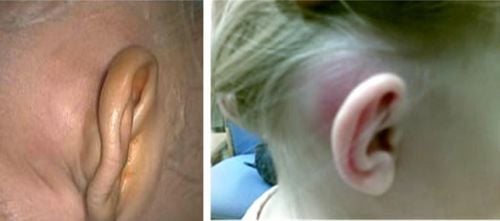
2.3. Total mastoid hollowing surgery. Purpose: Leveling the mastoid cavity, the upper middle ear mastoid sinus, the cavernous canal, removing the hammer bone, the incus, effective to solve the chronic suppurative inflammation of the upper middle ear, suppurative mastoiditis of the upper middle ear with there is inflammation of the bones. Indications: Chronic mastoiditis with extensive and extensive lesions. Technique: Mastoid osteotomy needs to be done within the confines of a triangle called the breakout triangle ABC. Peak A: Triangular apical chisel A corresponds to mastoid cave. Vertical line AC: 2mm behind the ear canal, AC line corresponds to the path of 3-wire VII segment Transverse line AB: perpendicular to AC, passing below of the lower temporal ridge and the upper pole of the ear canal. The horizontal line AB corresponds to the dura mater located deep below. Diagonal BC: Following the stony-clam joint, it corresponds to the cranial vein located deep below it. 2.4. Types of surgery for otitis - mastoid in some special clinical forms: Exterior mastoiditis in the neck requires an extended incision behind the ear, going 10 mm below the mastoid process, and removing all the fibers of the mastoid. of the sternocleidomastoid muscle, remove the entire mastoid until the posterior apex of the biceps attachment is exposed. Otitis - mastoid bone in children: because the mastoid system has not yet developed, the mastoid cave, the cavernous canal needs to be opened more shallowly than in adults. Temporomandibular mastoiditis: It is necessary to make an incision behind the ear and further forward above the ear canal, opening the mastoidectomy, the cavernous canal, and the mastoid sinus need to be extended towards the mastoid group.
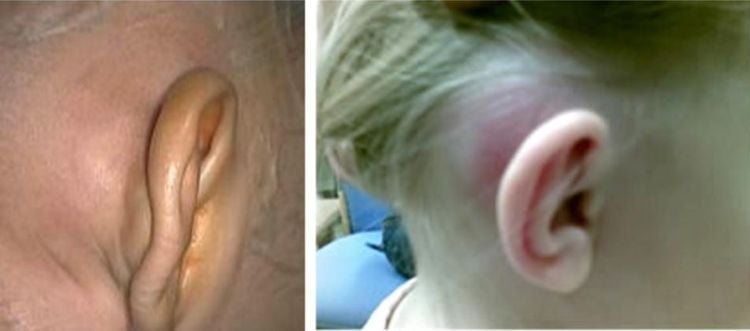
Hình ảnh viêm tai - xương chũm ở trẻ nhỏ
Vinmec International General Hospital is a high-quality medical facility in Vietnam with a team of highly qualified medical professionals, well-trained, domestic and foreign, and experienced.
A system of modern and advanced medical equipment, possessing many of the best machines in the world, helping to detect many difficult and dangerous diseases in a short time, supporting the diagnosis and treatment of doctors the most effective. The hospital space is designed according to 5-star hotel standards, giving patients comfort, friendliness and peace of mind.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.