This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Master, Doctor Trinh Van Dong - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Ha Long International Hospital
In recent years, diffusion magnetic resonance imaging has been applied to evaluate intracranial pathologies, such as stroke, trauma, infectious and neurotoxic diseases, especially especially in cerebral infarction.
1. Diffuse magnetic resonance concept
Diffusion-weighted Imaging (DWI) is an imaging pulse sequence of magnetic resonance imaging in which the signal intensity is determined by the diffusion effect of water molecules in biological tissues. .
In body tissues, water molecules move continuously and randomly in different directions, and is known as Brow motion or diffusion effect. The diffusion effect occurs at the molecular level, so changes in this effect allow us to evaluate the pathological process of biological tissue at a very early stage, especially in neural tissue.
Based on the principle of DWI imaging, we can understand that areas of biological tissue where water molecules are restricted from diffusion will increase the signal on DWI, conversely, regions where water molecules are not restricted. diffusion mechanism i.e. freely moving water molecules will decrease on DWI. However, the contrast of the DWI depends on many other factors, so to eliminate those factors, another parameter is introduced called the true diffusion coefficient ADC (this is not a pulse sequence which is merely a mathematical transformation to independently analyze the degree of diffusion of water molecules) and the average value of the ADC on a gray-and-white scale called the diffusion map (ADC map). . If the lesion is limited to diffusion, there will be an increase in the signal on the DWI and a decrease in the signal on the ADC map.
Chụp cộng hưởng từ khuếch tán (DWI-Diffusion-weighted Imaging)
2. Purpose and meaning of diffusion magnetic resonance technique
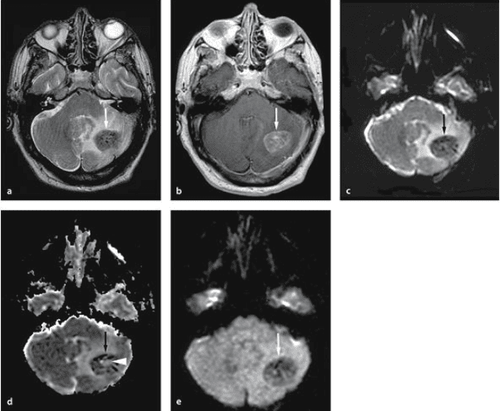
In recent years, diffusion magnetic resonance imaging is applied to evaluate intracranial pathologies, such as cerebrovascular accident, in trauma, infectious diseases - neurotoxicity. Especially in ischemic stroke, it allows to detect lesions in the fulminant stage, the diffuse pulse sequence for cerebral infarction has high sensitivity and specificity.
Applications for tumor assessment: Detecting tumors, evaluating tumor characteristics, distinguishing tumors from other lesions, monitoring and predicting response to treatment for benign and malignant tumors.
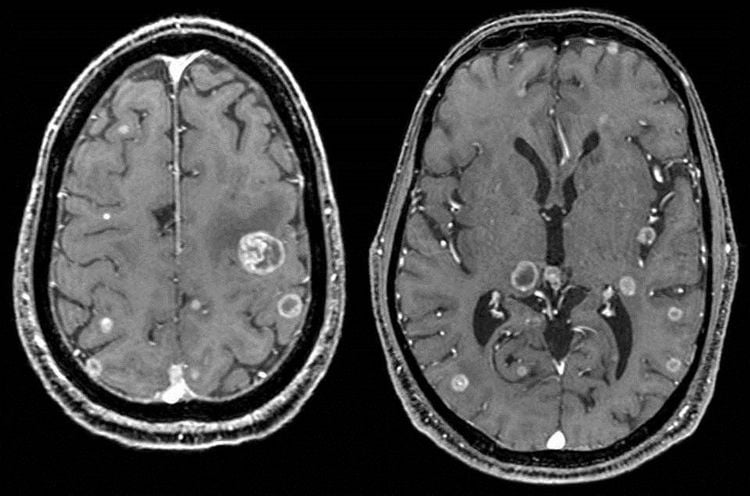
Chụp cộng hưởng từ khuếch tán giúp phát hiện u não
Recently, the use of whole-body DWI has been increasingly used to assess the overall lesion on the whole body.
In addition, using DWI 3D (diffusion tensor imaging) is one of the applications of DWI to map nerve pathways.
3. Indications and contraindications of Diffusion Magnetic Resonance Indications:
Cerebrovascular accident : Especially in cerebral infarction in the first hours to evaluate the spread of cell edema, use thrombolytic drugs Explain a cystic lesion: Necrotic tumor or abscess Evaluation Nature of the tumor: Tumor is few or many cells Assess the general lesion for patients with primary tumor to evaluate metastasis, or in cases of patients with lesions of secondary nature development of unknown origin u... Contraindications
Contraindications to DWI are the same as general contraindications to MRI.
Patient carries a pacemaker Patient carries a magnetic object such as surgical forceps, prosthetic heart valve, shrapnel in the danger zone, cochlear implant, ventricular valve, newly placed carotid stent (below) 2 weeks)... Patients with magnetic objects in the imaging area: intramedullary nails, artificial hip joints, metal screw splints... Severe patients have nearby resuscitation machines Relative contraindications: The patient is agitated, has a fear of lying in the scanner, and the patient is unable to lie still (sedation may be used before the scan).
Người bệnh cần được bác sĩ chỉ định chụp cộng hưởng từ khuếch tán
4. Diffuse magnetic resonance imaging procedure
Step 1: Place the patient in a strong magnetic field from 0.2 to 3 Tesla (T). Step 2: Broadcast radio to the patient. Radio waves reduce longitudinal magnetization and create new transverse magnetization. Step 3: Turning off the radio waves makes the protons no longer excited, gradually returning to the original state. Step 4: Build the image with the recorded signal: Fourier's mathematical method is applied to convert the received signals into information in space and recorded by the computer, then the computer will reconstruct the image. images of cross-sections based on recorded parameters.
5. Pros and cons of Diffusion Magnetic Resonance Advantages
In addition to the general advantages of the diffusion magnetic resonance imaging technique, there are also advantages:
It is a very sensitive technique to detect brain lesions at a very early stage of infarction, which improves the accuracy up to 95 %. It helps to distinguish between necrotic or abscessed lesions. Helps to evaluate metastatic lesions in body scan, detect primary lesions... Can evaluate micro-abscesses that other methods do not detect.
Chụp cộng hưởng từ khuếch tán tại Vinmec
Disadvantage
Diffuse MR imaging will not be used in cases of contraindications (as described above).
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE
SEE MORE
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) ) what is the benefit? When do you need a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan? When do you need a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan?