This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist II, Senior Doctor Doan Du Dat - General Internal Medicine Doctor - Department of Medical Examination and Internal Medicine - Vinmec Ha Long International Hospital.Disseminated intravascular coagulation or disseminated intravascular coagulation is one of the most severe disorders of the hemostatic system, characterized by the presence of many small clots within the lumen of blood vessels throughout the body. body. Clinical symptoms of disseminated intravascular coagulation are quite diverse, depending on the disease context. Treatment of disseminated intravascular coagulation includes supportive treatment to improve symptoms and address underlying causes.
1. Overview of disseminated intravascular coagulation
Disseminated intravascular coagulation or disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). This is a form of dysfunction of the blood-clotting system according to the thrombus-hemorrhagic flow and is a consequence of many different diseases. Diffuse intravascular coagulation syndrome is characterized by the formation of small thrombus scattered throughout the lumen of small blood vessels, followed by bleeding in multiple organ systems. bleeding on the skin and mucous membranes. Embolism due to the presence of blood clots was also noted, although sporadic at times. Patients with disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome often die from heavy bleeding.Diffuse intravascular coagulation syndrome is a serious problem that can be encountered in all specialties in the medical field. The detection and diagnosis of this syndrome is often suggested based on the symptoms and clinical picture. No laboratory test has sufficient sensitivity and specificity to confirm the diagnosis. Treatment of disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome should focus on treating the underlying cause, combined with the addition of coagulation factors to limit bleeding.
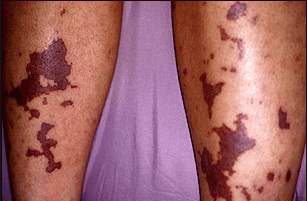
Xuất huyết trên da là một dấu hiệu của hội chứng đông máu nội mạch lan tỏa
2. Causes of disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome
Disseminated intravascular coagulation is not a disease but a syndrome that occurs secondary to a variety of conditions. The formation of thrombus within the lumen of small blood vessels occurs due to the activation of the coagulation system by many factors such as leukocytes, platelets, vascular factors, tissues, and pathogenic microorganisms such as bacteria. , fungi ... Currently, many studies have been conducted and found that disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome is present in malignancies, sepsis or septic shock, acidosis, hemolysis. Acute blood loss, systemic lupus erythematosus, autoimmune diseases, obstetric diseases such as postpartum haemorrhage, miscarriage, even amniotic fluid embolism after labor. Other causes of disseminated intravascular coagulation but less common may be burns, acute pancreatitis, snake venom, hypothermia, multiple trauma...In the pathogenesis of coagulopathy disseminated intravascular blood, the initial phenomenon is the disturbance of coagulation activity leading to the formation of blood clots. Subsequently, platelets and clotting factors are mobilized in greater amounts by the body and cause severe bleeding in the skin, mucous membranes and internal organs. Therefore, the main clinical manifestation of disseminated intravascular coagulation is heavy bleeding at multiple sites in the body.
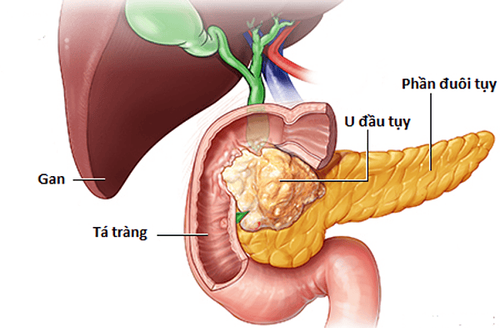
Viêm tụy cấp có thể là một nguyên nhân gây đông máu nội mạch lan tỏa
3. Clinical symptoms of disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome
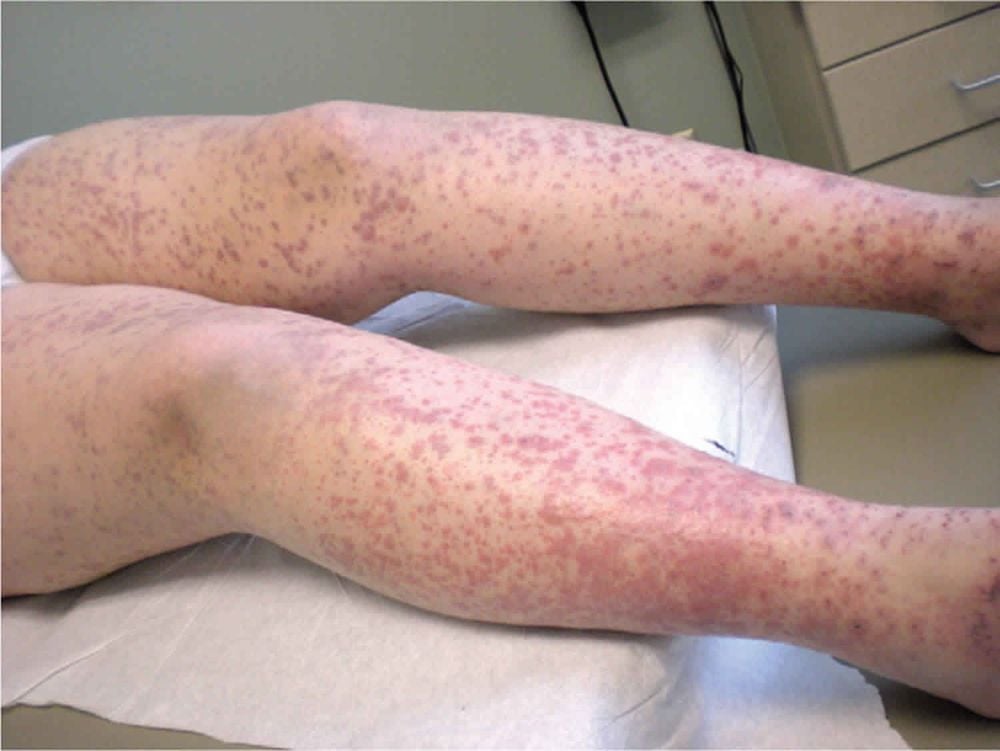
Bleeding in the skin and mucous membranes is a typical manifestation of disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome. The patient suddenly appeared bruised patches on the skin, especially at the injection sites, catheter placement and oozing bleeding in the oral mucosa and gums. Hemorrhage in such organ systems as the gastrointestinal tract and urinary tract with hematuria, hematemesis, and hematuria has also been reported.Besides, people with disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome are also detected by signs of blue-violet discoloration in the fingertips and toes due to lack of blood supply, blockage of blood vessels due to the formation of blood clots. of blood clots.
The patient's general condition in disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome is quite severe. The underlying causes vary from patient to patient. When bleeding is heavy and not well controlled, the patient is prone to hemorrhagic shock and multi-organ failure, which is life-threatening.
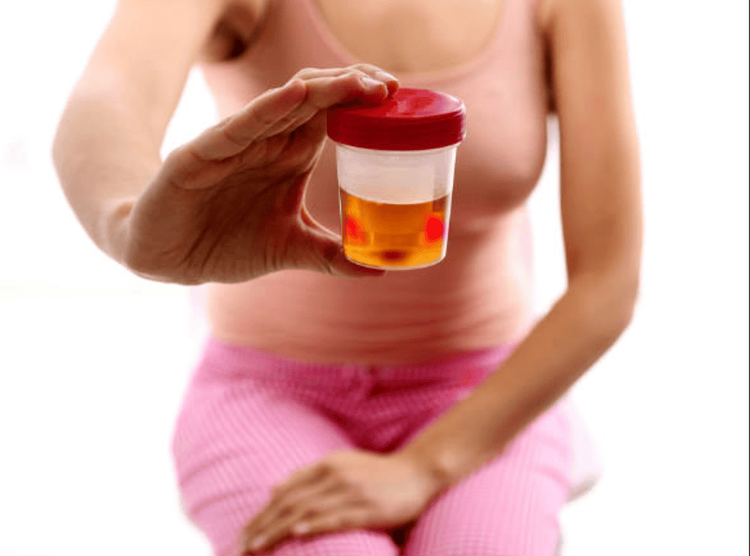

Một triệu chứng lâm sàng của hội chứng đông máu nội mạch lan tỏa là đái máu
4. Diagnosis of disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome
Currently, the diagnosis of disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome does not have specific and clear criteria. The establishment of a diagnosis should be made rapidly based on a combination of medical history, clinical manifestations and laboratory tests.Diffuse intravascular coagulation often occurs in a variety of clinical settings, including malignancies, sepsis, septic shock, malignancies, severe trauma, and disease. Obstetric problems such as postpartum hemorrhage, incomplete abortion, intrauterine growth arrest.
Clinical manifestations of disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome include signs of organ system bleeding, bruising on the skin and mucous membranes, cyanosis and necrosis of the fingertips, multi-organ failure, ...
Laboratory tests commonly indicated in the diagnosis of disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome include fibrin quantification, D-Dimer, PDF. Abnormalities present in disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome include thrombocytopenia, prolonged prothrombin time, decreased fibrin, increased D-Dimer, and increased PGF. These tests should be repeated throughout the course of treatment to assess the level of coagulation factor consumption as well as the effectiveness of the treatment.
Để chẩn đoán đông máu nội mạch lan tỏa, bác sĩ cần dựa các biểu hiện lâm sàng và các xét nghiệm cận lâm sàng.
5. Treatment methods for disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome
Diffuse intravascular coagulation syndrome is considered as a consequence of many different diseases, so the pathogenesis leading to this syndrome is not the same in all patients. Treatment of disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome should focus on treating the underlying cause and correcting the coagulopathy caused by deficiency of platelets and other clotting factors. In particular, the treatment of the underlying cause plays an important role, completely solving this blood clotting disorder.The addition of platelets and hemostatic factors is essential in the acute phase of the disease, although the etiology or pathogenesis of the disease has not been determined. Fresh whole blood, fresh plasma, platelets and fibrinogen are the blood products of choice for rehydration.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical professionals, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.