This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Trinh Thi Thanh Huyen - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.
Chlamydia is a common sexually transmitted disease caused by the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis during sexual contact or from mother to child during childbirth. It can lead to serious and difficult-to-treat complications, including infertility.
1. Chlamydia infection in men
In general, the manifestations of Chlamydia trachomatis infection in men are mainly urinary tract infections, in addition to some other sexually transmitted diseases.1.1. Chlamydia Trachomatis is the main cause of non-gonococcal urethritis, accounting for 30-60%. In men, 75% of cases have common clinical symptoms as follows:
Difficulty urinating: Painful, painful and painful urination; Urethral discharge : Mucus, milky white or clear, small to moderate amount; Red flute mouth, swelling inflammation; There are signs of epididymitis and prostatitis; No other pathologies were found such as: Swollen inguinal lymph nodes, painful foci in the urethra, herpes lesions in the mouth of the flute and penis.
Viêm niệu đạo gây đái buốt
One thing to note is that non-gonococcal post-gonococcal urethritis is also commonly caused by Chlamydia trachomatis (70-80%). Patients are at risk of having both diseases at the same time (15-35%), but Chlamydia will prolong the incubation period, and treatment for gonorrhea does not eradicate Chlamydia. In addition, gonorrhea urethritis is often accompanied by Chlamydia (accounting for 35 - 90%).
1.2. Epididymitis and Prostatitis In the past, the medical cause of epididymitis was unknown, but with tetracycline treatment, the disease will progress well, so there is a view that Chlamydia trachomatis is the cause. The clinical manifestations of epididymitis only on one side of the scrotum are:
Pain; Edema; Sensitive; Fever; No or no symptoms of urethritis.

Nam giới bị viêm mào tinh hoàn có triệu chứng đau
1.3. Proctitis 50% of cases of proctitis caused by Chlamydia Trachomatis when having male anal intercourse have the following manifestations:
anorectal pain; Bleeding; There is mucus discharge; Liquid diarrhea. Non-LGV Chlamydia trachomatis presents with a mild to severe clinical presentation. Gram stain of rectal fluid showed many polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Proctoscopy revealed damaged mucosa, easy to crumble, bleeding when touched.
1.4. Pharyngitis Pharyngitis caused by Chlamydia Trachomatis spread through oral sex often causes no symptoms or symptoms are not obvious.
1.5. Reiter's syndrome Reiter's syndrome is associated with Chlamydia trachomatis infection manifesting in the following conditions:
Urethritis ; Eye conjunctivitis; Arthritis ; There are characteristic lesions of the skin and mucous membranes. Immunofluorescence assays show that over 80% of patients with Reiter's syndrome have Chlamydia trachomatis infection.
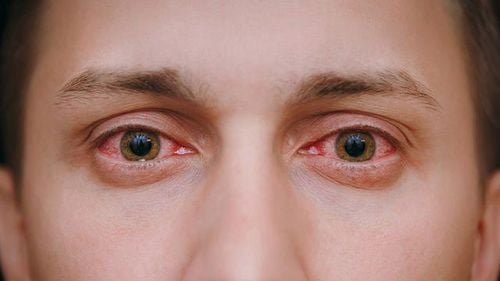
Viêm kết mạc mắt do nhiễm trùng Chlamydia trachomatis
2. Chlamydia infection in women
About 30% of female genital infections caused by Chlamydia Trachomatis infection have clinical symptoms, such as purulent vaginal discharge, lower abdominal pain, bleeding after intercourse or between periods, painful urination, difficulty and pelvic inflammatory diseases. . Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is a serious complication of urogenital Chlamydia Trachomatis infection, accounting for 18% with diverse clinical spectrum including:2.1. Cervicitis Most patients with cervicitis do not show symptoms (30 - 50%), about 1/3 have common local signs:
Mucous discharge or clear fluid; Enlarged gland with manifestations of edema, cervical congestion; Cervical bleeding easily; Spotting bleeding after intercourse. Gram stain of cervical secretions showed > 30 leukocytes/microfield, 1000X magnification. Swab test positive, cotton swab smeared on the uterus has yellow discharge.

Viêm cổ tử cung ở phụ nữ do nhiễm Chlamydia Trachomatis
Urethral discharge; Urethral mouth red or edematous; Difficult, harsh urination; Cervical discharge or cervicitis. However, the majority of patients with Chlamydia trachomatis urethritis have no clinical symptoms.
2.3. Inflammation of Bartholin's Gland Similar to gonorrhea, Chlamydia trachomatis also causes inflammation of the Bartholin's duct. Purulent Bartholin's gland inflammation can be caused by Chlamydia trachomatis alone or in combination with gonorrhea.
2.4. Endometritis More than 50% of patients with cervicitis and salpingitis also have disseminated bacterial endometritis. If Chlamydia trachomatis is not treated during pregnancy, a woman can develop fever and endometritis postpartum.
2.5. Fallopian tube inflammation is a complication of cervicitis caused by Chlamydia trachomatis, with very mild symptoms or no symptoms. However, scarring of the fallopian tubes can lead to ectopic pregnancy (9%) and female infertility (14-20%).
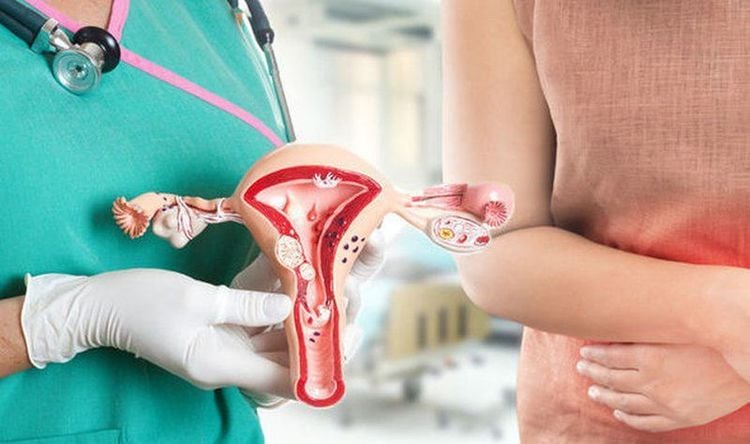
Một số bệnh lý phụ khoa do Chlamydia trachomatis gây ra
Pain in the right lower quadrant; Fever; Nausea or vomiting. Perihepatitis - Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome can occur after or at the same time as tubal inflammation. Clinically, the symptoms of sharp pain in the lower right flank need to avoid confusing cholecystitis and pleurisy.
3. Chlamydia infection in infants
Hình ảnh Chlamydia Trachomatis
3.1. Pneumonia Chlamydia pneumonia in infants appears 1-3 months after the baby is born with the following manifestations:
No fever; Cough pseudo-pertussis; There is mucus phlegm; Rapid breathing; Lungs have rales. Subclinical:
X-ray shows symmetrical interstitial infiltrates; Eosinophilia and Gamma globulinemia; IgM antibodies to Chlamydia. 3.2. Conjunctivitis Chlamydia conjunctivitis appears within 5-15 days of birth and is usually unilateral. Symptoms include edematous eyelid margins, purulent inflammation, red conjunctiva,...
To prevent urogenital infections caused by Chlamydia infection, people need to be thoroughly examined and treated definitively for infectious diseases. sexually. Condoms are the only birth control method that can help prevent chlamydia, as well as any other sexually transmitted disease. When detecting abnormal symptoms in the reproductive organs, you should stop having sex and quickly see a specialist for examination.
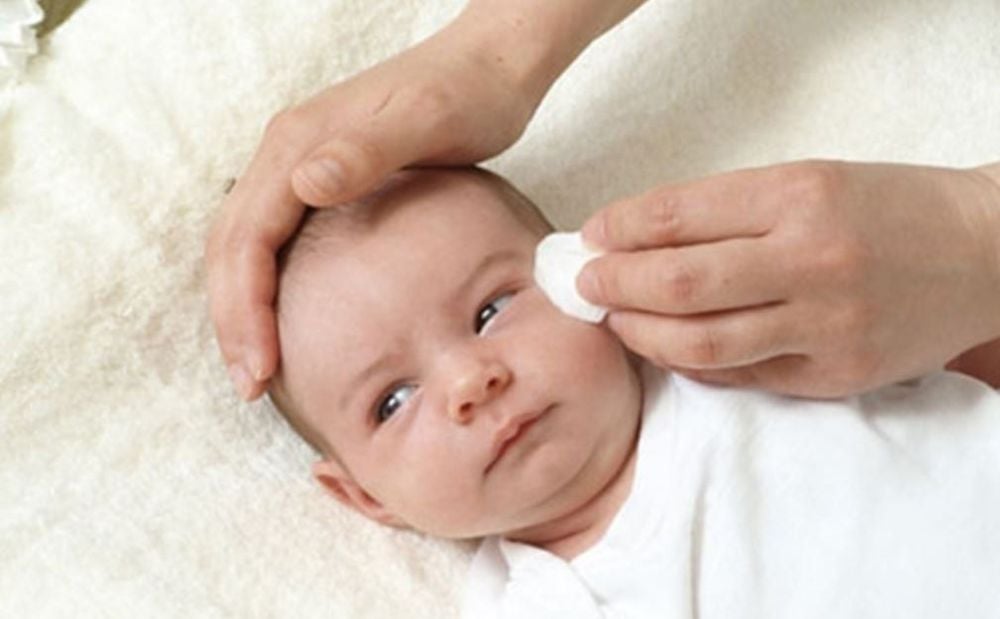

Viêm kết mạc ở trẻ sơ sinh
Currently, the doctor is an Obstetrician and Gynecologist at Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Recommended video:Periodic health check at Vinmec: Protect yourself before it's too late!