This is an automatically translated article.
Symptoms of discoid lupus erythematosus are often persistent and easy to recur. Although they do not cause itching, they greatly affect the patient's aesthetics and quality of life. Treatment of discoid lupus erythematosus at present only stops at supportive treatment to relieve symptoms, improve quality of life for patients but cannot be completely cured.
1. What is discoid lupus erythematosus?
Discoid lupus erythematosus (English name Discoid Lupus Erythematosus) is a common form of cutaneous lupus erythematosus, accounting for more than 50% of all cases. Discoid lupus erythematosus can completely progress to systemic lupus erythematosus, affecting many organs other than the skin such as kidneys, musculoskeletal, cardiovascular, neurological, but this rate is not high. , on average only about 5% of cases. It is a relatively benign, autoimmune disease, the exact cause of which is currently unknown.
Discoid lupus erythematosus is more common in women, the prevalence in the community is three times higher in women than in men. This is an autoimmune disease, so there are many links with genetic factors or local factors. The disease progresses more seriously if the skin lesions are exposed to a lot of ultraviolet rays in sunlight or a polluted living environment, there is an imbalance in the functioning of the endocrine systems in the body.

Bệnh lupus ban đỏ dạng đĩa thường gặp hơn ở phụ nữ
2. Causes of discoid lupus erythematosus
Discoid lupus erythematosus is classified as an autoimmune disease, with the exact cause of the disease not really understood. The most widely accepted hypothesis is the appearance of autoantibodies against antigens that are the body's normal, healthy skin tissues. Patients with discoid lupus erythematosus often have a pre-existing abnormal aetiology, when exposed to adverse conditions from the external environment or some internal factors, the disease will initiate and manifest. Some common trigger factors for discoid lupus erythematosus include:
Exposure to ultraviolet rays in the sun Polluted living environment Depletion, weakened immune system Psychological stress Disorders of functioning endocrine system in the body
Risk factors that increase your chances of getting discoid lupus are:
Race: African-American Age 25 to 50 Female Gender Having a family member with discoid lupus, disease systemic lupus or any other autoimmune disease.
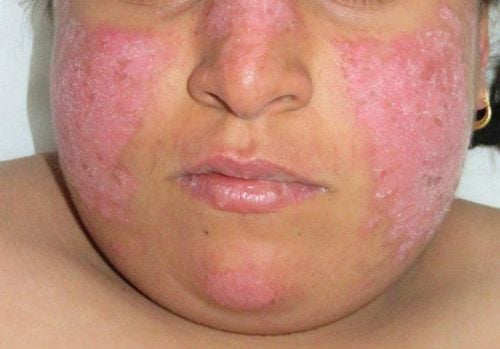
Bệnh nhân nữ mắc lupus ban đỏ dạng đĩa
3. Clinical symptoms of discoid lupus erythematosus
Discoid lupus erythematosus is clinically manifested mainly by abnormal skin symptoms. People with discoid lupus erythematosus often have an erythematous rash, atrophy of the skin, and patches of keratosis in some places. The most common first sign is a characteristic circular red or pinkish or pinkish papule or papule on the surface of the skin, accompanied by scabs. Scaly skin may be dry, simple at first, later becoming thicker, oily, sticky appear at the margin of erythema and change pigmentation. The affected areas of skin will thin out over time, leading to the formation of atrophic scars. Atrophic scars are small spots or concentrated in concave clusters, clearly demarcated, in the form of many white streaks, above the image of dilated small blood vessels, when touched, there is a slight pain. Common locations of atrophic scars in discoid lupus erythematosus include: bridge of the nose, cheeks, and facial skin in front of the ears on both sides to form a butterfly shape, and the scalp area corresponds to the hairline. The nails of patients with discoid lupus erythematosus are more fragile, bent, or deformed due to brittleness than those of the general population. Lesions of the disease do not cause itching, so there are rarely complications of skin infection but often appear persistent and easy to recur.
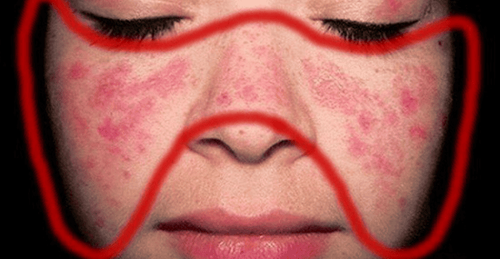
Bệnh lupus ban đỏ dạng đĩa vùng sống mũi và hai má
In discoid lupus erythematosus, areas of the skin that are not covered, exposed to a lot of ultraviolet rays in sunlight, such as the face, neck, hands, feet, ... are at risk. Muscle damage is highest, although lesions can appear anywhere on the body. The scalp, in addition to the appearance of red rashes with white scales and atrophic scars, also shows permanent hair loss without scarring.
Discoid lupus erythematosus develops into exacerbations when exposed to triggers and is well controlled with current treatments.
Although the discoid lupus erythematosus is quite characteristic clinically, establishing a definitive diagnosis for a case requires paraclinical facilities. The doctor will order blood tests to measure IgE antibody levels or detect disease-specific antibody antigens in the blood, and skin biopsy to observe histological characteristics of the skin to be investigated with lesions. characterized by the presence of IgE antibodies.
4. Treatment of discoid lupus erythematosus
Treatment of discoid lupus erythematosus is still challenging because there is currently no specific treatment to help patients stay healthy. The main current treatment goals include: limiting the spread of old lesions, limiting the formation of scars, and preventing the appearance of new lesions. Some groups of drugs commonly prescribed in the treatment of discoid lupus erythematosus include: Corticosteroids: These drugs have anti-inflammatory effects and limit the damage areas. Common side effects are thinning of the skin, thickening of the hair follicles. Corticosteroids can be used as topical or injected medications. Calcineurin inhibitors: This group of drugs is often used in the form of topical ointments to help suppress the local immune system, so it limits the areas of skin damage from spreading. A notable side effect of calcineurin inhibitors is an increased risk of skin cancer if taken for a long time. Some other drug classes: In some patients who do not respond or respond poorly to the above drug groups, some other stronger drugs may be prescribed such as chloroquine, methotrexate, mycophenolate, ... The medications listed above all belong to the group of drugs that need to be prescribed and used under the guidance of a doctor. Patients or family members are not allowed to self-treat to avoid unnecessary complications.

Điều trị bệnh lupus ban đỏ dạng đĩa bằng thuốc
5. Prophylaxis of discoid lupus erythematosus
Discoid lupus erythematosus wants to be well controlled, in addition to using drugs, it also requires a change in other lifestyle habits at the same time. Some proven measures to control symptoms and limit recurrence include:
Cover damaged areas with a coat, umbrella Avoid sun exposure Use sunscreen to avoid the effects of ultraviolet rays Do not use tobacco or alcohol Use gentle skin moisturizers that are less irritating that can support the skin's immune system Minimize the use of cosmetics If If you have a medical condition that requires drug treatment, people with discoid lupus erythematosus should consult a doctor because some medications can increase the skin's sensitivity to triggers. To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE
MORE:
SLE patients have should get pregnant and give birth? What disease is lupus? Dangers and complications of the disease Should patients with lupus erythematosus get pregnant and give birth?