This is an automatically translated article.
Lupus is an autoimmune disease that can affect any organ or part of the body. The organs that are susceptible to this disease are the skin, kidneys, heart, lungs, and eyes. How does lupus affect the heart and lungs?
1. How does lupus affect the heart?
Lupus erythematosus increases the chance of heart disease and stroke. This may be due to the long-term inflammation that accompanies lupus erythematosus. In addition, certain drugs such as steroids can also increase the risk of cardiovascular disease. Lupus erythematosus can cause myocarditis or inflammation of the lining around the heart, also called pericarditis. These conditions can cause a patient to experience sharp pain in the chest.
Patients with lupus are more likely to have clogged arteries that can lead to heart attacks and strokes at a younger age. There have been studies that point to the need for extra time, attention, and treatment for high blood pressure and other related problems in patients with lupus erythematosus.
In fact, the tendency for lupus patients to have an early heart attack and stroke has been known for decades. Several studies have pointed to known risk factors such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes as a cause of early heart disease and stroke. These factors are worsened or provoked prematurely by steroids used in the treatment of lupus erythematosus.
Thuốc Steroid điều trị lupus làm tăng nguy cơ đau tim và đột quỵ
Researcher Mary J. Roman, a cardiologist at Weill College of Medicine at Cornell University in New York, conducted a study of nearly 400 people, half of whom had lupus and half had lupus. The rest are not sick.
Research shows that people with lupus have more arterial plaque. Plaque buildup is especially more common in lupus patients younger than 40 years of age.
Plaque buildup is measured by ultrasound of the carotid arteries in the neck - an indication that plaque is also present in the heart arteries.
SLE patients under 40 years of age are nearly 6 times more likely to have plaque buildup than patients without lupus. Older patients also tend to do the same. Plaque buildup and blockages in the arteries are significantly more common in lupus patients than in those without lupus. This rate is up to 37% in patients with lupus erythematosus, while in normal people it is only 15%. This increased plaque buildup cannot be attributed to traditional risk factors such as smoking, blood pressure or cholesterol levels. Patients with lupus erythematosus with arterial plaque tended to be older, had lupus longer, and had more severe lupus, higher blood pressure, and higher levels of bad cholesterol (LDL) than lupus patients without. plaque.
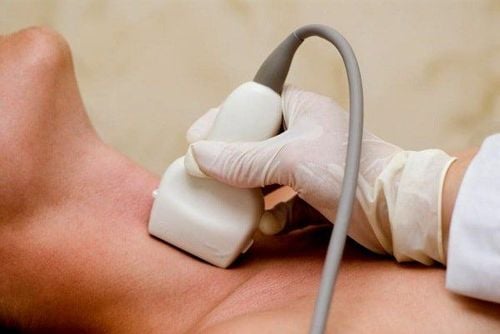
Siêu âm động mạch cảnh để kiểm tra khả năng tích tụ mảng bám
Some physicians treating lupus patients have failed to adequately treat high blood pressure, diabetes, obesity, and high cholesterol. This will increase the risk of heart disease in these patients.
In addition, the heart valves can also be affected by lupus erythematosus, thereby affecting the functioning of the heart, which can lead to heart failure.
Lupus ban đỏ cũng gây ảnh hưởng đến sự hoạt động của các van tim
2. How does lupus affect the lungs?
Lupus can also affect a patient's lungs, it can cause conditions such as:
Pleurisy: Inflammation of the membrane that covers the outside of the lungs, causing the patient to feel chest pain, pain often worsens with deep inhalation. Pneumonia: Lupus can cause pneumonia, making it difficult for patients to breathe and chest tightness. Sometimes scarring of the lungs makes breathing difficult. Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of modern facilities, medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in medical examination and treatment, patients can rest assured to visit. and hospital treatment.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.
Reference source: webmd.com