This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Vo Thi Thuy Trang - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Da Nang International General Hospital.The millions of neurons located in the colon work similarly to how the brain in the head works. What's more interesting is that this set of neurons can control intestinal muscles independently of the brain. The digestive system is able to push the stool down on its own without the central nervous system.
1. How does the digestive system work?
Contrary to the natural way other systems in the body work, the digestive nervous system is called the "second brain" by scientists because of its ability to function independently of the brain. What's most intriguing is that the millions of neurons in the gut actually evolved from ancient times to this.
The enteric nervous system consists of nerve cells located in the intestinal wall, about 9 meters long from the esophagus to the anus. This second brain contains about 100 million neurons, more than the spinal cord or the peripheral nervous system.
Countless nerve cells in the digestive system allow us to sense the contents of the intestines. The daily process of food digestion is quite complex, breaking down food, absorbing nutrients and expelling waste requires chemical processing steps, mechanical mixing and rhythmic muscle contractions. to move things on the way down.
Thanks to its own reflexes and senses, the second brain can control intestinal behavior independently of the brain, instead of being controlled remotely by the brain through the spinal cord. Thus, the work of digestion will be completely entrusted to the intestines. However, the complexity of the second brain cannot be explained through this process alone.
The digestive nervous system is full of important neurotransmitters that do more than simply process the digestion of food or cause an occasional upset stomach. This second brain also contributes to mental state and plays a key role in a number of diseases throughout the body. Despite its far-reaching influence, the second brain is not the center of any conscious thought or decision.
2. Activation of the nervous system of the “second brain”
The existence of a second brain has long been known in the scientific community. However, the explanation for the exact function of the gastrointestinal nervous system remained obscure until recently - when scientists from South Australia observed for the first time how the enteric nervous system performs its task. during bowel movements.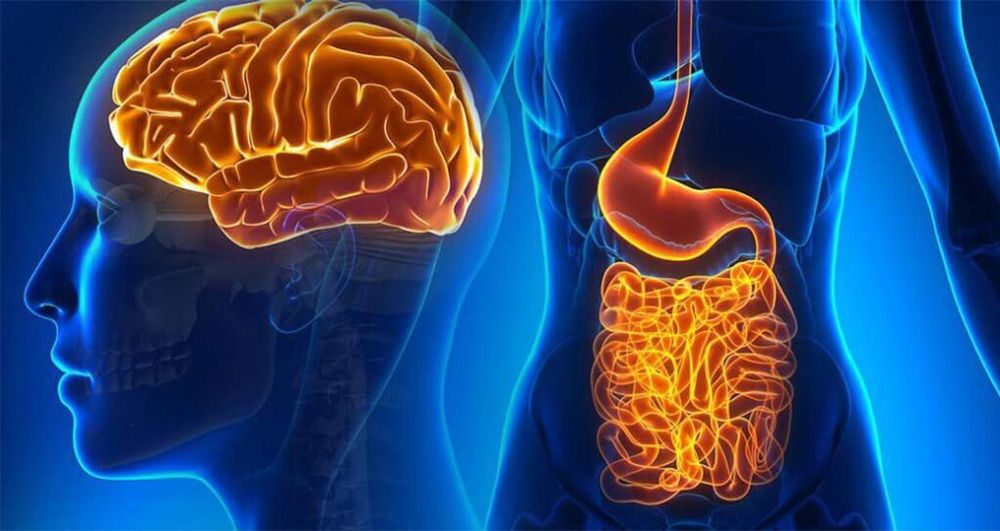
Hệ thần kinh tiêu hóa được so sánh như bộ não thứ 2
The team examined the colons of deceased mice, using an imaging technique programmed with electrophysiological recordings of smooth muscle. The method specifically detects rhythmic patterns going on inside the colons of mice.
The researchers used a mild electric shock to stimulate the colon to work. Once the colon was activated, the team was able to observe how the matrix of neurons inside the colon pushes waste products down the large intestine.
According to the explanation, millions of nerve cells in the digestive tract work together to create muscle contractions, pushing waste through the final point of the digestive system. This activity is called gastrointestinal cell activation, which helps stimulate parts of the intestinal muscles to contract the colon and move stool out of the body at a steady rate.
3. Digestive nervous system and diseases
Previous studies have determined that the gastrointestinal nervous system produces almost 95% of the body's serotonin and 50% of dopamine. In fact, a 2010 study found that osteoporosis is linked to serotonin produced by the gut.
Because antidepressants called selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) - increase serotonin levels, people taking these drugs often experience digestive upset as a side effect. In addition, daily feelings of happiness can also rely on messages from the lower brain to the upper brain. For example, vagus nerve stimulation is a useful treatment for depression.
Irritable bowel syndrome partly also arises from too much serotonin in the gut, and perhaps this is considered a 2nd brain psychosis.
Serotonin seeping out from the 2nd brain even plays a role role in autism - a developmental disorder in childhood. Many children with autism have gastrointestinal abnormalities, in addition to elevated levels of serotonin produced by the gut in their blood.
Other research is currently looking at how the second brain controls the body's immune response. In fact, at least 70% of the immune system (antibodies) targets the gut to expel and destroy foreign "invaders" (antigens). Meanwhile, one study found a link between traumatic brain injury and intestinal damage.
The second brain also affects our psychological state in other, more obscure ways. A large part of human emotions can be affected by the nerves in the gut. Butterflies in your stomach - the phrase for feelings of restlessness or nervousness - is seen as an example of a physiological stress response related to the digestive system or gastrointestinal (GI) disturbances that can alter a person's mood. an affected person.
Cảm xúc của con người có thể bị ảnh hưởng bởi hệ thần kinh tiêu hóa
4. The second brain can also be the first brain
The team concludes that the digestive nervous system activates cells that may be an ancient function of the body, undergoing evolution and preserved by the nervous system. In other words, neuronal activation from the colon could be the first functioning "brain" in the body, based on evidence that the enteric nervous system evolved before the central nervous system.The above study became the first observed example of neuronal activation in the enteric nervous system. Now that experts know how the nervous system of the digestive system works in a healthy body, it is possible to develop treatments for diseases of the colon.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: techtimes.com