This is an automatically translated article.
Article by specialist doctor II Khong Tien Dat - Radiologist, Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Ha Long International Hospital
PET/CT scan is one of the most advanced imaging techniques currently being applied in major hospitals in our country. Especially in the diagnosis of diseases related to cancer, cardiovascular and neurological diseases.
1. What is a PET/CT scan?
PET/CT is a combination of 2 methods PET and CT to bring an ideal image that allows doctors to diagnose early, comprehensively, and then decide on effective treatment methods. for patients. PET (Positron Emission Tomography) provides information about the function of organs in the body. CT (Computerized Tomography) provides images of anatomy and body structure. 1.1 When should a PET/CT scan? When prescribed by a specialist. When the patient wishes to have a scan to detect cancer early or evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment process. In this case, it is necessary to see a doctor for detailed advice before deciding to proceed with the scan. 1.2 What is PET/CT scan for?
1.3 Some important applications of PET/CT
Máy chụp PET/CT
Scan To PET/CT has the ability to detect lesions even when there is no change in anatomical structure. Find the site of the primary cancer lesion in patients with metastases. Helps to differentiate between benign and malignant (cancerous) tumors. PET/CT scan has high value in diagnosing cancer stage, deciding treatment attitude. Accurately assess the effectiveness of the treatment process. Thoroughly detect remaining cancer lesions or recurrence after treatment. Oriented for radiation therapy, ensuring the highest efficiency while minimizing damage to adjacent healthy tissue. Application of PET/CT for cardiovascular disease High value in assessing myocardial perfusion status and recovery ability after intervention. Application of PET/CT for Neurological Diseases Detecting epileptic foci, early diagnosis of degenerative Alzheimer's or Parkinson's diseases. 1.4 Where is a good place to take PET/CT? What is a good PET/CT site? There is a team of doctors and imaging technicians who are good, most experienced in PET/CT imaging techniques. Having a team of good specialists and good treatment plans on cancer, neurological and cardiovascular diseases to apply the results of the scan and treat the disease effectively. Using the modern PET/CT scanner system of the world's leading medical equipment manufacturers such as: GE (USA); Siemens (Germany); Phillip (Netherlands).
1.5 PET/CT Scan Procedure

Bệnh nhân cần nhịn ăn 6 giờ trước khi chụp
Prepare before the scan See a doctor for a thorough examination and advice Limit exercise for at least 24 hours before the scan. Limit smoking. Fast for at least 6 hours before your scan, and avoid energy drinks, sugar, and caffeine. Drink lots of filtered water. Diabetics need to keep their blood sugar in a normal range. Bring all the patient's medical records, especially X-rays, ultrasound, CT, MRI and blood tests (if any). While taking the patient dressing, the medical staff checks the patient's body readings and blood sugar. The patient received intravenous fluids and FDG injection, rested for 45 - 60 minutes, waiting for the drug to absorb. The patient underwent a full-body PET/CT scan. In some cases, the doctor may ask the patient for additional scans. The total time the patient spends in the imaging room is about 3-4 hours, and the scan time is about 20-30 minutes. After the scan, the patient rests in the storage room for about 2 hours so that the FDG is completely eliminated according to the patient's usual waste route. While resting, the patient should drink plenty of fluids and be served snacks. After the PET/CT scan, the patient does not need to follow any diet and can resume normal activities, but should limit contact with pregnant or lactating women within 3 hours of the scan. PET/CT scan results will be returned in 1-2 days.
1.6 Advantages and disadvantages of PET/CT
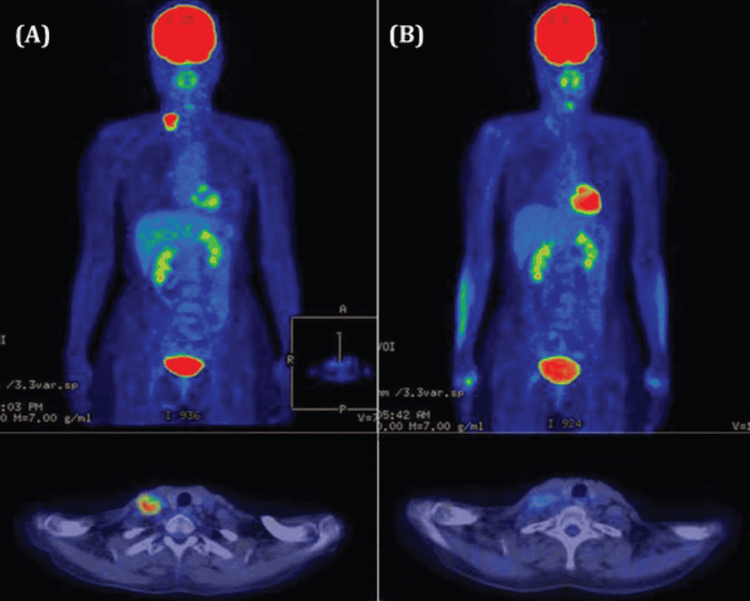
Kết quả chụp chụp PET/CT giúp chuẩn đoán chính xác
Advantages Fast, accurate diagnosis, with high sensitivity and specificity in determining the location of the primary cancer that imaging methods such as computed tomography (CT) scan, resonance imaging magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), ultrasound... not evaluated. Full body scan, metabolic abnormalities can be detected, early pathological images are recorded, even when there are no structural changes, helping to diagnose cancer early and accurately. . Evaluating the effectiveness of cancer treatment allows doctors to change treatment decisions if needed. PET/CT scan is also of high value in Cardiovascular and Neurological pathology. Cons The cost of the scan is too high compared to most patients, especially patients without Health Insurance. Long time to prepare and conduct the scan (total time in the imaging room is 3-4 hours) PET/CT scan is not a miracle for all cancer patients (needs to be consulted by a doctor before taking the scan). ). A small dose of radiation is injected into the body before the scan, the risk of radiation is very low, but there are risks. Mild allergic reactions to radiopharmaceuticals are possible, but are rare. However, it is necessary to inform your doctor or medical staff if you have an allergic reaction. PET/CT scan results still have false positives or false negatives in some cases (compared to pathological results). Be very cautious with pregnant and lactating women (need to inform your doctor or medical staff).
2. Whole-body magnetic resonance imaging
Các bác sĩ đang chuẩn bị chụp cộng hưởng từ MRI toàn thân cho bệnh nhân
Is a method of magnetic resonance imaging of all important organs in the body including:
Head: evaluates the skull, brain parenchyma, cerebral blood vessels, pituitary gland, eye sockets, facial software, ... Neck : evaluate the soft tissues of the neck, thyroid, salivary glands, ... Thoracic: evaluate the lungs, mediastinum, ... Abdominal: evaluate the liver, bile, pancreas, stomach, kidneys, ... Bones spine: evaluate the entire spine from the neck, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, paraspinal soft tissues, nerves, ... Hip pelvis: evaluate the pelvis, hip joints, bladder, and rectum colon, uterus and ovaries in women, prostate in men, ... Detailed, clear assessment of both bones and vital organs of the body. Can be performed even in people who have no symptoms or some abnormal symptoms in certain organs or have a family history who want a comprehensive examination, detecting both benign and malignant diseases.
2.1 Indications of magnetic resonance imaging People with no abnormal symptoms: detect congenital abnormalities or pathologies at an early stage with high sensitivity:
Benign diseases: disc herniation, vertebral collapse , benign diseases of the liver, kidney, inflammatory diseases, cysts, fibroids, ... Malignant disease: detected tumors in all organs such as bronchi, renal epithelium, liver, colorectal, lymphoma, other organs. bone tumor, soft tissue, ... Detecting cancer metastases, especially in brain, liver, bone, ... Post-traumatic assessment, monitoring treatment, ... 2.2 Contraindication to MRI (MRI) Cases where electronic devices are implanted in the body:
Brain clamps, blood vessels Place stents (metallic segments) in blood vessels Place a defibrillator or pacemaker of any type Metal in The person may move during the scan causing injury to the person taking the scan Less than 12 weeks pregnant. More than 12 weeks pregnant can have MRI without affecting the fetus
2.3 Cases to consider when taking full-body magnetic resonance imaging

Bênh nhân có hình xăm có thể bị nóng rát trong quá trình chụp
Not a contraindication of MRI but it will affect the image and make it difficult to observe. When taking, it is necessary to inform the technician and the imaging time may be longer than usual:
Metal is used in surgery. orthopedic, orthopedic, ... Dentures or braces Tattoos may be hot during the scan due to iron In case of claustrophobia, sedation may be used before the scan Small patient Age, excited, hyperactive 2.4 Preparation before the scan + Before going to the imaging facility:
Fasting for 4-6 hours to assess the abdomen for the most accurate results Bring previous examination documents, if any, such as super sound, X-ray film, computerized tomography film, ... + Before taking the picture:
Be carefully explained and exploit information in the questionnaire to ensure the safety and interests of the person taking the scan. Inform your doctor and technician of any health problems you have. It is necessary to change clothes for shooting, and at the same time do not bring metal objects into the shooting room such as jewelry, hairpins, watches, eyeglasses; hearing aids, dentures, ATM cards, phones, ... Parents, relatives when entering the room together also need to remove all metal and electronic items in the person. During the scan, in some cases, a contrast agent may be injected into the vein to help the doctor see the abnormality more clearly. Therefore, it is necessary to take a history of allergies to drugs, food, environment, asthma, ... usually this drug causes much less side effects than contrast medium in computed tomography. + During the shooting process:
Magnetic resonance imaging of the whole body is often used with a headset to reduce noise and help communicate with the technician outside the shooting room when needed, and at the same time listen to music to mental comfort during the shooting. The photographer needs to keep the shooting parts in a motionless position at the request of the technician, the movement will make the image not clear or misleading, affecting the results. During the scan, the scanner will make many scans, each time there will be noise, but the MRI scan is not painful for the scanner, you may feel a little heat but not much discomfort. + After taking the photo:
The photographer will be guided and helped to return to the changing room, put on normal clothes, sit and rest in the waiting room for about 3-5 minutes, then can move to the required positions. other examination. In case the photographer has to use injection, right after the end of the scan, the technician will help him move to the monitoring room after about 15 -30 minutes, then the needle will be removed, fixed to stop bleeding after withdrawal. needle, then move to the changing room, put on clothes again. Time to return results to customers ranges from 45 minutes to 1 hour depending on the difficulty and abnormalities of the photographer. For difficult cases, it will be necessary to consult to give the most accurate results for the patient. Possible results after total body magnetic resonance imaging:
Normal, or negligible abnormality: that is, the client is completely healthy or has abnormalities that do not affect the health of the examiner or the patient. no treatment needed. Risk of Abnormalities: There are abnormalities that require more in-depth laboratory evaluation or follow-up. Obvious abnormalities: based on the results of magnetic resonance imaging, the customer can use it to contact the hospital's specialists for treatment orientation. 2.5 Benefits of Whole Body MRI MRI is safe for the operator, especially for the whole body, many parts because it's a non-invasive technique and doesn't contain ionizing radiation. The contrast agent injected during an MRI is much less allergenic than the substance used in a CT scan. Whole blood vessels can be imaged without injection Assessing areas covered by bone, difficult to see in other imaging methods Detects benign and malignant diseases Lower cost than PET/ CT 2.6 Risks of MRI If the safety instructions of doctors and technicians are followed, the risks of MRI scans are almost non-existent. The risk of an allergic reaction to the contrast agent is rare, if any, and is usually mild and easily controlled. In addition to the above applications in whole-body magnetic resonance imaging, DWIBS is also used for analysis and evaluation in cancer pathology.
3. What is DWIBS?
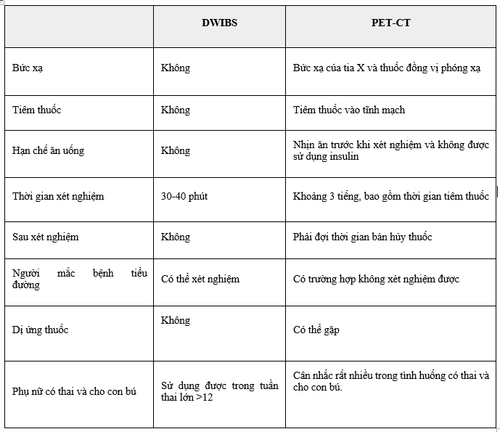
So sánh DWIBS và PET-CT
DWIBS is Diffusion-weighted Whole body Imaging with background suppression. DWIBS can be used to screen for cancer and metastases on a large scale throughout the body. Studies show that DWIBS is effectively used in the screening of some cancers, in the diagnosis of metastases, and in monitoring the progression of the disease. The DWIBS technique was first studied in Japan in 2004, and is still relatively new in Vietnam. Compared to PET-CT - the "whole body cancer screening" test, MRI is expected to be highly effective in detecting cancer. Below is a table comparing DWIBS and PET-CT.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health system nationwide to visit or contact the hotline here for support.