This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Tung Hoanh - Department of Resuscitation - Emergency - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.Pleural effusion is not a disease but a syndrome caused by many different diseases. To diagnose a pleural effusion as well as the cause of this condition, it is necessary to do tests for pleural effusion.
1. Causes of pleural effusion
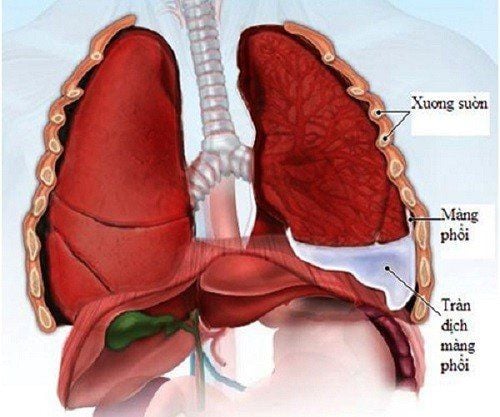
Causes of pleural effusion according to the pathogenesis:Due to increased hydrostatic pressure: If there is an increase in the difference between intravascular pressure and pressure in the pleural cavity, it will lead to an increase in the rate of fluid formation in the pleural cavity. pleural cavity through the Starling equation (starling equation). Causes: Right heart failure, left heart failure, pericardial effusion, superior vena cava occlusion syndrome. Due to decrease in capillary osmotic colloidal pressure, hypoalbuminemia: Found in cirrhosis, nephrotic syndrome, malnutrition. Due to increased capillary permeability due to inflammation, bacterial infections such as tuberculosis, cancer. Decreased pleural fluid reabsorption: The most common cause of pleural effusion is decreased pleural fluid reabsorption due to obstruction of the lymphatic drainage system of the pleural space. The lymphatic system in the mediastinum is blocked by tumor compression, by fibrosis. Due to increased venous system pressure: Increased central venous pressure will lead to decreased lymphatic flow into the venous system, causing pleural effusion. Elevated pleural pressure, or early atelectasis, can both lead to pleural effusion. The cause of pleural effusion according to biochemical tests is divided into effusion, exudation:
Permeation: Nephrotic syndrome, chronic renal failure, cirrhosis of the liver ascites, irreversible left heart failure, peritoneal dialysis, failure Thyroid, Malnutrition. Outbreaks: Tuberculosis, cancer, lung and pleural infections (bacteria, fungi, parasitic viruses such as amoebiasis, fascioliasis, fascioliasis), pulmonary embolism, systemic diseases (lupus, rheumatoid arthritis...). Pleural effusion with blood-colored fluid: Due to thoracic trauma, pleural cancer, cancer metastasis to the pleura, complications of pleural exploration procedures: pleural puncture, pleural biopsy, .. Common clinical causes of pleural effusion include:
Tuberculosis pleurisy Pneumonia Congestive heart failure Cancer Cirrhosis.
Tràn dịch màng phổi có thể do viêm phổi màng phổi gây ra
Trắc nghiệm: Làm thế nào để có một lá phổi khỏe mạnh?
Để nhận biết phổi của bạn có thật sự khỏe mạnh hay không và làm cách nào để có một lá phổi khỏe mạnh, bạn có thể thực hiện bài trắc nghiệm sau đây.2. Diagnostic tests for pleural effusion
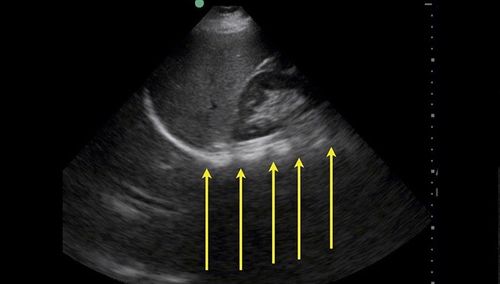
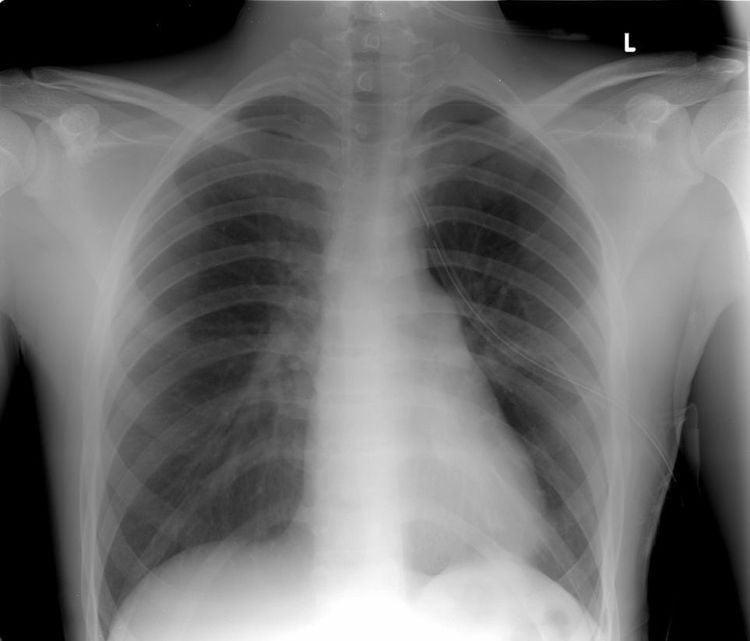
Chest X-ray: Small number of pleural effusions show only obtuse rib angle, the earliest is posterior rib angle on tilt film. Moderate pleural effusion shows a dark, uniform opacity, in the lower third of the lung, a curve can be seen with the concave side facing upward (Daoiseau curve). More pleural effusion: Blurring more than 1/2 of the lung, pushing the heart to the opposite side. In case of localized pleural effusion, it is necessary to combine ultrasound or computed tomography to determine the location.Pleural puncture with fluid: The gold standard.
In addition, the patient may be ordered to perform tests to diagnose pleural effusion including:
Test for cells in pleural fluid Microbiological test AFB in pleural fluid helps diagnose tuberculosis pleura PCR (polymerase chain reaction) results in TB diagnosis with high sensitivity and specificity. Test pleural fluid culture for other bacterial causes such as pneumococcal, staphylococci. fungi, parasites. Culture: pleural fluid culture, especially pleural biopsies, has in fact demonstrated a 2-3-fold increased ability to detect bacteria in tuberculous pleural effusions Tests for pleural effusion on immunohistochemical examination.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.