This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Doctor Department of Gastroenterology - Endoscopy, Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.
Intestinal obstruction is the stagnation of substances in the intestinal lumen. If left untreated, bowel obstruction can lead to bowel perforation. This condition causes the contents of the intestine, where many bacteria are found, to spread to the body cavities and lead to death. It is necessary to diagnose and treat intestinal obstruction promptly to avoid damage to the intestines, which greatly affects the patient's health.
1. Symptom diagnosis
Intestinal obstruction is divided into mechanical bowel obstruction and mechanical intestinal obstruction. The process of diagnosing intestinal obstruction is based on many different methods and tests to accurately assess the disease state, cause, and make a differential diagnosis.
1.1. The patient will have symptoms such as:
Abdominal pain: Sudden pain, writhing pain beyond tolerance, the patient may faint Vomiting: if the obstruction is high, the patient will vomit profuse, early vomiting. If the site of obstruction is low, the patient will vomit late and vomit less. Vomiting of food at first, vomiting of bile after the end of the meal, and longer vomiting of fecal-like substances. Constipation: This is a symptom with very important diagnostic value. Constipation occurs when the patient has an early stage of high obstruction and is still able to defecate. 1.2. Entities Abdominal distention: The high obstruction is less distended, the lower obstruction is more distention. All clutter is due to occlusion. Single-site distention is caused by volvulus, and distention of the abdomen is due to volvulus of the sigmoid colon. Floating bowel. Snake sign.

2. Examination
2.1. Palpate the abdominal wall The abdomen is soft. Palpable tumor: may be due to foreign body in intestine, worm tuft, intussusception mass, intestinal wall tumor. Typing: There is reverberation due to the vapor. There is a scar on the abdominal wall: suggesting a diagnosis of postoperative bowel obstruction, palpable rectal cancer. 2.2. Examination of the hernia orifice Examination of the hernia is a mandatory rule when diagnosing intestinal obstruction.
2.3. Rectal examination The rectal balloon is empty, palpable rectal cancer.
2.4. Body as a whole The pain caused by intestinal obstruction accompanied by vomiting causes the patient to feel tired, feverish, dehydrated, and lose electrolytes.
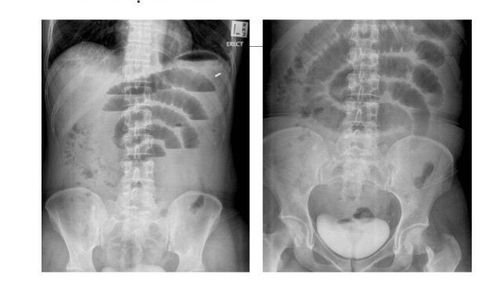
3. X-rays
X-ray helps:
Early diagnosis of intestinal obstruction. Differential diagnosis of intestinal obstruction due to any cause, early intestinal obstruction after surgery, mechanical or functional intestinal obstruction. Indicate the location of the obstruction: High or low obstruction of the small or large intestine. Indicate whether there is fluid in the abdomen. However, for an accurate diagnosis, an X-ray of bowel obstruction is not always the most feasible method.
4. Ultrasound
This method is often used to identify intestinal obstruction in children.
Ultrasound image in people with mechanical intestinal obstruction:
Large bowel lumen (colon > 3cm, colon > 5cm). The intestinal wall thickness varies. Normally, the intestinal wall is about 3mm - 5mm thick. Intestinal lumen decreased in the first stage, intestinal lumen increased in the later stage due to edema. The intestinal lumen contains a lot of fluid, gas and other substances that increase the sound. Increased peristalsis over the site of obstruction, especially the forward, backward and vortex movements of fluid in the intestinal lumen. A loop of bowel completely lost motility. Other bowel loops remain and peristalsis increases. Ultrasound results of different times the abdominal fluid increased rapidly and increased much. Using the appropriate cross-section can find the cause and location of the blockage.
5. CT and magnetic resonance imaging
Computed tomography (CT) scans and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) provide clear image results, helping to diagnose more accurately than X-rays. The obtained images also clearly show the location of the blockage, the extent of intestinal damage, the cause of the intestinal obstruction.
In addition, there are other diagnoses such as blood tests and biochemistry, differential diagnosis.
At Vinmec International General Hospital, it is fully equipped with today's most advanced methods of diagnosis and treatment of intestinal obstruction. There is a team of well-trained and experienced gastroenterology specialists; professional medical service quality, prompt examination and timely treatment for many difficult cases.
For detailed advice on bowel obstruction, please come directly to Vinmec health system or register online HERE.