This is an automatically translated article.
Immunohistochemistry and lymphoma classification is a complex process. This method can test CD 30+ immunomarker.1. Perspectives on diagnosis of immunohistochemistry
Performing immunohistochemistry to classify lymphomas is a rather complicated procedure. Over the years of research, medical methods are constantly being improved to achieve the most accurate results. In addition, changes in gene structure and body mechanisms over time also cause difficulties, making the analysis process increasingly complicated.We all know, lymphoma receptors appear in cells. This is a characteristic of the immune system, which helps the body maintain stability. However, the morphology and function of each type of lymphoma are not the same. Therefore, histological examination is necessary to differentiate between benign lymphoma and malignant lymphoma.
The documents are few and there are not enough data, so it was difficult for the research process. Therefore, there are two problems to be solved: Classification of lymphomas found in the lymph nodes by phenotype and assessment of CD30+ immune markers according to the classification structure of those lymphomas.
2. Selected subjects and research methods for immunohistochemistry
Lymphomas in each body are different and difficult to collect. Based on the available samples, the scientists carried out a cut and staining and determined that about 30 samples were benign nodes.Classification according to lymphoma morphology:
In terms of morphological characteristics, small cells will be 6 - 12 cm in size and the infectious substance is clumped. Large cells are called tumor cells, the maximum size is 30 cm. Analysis of the cells revealed nuclei not of the same size and also vesicles. Notched cells and small cells have the same size, but the difference is that notched cells will have a twisted shape, shrinking at many angles.
Small cells without nicks found in size ranged from 13 -20 cm, the cell nucleus was round and prominent with each granule. Immunoblasts are larger than non-knotted large cells, have large nuclei, and are centrally located or attached to the periphery. Lymphoblasts are about 15 cm in size, evenly distributed, often without nuclei.
CD30+ immunohistochemical staining technique:
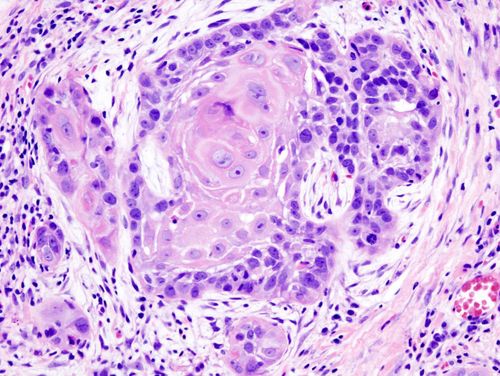
When performing immunohistochemical staining, the steps will be tested and performed sequentially. In which, commonly used antibodies are CD3, CD5, CD10, CD20, CD23, CD30, CD43, CD45RO, CD35, CD68, CD79a, BCL 2, KAPPA, LAMBDA, ALK 1, cyclin D1, Ki-67. The lymphomas used in the study have been classified into 2 cell types, T and B. The results of exposure also produce a common marker of T and B cells with lymphoma
The B cell line will be positive for antibodies. CD20 and CD79a. At the same time, they did not show the hidden traces of the T cell line but found the CD5 and CD43 imprints. The T cell line has immunoblotting with CD3, CD5, CD43 and CD45RO. According to the results, the percentage of B cell lineage accounts for the majority, the rest are T cells and other unidentified cells. The frequency of expressing immunological markers is based on statistics that appear clearly on the CD30+ imprint.
3. Lymphoma immunohistochemistry test results
Based on reports and CD30+ immunohistochemistry, immunohistochemistry remains a highly reliable test. Therefore, if immunohistochemistry is performed in cancer, it is hypothesized that it is possible to find out whether the tumor is benign or malignant. In each study, the expression rate of the immunological markers of lymphoma varied due to many factors. Much of the difference is due to the fact that the sample is taken in the nodal or extranodal region. There will be more T lymphocytes outside the lymph nodes.The immunomarker data in each antibody is statistically significant biologically. This can help identify follicular lymphoma production. However, the results showed that the immunomarker was more significant when using CD21, CD35 and BLC 2 to differentiate lymphomas.
Of the CD30+ immunomarker, CD 43 expressed the fewest lymphoma cells. Meanwhile, CD45Ro has a rate of 43.75%. B-lymphoma does not manifest in either of these markers, so the test is useful for early detection of lesions.
4. Significance of the CD30+ . immune marker
In one biopsy report, scattered CD30+ cells were observed. They are clinically correlated to exclude the risk of lymphoproliferative disorders. Disorders of T-cell lymphoproliferation in primary skin CD 30+ immune markers are quite common, second only to mycosis fungoides and Sezary's syndrome.Positive expression of CD30 has been observed in major cellular changes in patients with MF lymphoma, hodgkin's or some other disordered response. The CD30 receptor mediates the survival of cells attacked by the protein. Thanks to protein binding, they are believed to induce necrosis and reduce tumor size. CD30+ can be present in T and B cell lines.
It is not true that the absence of the CD30+ immune marker means the absence of cancer cells. They can influence the cancer diagnosis process if judgment is based on appearance. Especially cutaneous lymphoma should pay more attention when observing these cells.
Patients during treatment should be monitored and biopsied for the most accurate assessment. In some rare cases, the results may be erroneous, affecting the judgment, so statistical periodic checks will increase the reliability.
The positive expression of CD30 at clinical biopsy shows a correlation in some lymphomas and CD30. Therefore, clinical monitoring and accurate judgment will give meaning to the process of assessing whether the outcome is caused by cell damage or cancer.
Lymphoma immunohistochemistry has great biological significance. The research results make an important contribution to the diagnosis of lymphoma type. From there, select targeted drugs to kill cancer cells. The CD30 immune marker plays an important role in the pathology of Hodgkin's lymphoma and some other types of peripheral T-cell lymphoma. Brentuximab vedotin with drug-antibody conjugation targeting CD30 has demonstrated efficacy against cancer cell growth in these conditions and is recommended for use in international guidelines and guidelines. in Viet Nam.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Document supported by Takeda company.