This is an automatically translated article.
Lung abscess is a collection of pus in the lung parenchyma due to acute necrotizing inflammation not tuberculosis, after oozing pus to form a cavern. Left untreated, a lung abscess can lead to sepsis, heart failure, kidney failure, and death within a few weeks.1. What is a lung abscess?
Lung abscess is an acute inflammation of the lung parenchyma without tuberculosis, causing necrosis and destruction of alveolar membranes, capillaries, formation of a neoplastic cavern filled with pus, the pus of the abscess is necrotic substances and leukocytes. chemical. Lung abscesses may have one or more foci. Chronic lung abscess is an abscess when medical therapy for more than 6 weeks fails.The causative agents of lung abscess are usually bacteria, fungi, and parasites (amoeba). Predisposing factors for lung abscess include alcoholism, immunosuppression due to HIV or immunosuppressive drugs.
2. Diagnosis of lung abscess
2.1. Clinical symptoms
Patients with lung abscess often have the following signs:Fever: 38 degrees 5 - 39 degrees C or higher, may be accompanied by chills or not. Chest pain on the side of the lesion, possibly with abdominal pain in patients with lower lobe lung abscess. Coughing up purulent sputum, sputum often has a foul or rotten smell, may produce a large amount of pus, sometimes it may produce pus mixed with blood or even cough with blood. There may be cases of only a dry cough. Shortness of breath, there may be signs of respiratory failure: tachypnea, cyanosis of the lips, extremities, decreased PaO2, decreased SaO2. Pulmonary examination: can see crackles, crackles, snoring, sometimes see cave syndrome, consolidation syndrome.
2.2. Subclinical
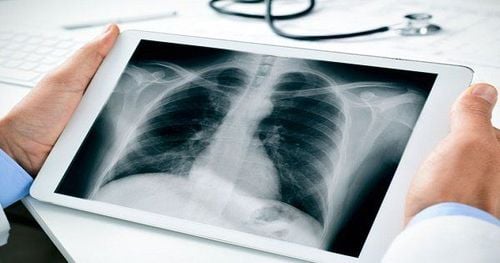
Blood count: usually see white blood cell count > 10 giga/liter, erythrocyte sedimentation rate increased. Chest X-ray: cavernous usually has a relatively even wall with water vapor level. There may be one or more abscesses, unilateral or bilateral. Direct endoscopic staining and bacterial culture from sputum, bronchial fluid or abscess pus. Blood culture when fever > 38.50C. Do an antibiotic if bacteria are found.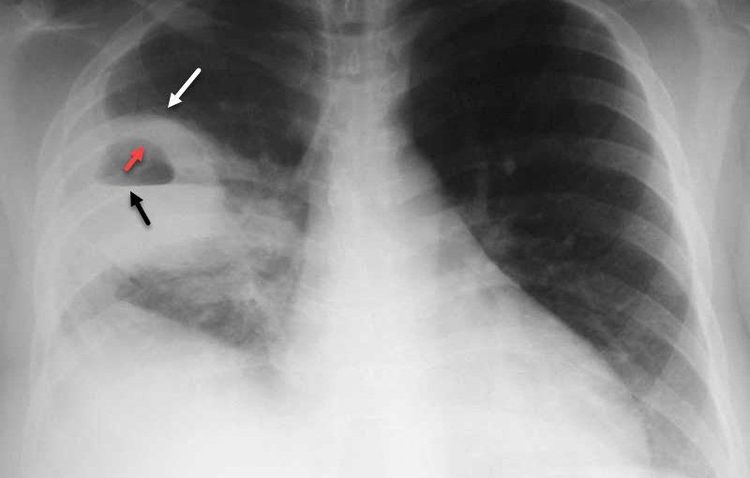
Chụp phim X quang phổi - áp xe phổi
3. Treatment of lung abscess
Treatment of lung abscess includes methods: medical treatment (antibiotics) and surgery.3.1. Internally medical treatment
Antibiotics:Principles of antibiotic use:
Combination of 2 antibiotics, intravenously or intramuscularly. High dose right from the start. Use drugs immediately after obtaining microbiological diagnostic specimens. Change antibiotics based on clinical course and antibiogram if available. Duration of antibiotics for at least 4 weeks (may be extended to 6 weeks depending on clinical and chest radiographs) Abscess drainage:
Postural drainage, thoracic pulsation: based on chest x-ray or computed tomography, choose patient position for drainage, combined with chest vibrating chest. Flexible bronchoscopy to aspirate pus in the bronchi to help drain the abscess. Flexible bronchoscopy also helps detect lesions causing bronchial obstruction and remove bronchial foreign bodies if present. Puncture drainage of pus through the chest wall: applied to the peripheral lung abscesses, the abscesses do not communicate with the bronchi; The abscess is close to the chest wall or attached to the pleura.
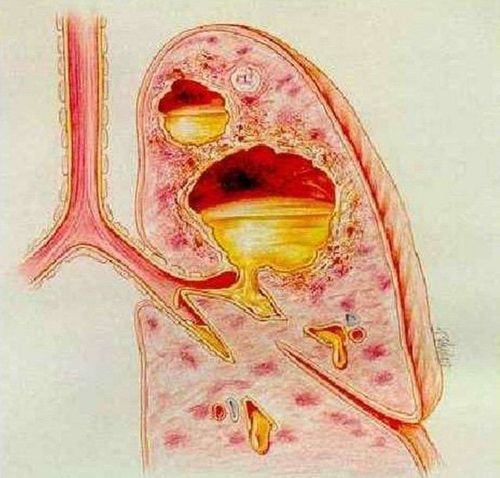
Ổ áp xe phổi
Ensure nutrition Ensure water-electrolyte balance, acid-base balance. Pain relief, fever reduction.
3.2. Surgical treatment
Surgery to remove lung segments or lobes or the whole lung depending on the extent of spread with the patient's condition and respiratory function within the allowable limits (FEV1 > 1 liter compared to the theoretical number):Abscess > 10 cm. Chronic lung abscess with medical treatment failed. Recurrent hemoptysis or severe, life-threatening hemoptysis. Abscess associated with severe focal bronchiectasis. Complications of bronchoalveolar fistula
4. Pulmonary abscess rehabilitation
Rehabilitation of lung abscess by physical therapy is only applied when the lung abscess has an outlet to the trachea and the patient has no fever.4.1. Purpose
Clean the pus cavity, helping the pus in the abscess to drain out easily. Increased respiratory function.4.2. Programme
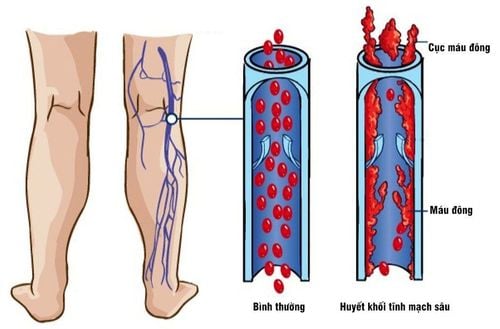
Clear pus by effective cough methods, applying drainage techniques in combination with patting and vibration. These methods are applied depending on the overall condition and health of the patient. Practice diaphragmatic breathing in different positions, pay attention to the early stages of physiotherapy, do not do diaphragmatic breathing in the position of the patient's lungs lying below because it will cause air retention in the abscess and do not apply deep breathing. Pay attention to the exhale. If the patient with lung abscess is indicated for surgery, the same physical therapy will be applied as the patient before and after thoracic surgery. Before surgery: the patient received psychotherapeutic treatment, guided on how to clear the airway, increase respiratory function, prevent chest deformity, maintain range of motion of the joints. After surgery: Exercise program like patients after thoracic surgery. The purpose is as above and must practice physical therapy as soon as possible, must mobilize the limbs to avoid venous thrombosis. Before discharge from the hospital: Encourage the patient to practice according to the exercises that have been instructed. Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consulting services. and comprehensive, professional medical treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health system nationwide to visit or contact the hotline here for support.