This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Hong Hai - Radiologist - Department of Diagnostic Imaging and Nuclear Medicine - Vinmec Times City International Hospital.Calcifying shoulder tendonitis is one of the most common causes of chronic shoulder pain. However, not everyone knows about this disease. To diagnose calcified tendonitis in the shoulder requires some imaging techniques such as X-ray,...
1. How is calcified shoulder tendonitis called?
Calcifying shoulder tendonitis is a buildup of calcium in the tendons of the shoulder. This condition can irritate the surrounding tissues where calcium accumulates and make shoulder pain worse.Calcified shoulder tendonitis is divided into two different types, which are:
1.1. Degenerative calcification
The wear and tear and damage caused by aging are the main causes of degenerative calcification. As we age, the blood supply to the rotator cuff tendons decreases, making the tendon weaker.Due to the wear and tear and damage that occurs when we move our shoulders, the ligaments break and tear, just like a rope wears down over time. Then calcium is deposited at the damaged ligament to heal the wound.
1.2. calcification reaction
So far, the cause of this condition is unknown. The calcification response does not appear to be related to age-related degeneration. This condition is more likely to cause shoulder pain than degenerative calcifications.According to doctors, the calcification reaction has three stages as follows:
Pre-calcium stage: in the early stages, the ligaments change in a way that makes it easier for calcium deposits to form. Calcification stage: at this stage, calcium crystals are deposited in the tendon. The body then absorbs these accumulated calcium. Pain is most likely to occur during this stage. Post-calcification phase: after the body reabsorbs calcium accumulated in the tendon, the tendon will be restored with new tendon tissue. Calcification of the shoulder tendonitis is quite common, most commonly seen in adults aged 40-60 years. Accordingly, women are also more susceptible to this disease than men.
MORE: Causes of tendonitis in the shoulder joint
2. Causes of calcified shoulder tendonitis
Until now, we still don't know the exact cause of calcific tendinitis. The calcification reaction is even more mysterious, it usually occurs in young patients and in many cases resolves on its own without the need for treatment.Condition, worn out tendon, severely damaged, aging or a combination of these factors increase the risk of degenerative calcification. Some researchers think that calcium builds up because tendon tissues don't get enough oxygen. Other researchers suggest that pressure on the ligaments can damage them, causing calcium to deposit.
Calcium accumulation can result from the following factors:
Genetic factors Cell growth Abnormal activity of the thyroid gland Due to the action of anti-inflammatory substances produced by the body Metabolic diseases like diabetes.

3. Symptoms of calcified shoulder tendonitis
During calcium build-up, you may feel only mild to moderate shoulder pain, or you may not feel any pain at all. For some reason, calcific tendinitis is primarily painful as the calcium that builds up is reabsorbed.Shoulder pain and stiffness can cause you to lose shoulder mobility, even lifting your arm can cause pain. At its most severe, shoulder pain can interfere with your sleep.
If you or your loved one has any of the above symptoms, go to the doctor as soon as possible to be examined by a specialist, find out the cause, and then have a timely treatment.
4. What medical techniques help diagnose calcified shoulder tendonitis?
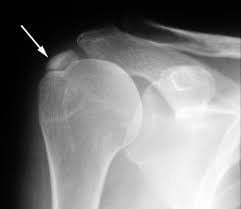
First, your doctor will ask you about your symptoms. Next, your doctor will perform a physical exam of your shoulder joint to check your shoulder range of motion and identify your pain points.However, the shoulder pain and limitation of motion of calcified tendonitis in the shoulder are easily confused with other shoulder pain, so the first-line diagnostic method is a shoulder radiograph. X-ray images will clearly show calcium deposits in the tendon and locate the calcified tendon.
Once it's been determined you have calcified shoulder tendonitis, you'll need several more shoulder X-rays from time to time. The purpose of this is to help the doctor monitor changes in the degree of calcification in the shoulder. Based on changes in calcium buildup, your doctor can determine if your condition will heal on its own or require surgery.
If the calcifications are small, new, and limited to x-ray evaluation, it may be necessary to combine CT or MRI of the shoulder joint for further evaluation. However, shoulder X-ray is still the first, cheap and easy-to-use imaging method.
5. Treatment of calcified shoulder tendonitis
Most cases of calcified shoulder tendonitis can be treated medically without surgery. Specifically:5.1. Drugs for the treatment of calcified shoulder tendonitis
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are the first choice in the treatment of calcified shoulder tendonitis. In addition, your doctor may also recommend corticosteroid injections to help reduce pain or swelling.5.2. Non-pharmacological treatments for calcified tendonitis
In mild to moderate cases of calcified shoulder tendonitis, your doctor may treat you with the following non-drug methods:Peripheral shock wave therapy (ESWT): this uses a device A small hand-held device that creates mechanical shocks to the shoulder, near the calcification site. Although using higher frequencies is more effective, it can be painful. So if you feel uncomfortable let your doctor know. Your doctor can tailor the shock waves to a level that's right for you. Peripheral shock wave therapy can be performed once a week for 3 weeks. Radial shock wave therapy (RSWT): This method uses a hand-held device to deliver low-to-moderate-energy mechanical shocks to the calcified portion of the shoulder. This method also produces effects similar to ESWT peripheral shock wave therapy. Therapeutic ultrasound: This method uses a hand-held device that generates high-frequency ultrasound waves at the calcification points. The ultrasound helps to break up the calcium crystals, which is usually painless. Percutaneous needle: this is a more invasive method than other non-surgical methods. After local anesthesia, the doctor will use a needle to make small holes in the skin. This is a manual method of removing calcium build-up. This method can be performed with the help of ultrasound to help guide the needle into the correct location of the calcification.
5.3. Surgical treatment of calcified shoulder tendonitis
About 10% of patients with calcified shoulder tendonitis require surgery to remove calcium buildup. Depending on the location, size and amount of calcium accumulation, your doctor will advise you on the appropriate surgical method. Surgical methods include:Open surgery Laparoscopic surgery Both of these surgical methods are aimed at removing calcium deposits. Recovery time from surgery depends on the size, location, amount of calcium build-up, and type of surgery.
6. Shoulder rehabilitation after treatment of calcified shoulder tendonitis
6.1. Non-surgical recovery
Your doctor or physical therapist will guide you through a series of gentle range of motion exercises to help restore shoulder mobility. Over time, you will perform exercises that limit a greater range of motion and increase muscle strength.
6.2. Rehabilitation of shoulder joint after surgery
Recovery time after surgery varies according to the actual condition of each patient. In some cases, full recovery of the shoulder joint can take 3 months or longer. Recovery from laparoscopic surgery is usually faster than open surgery.After open or arthroscopic surgery, the doctor may recommend that the patient wear a belt for several days to support and protect the shoulder.
You should also attend physical therapy sessions for 6-8 weeks. Physical therapy usually starts with some stretching exercises to limited range of motion exercises. Usually you will be asked to increase some light weight activity after 4 weeks.
In summary, if the patient is suspected of having calcified tendonitis in the shoulder, the doctor may assign the patient to perform an X-ray method for differential diagnosis, thereby determining the stage of the disease to give a treatment plan. effective treatment.
Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital has been and continues to be fully equipped with modern diagnostic facilities such as: PET/CT, SPECT/CT, MRI, ultrasound, X-ray..., testing blood marrow analysis, histopathology, immunohistochemistry, genetic testing, molecular biology tests, as well as a full range of drugs to treat diseases, including musculoskeletal diseases . Accordingly, the process of examination and accurate diagnosis of the disease is carried out by experienced and qualified doctors.
After an accurate diagnosis of calcified tendonitis in the shoulder, the patient will be consulted to choose the most appropriate and effective treatment methods. Especially, now to improve service quality, Vinmec also deploys many packages of general health check-up that can detect diseases early for timely examination and treatment.
To be examined with a team of experienced and specialized specialists at Vinmec, you can contact and book an appointment at the website.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.