This is an automatically translated article.
Hepatitis is a condition that damages the liver parenchyma, causing the liver's functions to decline. There are many causes of hepatitis, of which half are caused by viruses. Viral hepatitis needs to be diagnosed and treated early to prevent the disease from progressing to liver failure, cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma.1. Common hepatitis viruses
Liver is a large organ of the body with important functions including
Metabolism: protid, glucid, lipid Producing and excreting bile Protein synthesis: Coagulation factors, plasma proteins Storage of important substances Body's vitals: Glucose, iron,... Bile production and excretion Detoxification function Hepatitis viruses include: Hepatitis A virus (HAV), hepatitis B virus (HBV), hepatitis C virus (HCV), hepatitis D virus (HDV), hepatitis E virus (HEV), hepatitis G virus (HGV). In which, mainly HAV, HBV, HCV are common.
Hepatitis A virus : Hepatitis A virus was discovered in 1973, transmitted through food. Patients infected with HAV usually have a benign progression, complete recovery, without the status of a healthy person carrying the bacteria. disease has been vaccinated.
Hepatitis B virus : The incidence of hepatitis B is high. HBV is the only virus whose core acid is DNA. There is a vaccine to prevent hepatitis caused by hepatitis B virus
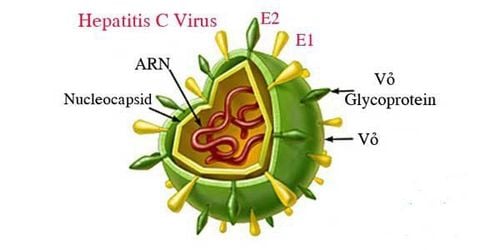
Hepatitis C virus: Discovered since 1989. The virus has genetic diversity due to many genotypes, so the body's immune response to the disease is poor. , after recovering, the body is still at risk of re-infection. Currently, there is no vaccine to prevent the disease.
Hepatitis D virus was discovered in 1977. HDV is an incomplete virus, it has only RNA core. To become a complete virus it requires HBsAg (HBV Surface Antigen) to form a cell envelope. Therefore, a person infected with Hepatitis D Virus is definitely infected with HBV.
Viêm gan là tình trạng tổn thương nhu mô gan, khiến các chức năng của gan bị suy giảm
Hepatitis E virus is like HAV, HEV is transmitted through food. In pregnant women, especially in the third trimester, if infected with HEV, there is a high risk of developing malignancy.
Hepatitis G virus has up to 25% homogeneity with HCV. About 70% of patients have no clinical manifestations of viral hepatitis caused by HGV.
2. General clinical symptoms of viral hepatitis
The disease progresses through 3 stages including: incubation period, onset stage, yellow phase, regression and recovery phase
Incubation period Depending on the virus, the incubation period is different. For example, hepatitis A has an incubation period of 1 to 6 weeks, that of hepatitis B and C is 1 to 6 months, and hepatitis D. E is 1 to 3 months shorter.
Onset period The disease may have a sudden or insidious onset with nonspecific symptoms such as fatigue, anorexia, muscle and joint pain, upper respiratory tract symptoms (rhinorrhea, pharyngitis.. .), digestive disorders (constipation or diarrhea). Dull, continuous pain in the right upper quadrant or epigastrium accompanied by fever (Need to differentiate with diseases with surgical abdomen). Fever can be high but usually does not exceed 39.5 degrees, when the fever starts to decrease is when stage 2 - jaundice begins.
Amblyopia Patients with mild and moderate disease when entering the diapause phase feel good eating and getting better. As for severe patients, when entering the luteal phase, the disease gradually worsens: fatigue, loss of appetite, discolored stools, hepatomegaly and spleen may be enlarged. Due to the deposition of bilirubin in the skin, the patient is very itchy.
Tests show that AST, ALT are elevated, total blood bilirubin is increased, mainly direct bilirubin is increased. Prothrombin time is prolonged. Polymorphonuclear leukocytes may be normal or decreased, elevated when the patient has superinfection.
Regression and recovery phase Usually begins when the patient has an episode of polyuria, clinical symptoms gradually subside.

Bệnh viêm gan siêu vi gây ra các triệu chứng chán ăn, mệt mỏi,..
3. Differential diagnosis Viral hepatitis
Differential diagnosis of the disease in the prodromal stage with other viral infections such as influenza, upper respiratory tract infections,... The phlegm phase needs to be distinguished from other viral infections such as CMV, herpes simplex, .. .or diseases that cause jaundice,...
4. Treatment of viral hepatitis
Depending on the disease, there will be different treatment directions, but the general rule to treat viral hepatitis is
Patients have a reasonable rest regime: During pregnancy, you should lie down. Rest and avoid vigorous activity. Diet should be reduced (oil, fat, ...) should eat reduced protein foods, fresh fruits, vitamins. Limit stimulants, drugs, chemicals that are toxic to the liver. Treat when the patient is symptomatic.
5. Prevention of viral hepatitis
Depending on the route of the disease, we have a basis for disease prevention:
Hepatitis A: The disease is transmitted through food, so wash your hands after going to the toilet and before eating. There is a vaccine for the disease. Hepatitis B: A blood-borne disease (from mother to child, blood transfusion, unprotected sex, sharing needles). After being suspected of having an infection, first aid is needed. Clean the wound and at the same time take medicine to prevent HBV. There is a vaccine to prevent HBV. Hepatitis C: A blood-borne disease (from mother to child, blood transfusion, unprotected sex, sharing needles. Like hepatitis B, after suspected injury, it is necessary to clean up after suspected injury. wound, taking medicine Hepatitis D: Vaccination with hepatitis B vaccine has the effect of preventing hepatitis D. Hepatitis E is similar to hepatitis A.
Dự phòng bệnh viêm gan siêu vi bằng cách tiêm chủng vacxin
Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital has Hepatobiliary Screening packages, which help detect Hepatitis Virus at an early stage even when there are no symptoms. In addition, the comprehensive hepatobiliary screening package helps customers:
Assess the liver's ability to work through liver enzyme tests; Evaluation of bile function; vascular nutrition; Early screening for liver cancer; Perform tests such as Total blood cell analysis, blood clotting ability, screening for hepatitis B, C; Assessment of hepatobiliary status through ultrasound images and diseases that have the potential to affect liver disease / make liver disease worse; In-depth analysis of parameters to evaluate hepatobiliary function through laboratory and subclinical; the risk of affecting the liver and early screening for hepatobiliary cancer. To register for examination and treatment of hepatobiliary diseases at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.