This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Vu Huy Binh - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.
Gastrointestinal bleeding is bleeding out of the gastrointestinal tract and into the gastrointestinal tract. This is a dangerous medical emergency, if not diagnosed and treated promptly, it can affect the patient's life.
1. Diagnosis of gastrointestinal bleeding
Gastrointestinal bleeding is a dangerous medical and surgical emergency, patients need to be hospitalized to be examined and treated as soon as possible. If delayed, gastrointestinal bleeding can cause life-threatening complications for the patient.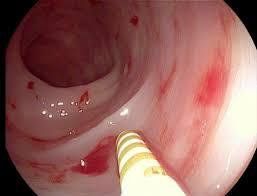
Your doctor will probably need to check your stool for hemorrhagic blood in the stool. Iron supplements, bismuth subsalicylate (Peto-Bismol) or other foods such as beets can cause stools to appear colored like gastrointestinal bleeding.
Blood tests help determine the extent of the bleeding and whether the patient is anemic.
Gastric lavage is a procedure that can be used to determine whether bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract is high or low.
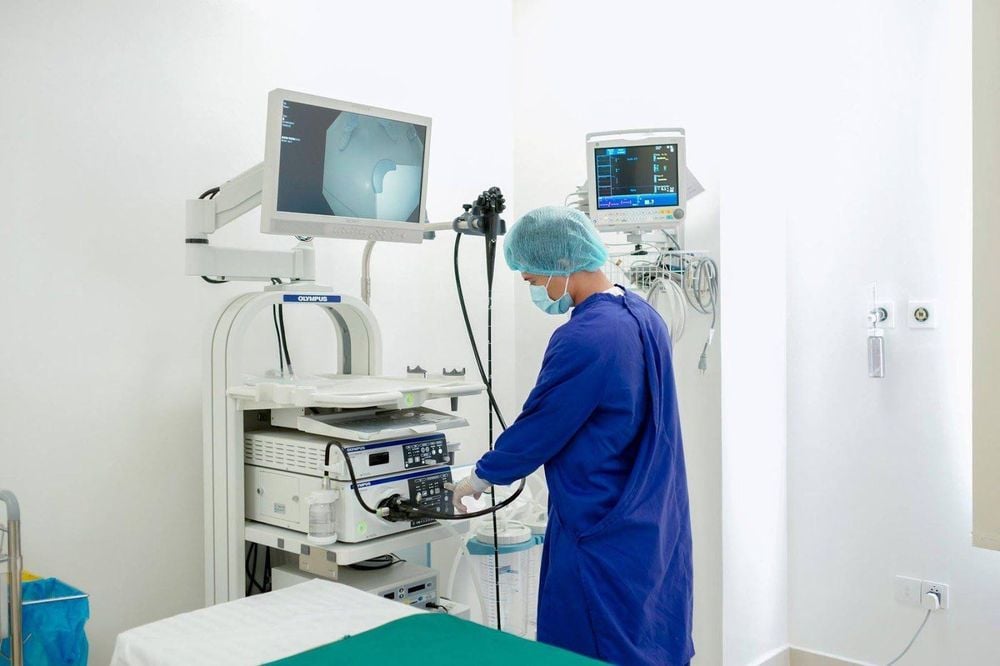
Gastroscopy is the most common diagnostic method to find the etiological source of gastrointestinal bleeding. The endoscope used is a small flexible tube with a camera attached. The endoscope can also be passed through the rectum to view the large intestine, a procedure called a colonoscopy.
Bleeding that cannot be detected by endoscopy is called occult bleeding, the doctor may need to repeat endoscopy or use other procedures to find the cause of the occult bleeding.
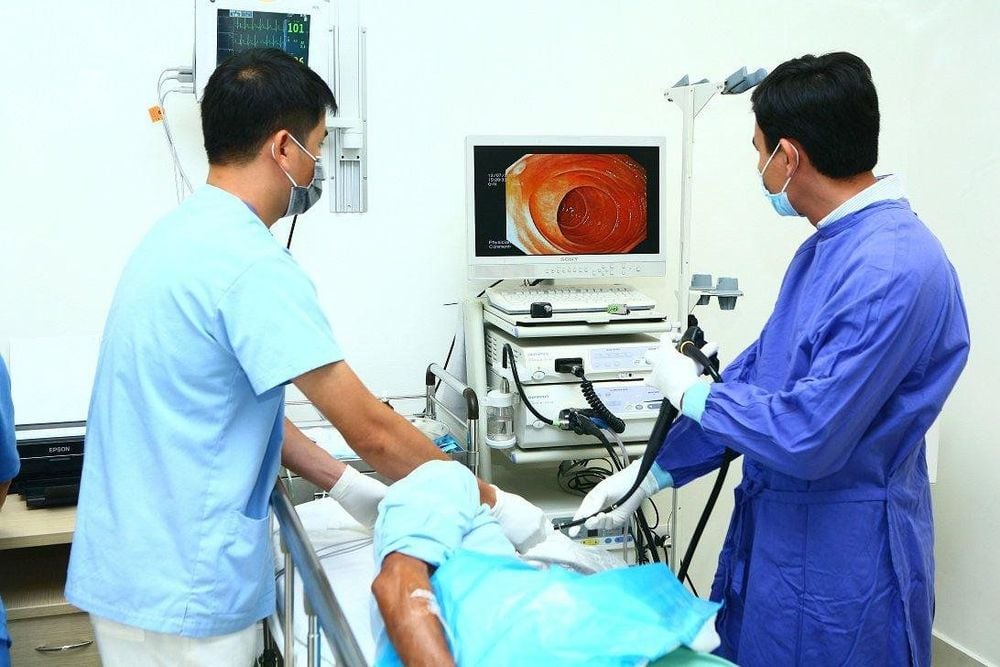
+ Small bowel endoscopy with push tube: a long endoscope is used to examine the upper part of the small intestine.
+ Small bowel endoscopy with double balloon: The ball is mounted on the endoscope to help the endoscope move through the entire small intestine.
+ Capsule endoscopy: The patient swallows a capsule containing a small camera inside. The camera transmits the images to a video monitor as it passes through the digestive tract.
Some other procedures that can be used in diagnosing the source of gastrointestinal bleeding:
Barium X-ray
Baryt is a contrast agent that helps to see the GI tract through X-ray, liquid contains baryt can be swallowed or inserted rectally but rarely used
Radioisotope scanner
A small amount of radioactive material will be injected into the patient's vein. When radioactive material escapes from the lumen, it means there is bleeding, and this method is also rarely used at present.
Angiography
The doctor will inject contrast material into the patient's vein so that the blood vessels can be seen on an X-ray or computed tomography scan. In the area of bleeding, this contrast will flow out.
Exploratory laparotomy
If the above methods fail to identify the source of the bleeding, an exploratory laparotomy may be necessary to examine the gastrointestinal tract.
2. Treatment of gastrointestinal bleeding
Treatment of gastrointestinal bleeding requires first placing an intravenous line to give fluids, possibly a blood transfusion if the bleeding is severe. However, in some cases of severe bleeding, resuscitation and emergency fluid or blood transfusions are required.
If endoscopy fails, angiography may be indicated to inject drugs or other substances into the blood vessels to help control some forms of bleeding. If endoscopy and angiography are not available, other treatments or surgery will be performed to stop the bleeding.
To prevent recurrent gastrointestinal bleeding, doctors can treat diseases that cause bleeding such as:
Infection with H. pylori and other bacteria Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) Stomach ulcers, colon Hemorrhoids Inflammatory bowel diseases It can be said that Endoscopy is the most common tool for diagnosing and treating gastrointestinal bleeding, so it is preferred by hospitals. The traditional endoscopic methods still have many disadvantages such as: Poor image quality, difficult to observe lesions, uncomfortable for patients, high possibility of complications...
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.