This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Viet Thu - Doctor of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine - Department of Diagnostic Imaging and Nuclear Medicine - Vinmec Times City International General Hospital. Dr. Nguyen Viet Thu has more than 20 years of experience working in the field of diagnostic imaging, former Secretary of the Hanoi Department of Radiology, directing the lower level in the field of Diagnostic Imaging.Head and neck cancer, if detected and treated early, has a very high cure rate and can minimize the bad complications of the disease. Therefore, early diagnosis of head and neck cancer is very important in the treatment of the disease.
1. What is head and neck cancer?
Head and neck cancer is a group of cancers that usually begin in the squamous cells of the lining of the mouth, larynx, pharynx (pharynx), salivary glands, nasal cavity, and paranasal sinuses.Head and neck cancer is twice as common in adults over 50 years of age and in men. Risk factors include:
Age Gender Alcohol and tobacco use Exposure to radiation or asbestos Poor oral hygiene Ethnicity, especially of Asian descent (oropharyngeal cancer) Viral infection HPV .

2. Symptoms of head and neck cancer
Typical symptoms often include: Persistent sore throat, difficulty swallowing, mouth sores that won't heal, and a hoarse voice. Other symptoms depend on the location of the cancer, but can typically include:Unexplained bleeding in the mouth Red or white patches in the mouth Swelling of the jaw Difficulty opening the mouth Ear pain, frequent headaches Pain when swallowing Difficulty breathing and/or speaking Chronic sinus infection Toothache, gum pain, loose teeth Unexplained nosebleeds Face numbness or paralysis Hearing loss Painless mass in the neck.
3. How is head and neck cancer diagnosed and evaluated?
3.1 Nasopharyngeal Endoscopy This endoscopic technique uses a flexible, lighted optical instrument called an endoscope to examine the nasal cavity and pharynx. With the help of a local anesthetic, an endoscope is inserted into the oral cavity or nose to take pictures and evaluate abnormal lesions.
3.2 Panorama Dental X-ray Takes all teeth in one image, including teeth, upper and lower jaw bones, surrounding soft tissue structures, it can help detect lesions in the imaging area .
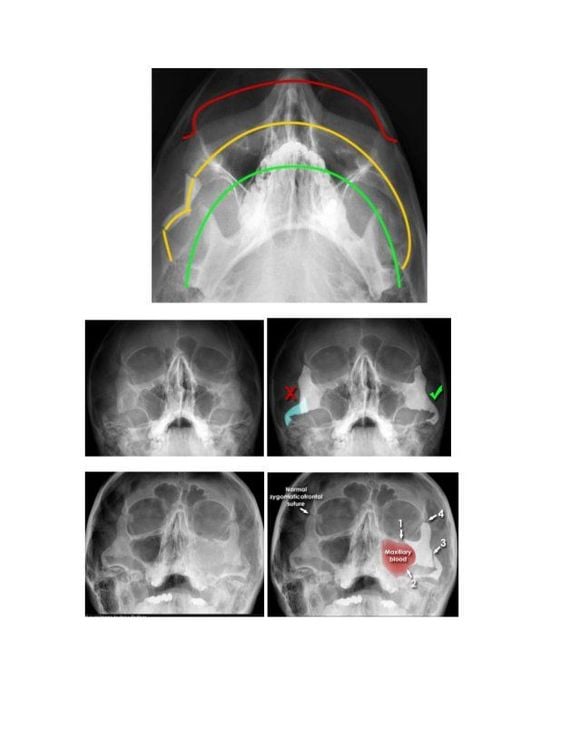
Extraction of wisdom teeth, underground teeth and complicated endodontic cases. Detect and diagnose diseases of the maxillofacial region such as tumors, temporomandibular joint disorders and maxillary sinus disease. 3.4 CT Sinus Imaging This technique provides images of the patient's paranasal sinus cavities. The image of slices created during a CT scan can be reconstructed in three-dimensional (3D) directions and images. It is mainly used for sinus and nasal cavity cancer detection and treatment planning.
3.5 Head CT Like CT of the sinuses, CT of the head can help detect abnormalities of the paranasal sinuses and nasal cavity, and high-slices help detect lesions of the brain parenchyma.
3.6 Chest CT High-risk head/neck cancer is lung metastases. Your doctor may order a routine chest X-ray or CT scan of the chest to investigate.
If these tests do not detect lesions, no further steps may be needed. However, the doctor wants to monitor this area, so he can re-order it at later visits. If these tests suspect malignancy, your doctor may recommend a biopsy of the lesion.
Biopsy can be performed safely under the guidance of ultrasound, computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).

3.8 PET/CT Scan Is a diagnostic technique in nuclear medicine that combines positron emission tomography (PET) and CT scan to produce accurate images of anatomical location and abnormal metabolic activity. usually of injury. It can detect head and neck cancer, determine if it has metastasized, assess effectiveness, plan treatment, and assess the possibility of tumor recurrence.
4. Head and neck cancer treatment
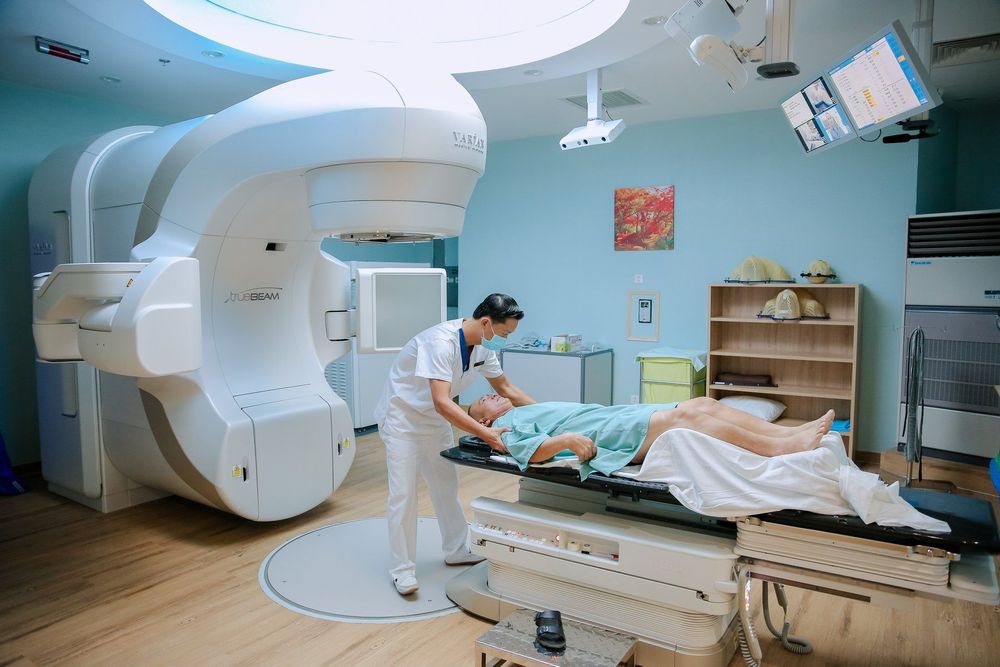
Tumors in the head/neck region can be treated with radiation therapy. Surgery may be performed depending on the effectiveness of radiation therapy.
Recent studies have shown that chemotherapy given at the same time as radiation therapy is more effective. Therefore, radiation therapy sometimes includes chemotherapy if the cancer is advanced (stage III or stage IV). Chemotherapy can be given in a variety of ways, including a low daily dose, a weekly moderate dose, or a relatively higher dose every three to four weeks.
Typically, radiation therapy procedures to treat head/neck cancer include:
External Beam Therapy (EBT): A method that delivers a high-energy X-ray beam or beam. protons to the site of the tumor. The radiation beam is generated outside the patient (usually with a linear accelerator for Proton beams) and is targeted at the tumor site. These beams of radiation can kill cancer cells, and tailored treatment plans allow the surrounding normal tissue to remain uninfected. Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT): An advanced high-precision radiation therapy modality that uses computer-controlled X-ray accelerators to deliver precise radiation doses to malignant tumors properties or specific areas within the tumor. The radiation dose is designed to match the three-dimensional (3D) shape of the tumor by adjusting - or controlling - the intensity of the radiation beam to focus a higher radiation dose on the tumor while minimizing radiation exposure to healthy cells. Currently, Vinmec International Hospital has applied radiation therapy to patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Initial results are positive and many patients are elderly but well tolerated. Depending on the location of the lesion, it will be combined with local and regional thermogenic therapy.
The Department of Oncology - Radiation Therapy at Vinmec is fully equipped with cancer treatment modalities: From surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, radiosurgery, pain relief treatment and reasonable nutritional care. The diagnosis is made carefully: blood tests, X-rays, ultrasound, computed tomography (CT scan), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), myelogram, myelogram, biopsy , immunohistochemistry, diagnosis by molecular biology...
The treatment process is closely coordinated with many specialties: Department of Diagnostic Imaging and Nuclear Medicine, Blood Test and Biochemistry , Department of Cardiology, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Department of Endocrinology, Department of Rehabilitation, Department of Psychology, Department of Nutrition, Department of Pain Treatment and Palliative Care, in order to provide patients with the optimal treatment regimen and most reasonable cost.
For detailed information, please contact the hospitals and clinics of Vinmec health system nationwide.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: radiologyinfo.org
SEE MORE
What types of cancer are there in head and neck cancer? Cut all types of tumors in the scalp and neck with a diameter of more than 10cm Learn about head, face and neck cancer