This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Resident Doctor Trinh Ngoc Anh - Department of General Internal Medicine - Vinmec Times City International HospitalDiabetic nephropathy is a serious complication of kidney disease in patients with type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes. Approximately 25% of diabetic patients develop renal complications.
1. Diabetic Kidney Disease Diabetic kidney disease affects the kidneys' ability to work every day to eliminate waste products and excess fluid from the body. The best way to prevent or delay diabetic kidney complications is to maintain a healthy lifestyle and treat diabetes and high blood sugar.
Over the years, this condition will slowly affect the kidney's filtering system. Early treatment can prevent or slow the progression of kidney disease, thereby reducing complications. Kidney disease can progress to kidney failure, or end-stage kidney disease. Kidney failure is a life-threatening condition that is usually treated with dialysis or a kidney transplant.
2. Symptoms of Diabetic Kidney Disease In the early stages of diabetic nephropathy, you may not have any symptoms or signs. In the later stages, symptoms and signs include:
More difficult blood pressure control Presence of protein in the urine Edema in the feet, ankles, hands or eyes Increased urination Decreased need to use insulin or diabetes medications Confusion or difficulty concentrating Difficulty breathing

Khó thở là một trong các triệu chứng bệnh thận do đái tháo đường
Loss of appetite Nausea and vomiting Persistent itchiness Fatigue
3. Factors that increase the risk of diabetic kidney disease
Diabetes mellitus type 1 and 2 itself is a risk factor for diabetic nephropathy. There are also a number of other risk factors that can increase the occurrence of diabetic nephropathy, including:
Uncontrolled high blood sugar Uncontrolled high blood pressure Smoking tobacco High blood cholesterol Money a family history of diabetes or kidney disease. 4. Complications of diabetic nephropathy Complications of diabetic nephropathy can progress over months or years and include:
Fluid retention, which can lead to swelling in the hands and feet, high blood pressure, or fluid in the lungs (pulmonary edema) Increased levels of potassium in the blood Heart and blood vessel disease (cardiovascular disease), which can lead to stroke Damage to the blood vessels of the retina in the eye (retinopathy) Anemia Pain in the feet, erectile dysfunction, diarrhea and other problems related to nerve and blood vessel damage
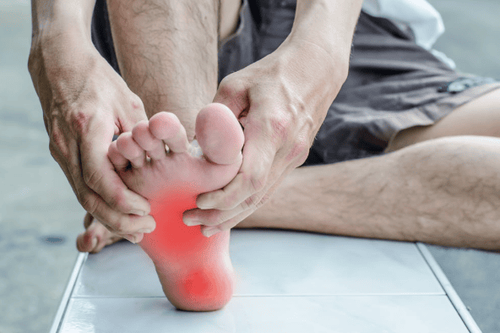
Người bệnh xuất hiện triệu chứng đau tại bàn chân do biến chứng gây ra
Complications on pregnant women can affect both mother and baby Irreversible kidney damage (end stage kidney disease), even need dialysis or a kidney transplant to maintain life.
5. Prevention of diabetic kidney disease
To reduce the risk of developing diabetic nephropathy, it is necessary to:Effective treatment of diabetes will help prevent or delay progression of diabetic nephropathy Control blood pressure or other conditions Follow guidelines using over-the-counter medications, especially some pain relievers, can cause decreased kidney function Keep a healthy weight with physical activity Don't smoke
6. Diagnosing Diabetic Kidney Disease
In addition to the signs, symptoms and personal and family history, some of the following tests can be used:
Blood test: To assess the status of blood sugar, blood fat, kidney function, electrolytes ( especially blood potassium). Urinalysis: To detect the presence of protein in the urine, which is an early sign of kidney disease. Diagnostic imaging: X-ray of the urinary system, ultrasound of the urinary system can be used to detect comorbidities (kidney stones, urinary tract infections, urinary system tumors...), these cases More difficult cases can use CT scanner, MRI (magnetic resonance) of the urinary system. Kidney biopsy: Often used to pinpoint the exact cause of kidney damage in difficult cases.

Xét nghiệm nước tiểu giúp bác sĩ chẩn đoán bệnh thận do đái tháo đường
7. Treatment of diabetic kidney disease
Principles of treatment:
Control blood pressure: Target less than 140/90 mmHg Blood sugar control: Target HbA1c less than 7% Correct dyslipidemia (Cholesterol and Triglyceride) in blood Control Calcium and Phosphorus balance in the blood to ensure bone health Reduced protein in the urine. Treatment of patients with end-stage renal disease:
Dialysis: is a way to remove waste and excess fluid from the body instead of the kidneys, there are two forms: Cyclic dialysis: Usually performed 3 times a week , requires the support of machines and must be performed in medical facilities. Peritoneal dialysis: Can be done at home. Kidney transplant Symptom control to improve the quality of life of patients At Vinmec International Hospital, we always deploy a screening package for diabetes and dyslipidemia to help detect pre-diabetes early, Accurately classifying diabetes type, developing a nutritional regimen, monitoring to minimize the risks and complications caused by diabetes.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.