This is an automatically translated article.
Chronic glomerulonephritis is a disease with glomerular damage, progressing from prolonged acute glomerulonephritis. Chronic glomerulonephritis, if not treated well, can lead to kidney failure, causing many consequences to the health and life of the patient.
1. Causes of chronic glomerulonephritis
There are many causes of chronic glomerulonephritis, but there are some cases where the patient has an unknown cause.
The most common is chronic glomerulonephritis secondary to progressive glomerular disease. An example is collagenose glomerulonephritis (systemic lupus erythematosus), an autoimmune disease, common in women (95% of cases). Or glomerular damage due to vascular disease, inflammation of small blood vessels in many organs, mainly the lungs and kidneys.
Chronic glomerulonephritis can also occur in patients with hemophilia (Scholein-Henoch disease). Certain metabolic disorders can also complicate chronic glomerulonephritis, such as diabetes.
People with liver disease caused by hepatitis B and C viruses can also have chronic glomerulonephritis complications, but the rate is low.
Chronic glomerulonephritis can also be a progressive consequence of acute glomerulonephritis caused by endocarditis caused by group D streptococci or pharyngitis by group A streptococcus (S. pyogenes).
There have been cases of chronic glomerulonephritis as a result of malaria, syphilis caused by Treponema paildum or leprosy caused by Mycobacterrium leprae.
In addition, chronic glomerulonephritis can also originate from malignancies such as acute leukemia, chronic leukemia, ganglion sarcoma or poisoning by some heavy metals such as gold salt poisoning.
2. How long does it take for acute glomerulonephritis to progress to chronic glomerulonephritis?
Viêm cầu thận cấp sau 3 tháng điều trị không tốt tiến triển thành viêm cầu thận mạn
When acute glomerulonephritis occurs for more than 3 months and does not go away due to untreated or interrupted treatment, it will turn to chronic glomerulonephritis. Symptoms at this time depend on the degree of kidney failure or may not have kidney failure.
The most important signs of chronic glomerulonephritis are high blood pressure, persistent proteinuria and red blood cells. The disease often progresses in stages and the symptoms of hematuria, proteinuria, and hypertension gradually increase over the years.
3. Tests to identify chronic glomerulonephritis
To determine the stage of glomerulonephritis, the patient needs to do tests to evaluate kidney function. Renal status can only be accurately assessed by renal biopsy, reading the structures of renal units under the microscope. Current tests only approximate kidney function, so a combination of tests is needed.
Biochemical tests Creatinine, BUN (Blood Urea Nitrogen) are products of the body's protein metabolism, excreted by the kidneys in the urine. These indicators increase in the blood as kidney function deteriorates.
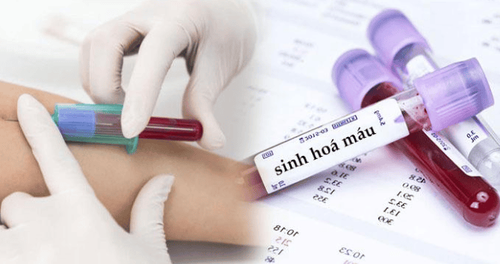
Xét nghiệm sinh hóa đánh giá chức năng thận
For more accuracy, tests for urea/blood and urea/urine, creatinine/blood, and creatinine/urine are often performed in parallel to calculate creatinine clearance. Normally, creatinine clearance is 70-120 mL/min. Decreased creatinine clearance reflects a decline in renal function
Electrolytes Renal dysfunction causes an imbalance of electrolytes in the body.
Sodium (Sodium): Normal blood sodium 135-145 mmol/L. People with kidney failure, low blood sodium.
Potasium (Potassium): Normal blood potassium 3.5- 4.5 mmol/L. Hyperkalemia in patients with renal failure due to decreased renal excretion of potassium.
Blood calcium: normal blood calcium 2.2-2.6 mmol/L. Renal failure is manifested by hypocalcemia accompanied by increased phosphate.
Disorders of acid-base balance Normal blood pH is maintained at 7.37 - 7.43, kidney failure reduces the elimination of acids formed in the body's metabolism or bicarbonate loss causes metabolic acidosis for body.
Blood uric acid On average, blood uric acid in men: 5.1 ± 1.0 mg/dL (420 μmol/liter), women 4.0 ± 1mg/dL (360 μmol/liter). Increased uric acid in the blood can be the cause of kidney damage, but it can also be the result of kidney failure that cannot be eliminated.
Total urinalysis Normal urine density: 1.01 - 1.020 (24-hour urine of normal adults with a density range of 1.016 - 1.022). Early kidney function decline will reduce concentration thickening of the urine, leading to a decrease in urine density.

Phân tích nước tiểu để đánh giá chức năng thận
Characteristic of proteinuria due to glomerular disease is persistent and usually > 0.3 g/l. Increased proteinuria is seen in diseases causing glomerulonephritis, acute glomerulonephritis due to drug or toxic chemical intoxication, renal failure, systemic diseases affecting the kidneys: hypertension, diabetes mellitus, lupus erythematosus ..
Serum albumin Normally, serum albumin has about 35 - 50 g/L, accounting for 50 - 60% of total protein. Albumin is strongly reduced in acute glomerulonephritis.
Total plasma protein Normal: 60 - 80 g/L
Total plasma protein reflects glomerular filtration.
Abdominal ultrasound Detects hydronephrosis due to ureteral obstruction. If the kidneys are bilateral, it can cause acute renal failure or chronic kidney failure.
Kidney biopsy Chronic glomerulonephritis will reduce the body's resistance, so the patient is susceptible to respiratory infections, urinary tract infections...
Acute glomerulonephritis can progress quickly quickly into chronic glomerulonephritis, causing many consequences to the health and life of patients. Therefore, patients with acute glomerulonephritis need to actively treat according to the doctor's schedule.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.