This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by MSc Nguyen Van Phong - Internal Medicine and Cardiology Interventionist, Cardiovascular Center - Vinmec Times City International General Hospital. The doctor has more than 15 years of experience in the field of cardiology.Percutaneous coronary intervention is a technique that uses a catheter (catheter) through the skin to insert a small balloon into the angioplasty of the blocked coronary artery and place a stent to re-open the blood flow. Along with the improvement of technology, the development of new coronary stents has helped to solve the stenosis in the coronary arteries, helping to improve myocardial perfusion under all conditions of strenuous activity of the heart. patient.
1. History of development of coronary stents
The first coronary artery disease treatment was coronary artery bypass graft surgery performed in 1960. This is invasive surgery, using an artery or vein from another area of the patient's body by bypass. from the aorta into the coronary artery. Surgery is usually performed when the patient's heart is temporarily stopped and cardiopulmonary resuscitation methods are used.It was not until 1977 that coronary intervention was performed. This is a minimally invasive method that uses only a very small incision to insert the catheter at the balloon end, threading it to the point of obstruction. The balloon is then inflated to widen the blockage, restoring blood flow.
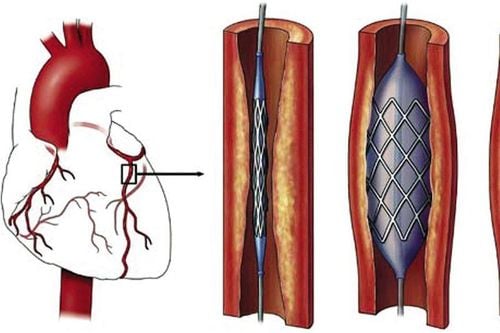
It was not until 1986 that coronary stents were used for the first time in France and approved by the FDA as an official treatment method in the US since 1994. Over the years, coronary stents have improved. significantly to meet the treatment needs of each patient:

2. Situation of coronary stenting interventions in Vietnam
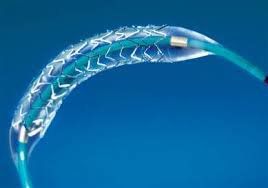
To provide cardiovascular patients with standard, scientific and asymptotic treatment programs in the US at a reasonable cost. Vinmec International General Hospital has implemented the first comprehensive cardiovascular treatment program in Vietnam. This program will help patients enjoy the full advantage of the package treatment model and receive the care of leading cardiologists. The current cardiovascular program at Vinmec, in addition to applying coronary interventional stenting techniques, also includes percutaneous aortic valve replacement, aortic-coronary bypass surgery to help patients treat Myocardial ischemia due to narrowing of the main coronary arteries and branches with a size greater than 1mm, minimizing the risk of coronary stents as well as the risk of restenosis after intervention.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.