This is an automatically translated article.
Determining the patient's blood group before donating or receiving blood is extremely necessary and important. Currently, ABO/Rh blood grouping by test tube technique is the most commonly used method of blood group determination.
1. When to conduct blood grouping?
Anyone can do an ABO/Rh blood type test when needed. Besides, there are certain cases where blood group needs to be determined:
Identify the blood group of the donor and recipient before blood transfusion. Determine the donor's blood type, bone marrow, tissue to see if it's compatible with the recipient. Use the results of blood group determination for blood group determination purposes. Pregnant women need to have ABO/Rh blood group to assess the compatibility between factors in the blood of mother and baby.

Phụ nữ mang thai nên định nhóm máu hệ ABO/Rh
2. ABO/Rh blood grouping by test tube technique
There are two main blood group systems, the most important and common are the ABO blood group and the Rh blood group.
2.1 ABO blood group The ABO blood grouping principle The ABO blood group was discovered by the scientist Karl Landsteiner in 1901. This is considered the most important blood group in blood transfusion practice. determination of blood groups of the ABO system is made on the basis of A antigens and B antigens whether or not present on the surface of red blood cells; presence or absence of A and B antibodies in the serum sample.
ABO blood grouping means determining whether a person is blood type A, blood group B, blood group AB or blood type O . The determination of this blood group needs to be carried out by two methods: serum and red blood cells.
ABO blood grouping technique is based on the principle of agglutination reaction.
ABO blood grouping process After preparing all the necessary tools and chemicals, the medical staff receives the patient's specimen to start the blood grouping.
Blood tubes without anticoagulation will be centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 3 minutes and then separated for serum. Simultaneously wash the patient's red blood cells with 0.9% NaCl 3 times and make a 5% suspension.
It is necessary to prepare 2 sets in which each set contains 6 clean test tubes labeled with anti A, anti B, anti AB, red blood cells sample A, red blood cells sample B and red blood cells sample O.
After that, the doctor ABO blood grouping was performed by two methods: serum samples and red blood cells. This operation will be repeated 1 more time to ensure accuracy.
If the results of the two groupings match, the blood type A, B, AB, or O mark will be stamped on the test sheet. Conversely, if the results between two blood groupings are not compatible, the initial steps should be rechecked and the test repeated.
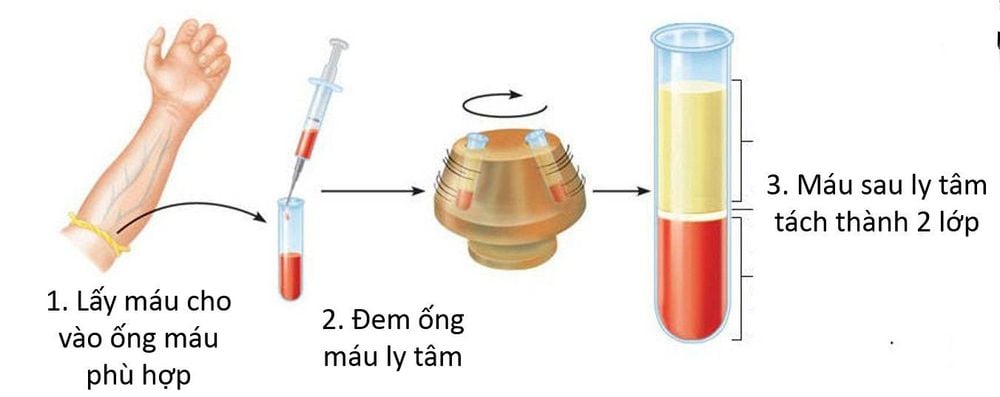
Ống máu sẽ được ly tâm
2.2 Rh blood group The principle of Rh blood grouping The second most important blood group system in blood transfusion practice is the Rh blood group system. This blood group was discovered by scientists named Kahl Landsteiner and Wiener in 1940. Rh blood group has a fairly rich number of antigens up to about 50 different antigens, of which 5 are D and C. , c, E, and e. In particular, the D antigen is the most important.
Rh (D) blood group is determined based on the presence or absence of D antigen on the surface of red blood cells. Thus, a person who has the D antigen on the surface of the red blood cells is called a person with Rh (D) blood group positive, whereas a person with Rh (D) negative blood group is a person without D antigen on the surface. erythrocytes.
Rh blood grouping technique is performed based on the principle of agglutination reaction.
Nhóm máu Rh(-) và Rh(+)
Rh blood grouping procedure Necessary tools, chemicals and biological products should be fully prepared before conducting blood grouping. After receiving samples from patients, medical staff will conduct analytical tests.
First, add 1 drop of anti-D sample serum into the prepared test tube. Then add 1 drop of 5% red blood cell suspension (erythrocytes washed with 0.9 % NaCl). Mix test tubes and centrifuge at 1000 rpm for 1 min. Tilt and shake the test tube gently to read the agglutination.
In case of reaction with agglutination, it means that D antigen is present on the surface of the red blood cells, or the blood grouping result is Rh (D) positive. If the reaction is not agglutinative, then it can be concluded that the blood group is Rh (D) negative because there is no D antigen on the surface of the red blood cells.
ABO/Rh blood grouping is important for transfusion practice to minimize the risk of incompatibility between blood donors and recipients. Any mistake can put the patient's life in jeopardy.
SEE ALSO:
The role of determining blood group before blood transfusion Why is it important to proactively take a general blood test to detect disease? How to classify blood type