This is an automatically translated article.
This article is written by Master, Doctor Ton Nu Tra My - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Subarachnoid hemorrhage causes compression and damage to brain cells, potentially threatening the patient's life. Early diagnosis and timely management help limit the risk of death and injury from subarachnoid hemorrhage.
1. What is a subarachnoid hemorrhage?
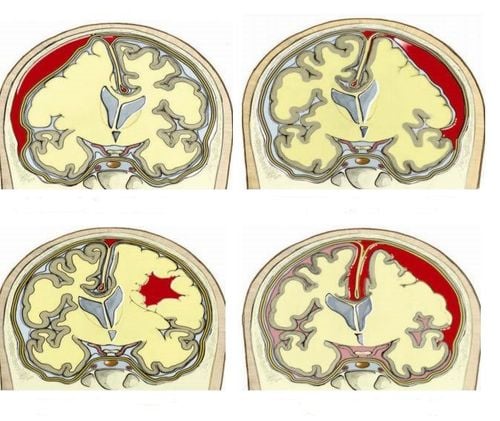
The meninges are composed of dura, arachnoid, and soft membranes. In which, the arachnoid membrane is the second layer in the structure of the meninges, in between the dura mater and the soft membrane. The subarachnoid space is a space filled with cerebrospinal fluid, located between the arachnoid and soft membranes.Subarachnoid hemorrhage is bleeding into the subarachnoid space. This condition can have many causes, resulting in increased pressure affecting brain cells.
Causes of subarachnoid hemorrhage include:
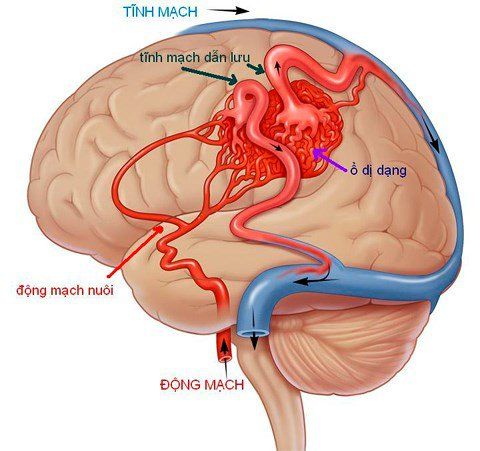
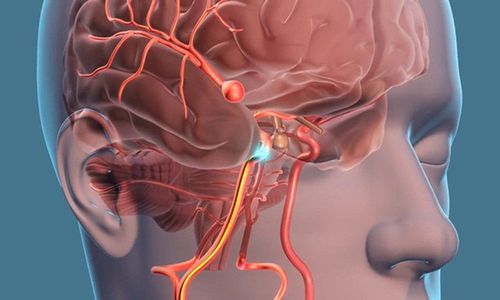
Trauma: Head trauma can lead to rupture of cerebral blood vessels causing subarachnoid hemorrhage. Cerebral aneurysm rupture: This is the main cause of up to 80% of cases of subarachnoid hemorrhage that are not caused by trauma. Normally, the artery wall is made up of a layer of muscle with high elasticity to ensure that it can push blood to nourish the body without breaking. For some reason, the walls of the blood vessels in the brain are weakened and cannot withstand the pressure of the blood flow, forming bulges. These bulging sacs are shaped like grapes in the segments of blood vessels, they can be stressed and burst at any time. Especially the risk is higher after a brain injury.

2. How to diagnose subarachnoid hemorrhage?
For diagnosis, it is necessary to rely on a number of clinical and paraclinical manifestations:
Clinical signs:
For the cause of aneurysms, there may be some warning signs before aneurysm rupture such as: Pain Chronic headache, decreased vision, drooping eyelids, dilated pupils... Due to a large amount of blood spilling out in the subarachnoid space when bleeding occurs, it causes increased intracranial pressure with clinical manifestations such as: Pain sudden headache, severe pain, nausea and vomiting, stiff neck, impaired consciousness, possible weakness of limbs, sensory disturbances, convulsions. With severe bleeding, the patient suddenly has a severe headache, then may go into a coma. Signs of subarachnoid hemorrhage can be seen after exertion or head trauma. May be related to a family history of vascular malformations or ruptured aneurysms.

Subclinical: Laboratory measures used for early diagnosis of subarachnoid hemorrhage include
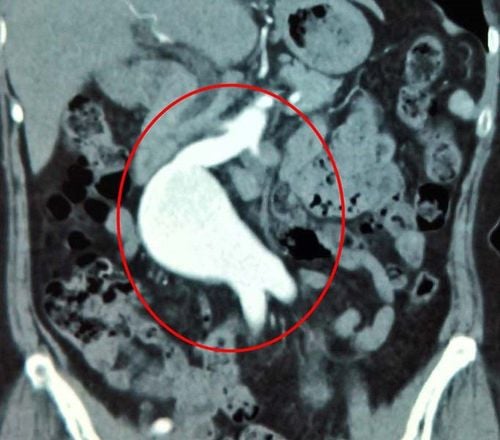
Computed tomography is the first choice to use if clinical signs suggest a ruptured cerebral aneurysm. . On the CT scan, the subarachnoid space is shown to increase darkening, most clearly within the first 3 days and the degree of hyperdense decreases over time. There is a high accuracy rate if subarachnoid hemorrhage is suspected, and the sensitivity of early imaging is high and decreases over time. Magnetic resonance: Better in evaluating patients with large aneurysms, vascular lesions, subacute subarachnoid hemorrhage. However, these aneurysms are too small to be detected on MRI. Indicated in patients unable to undergo CT or angiography. False positives or negatives may occur. Cerebral angiography: This is considered the standard imaging technique to detect cerebral aneurysms, cerebral vascular malformations and cerebral arteriovenous fistulas. An angiogram can know: How many cerebral aneurysms there are, which aneurysms cause bleeding, size, location and shape of aneurysms; allow evaluation of treatment options. The method has a high accuracy rate, very low false negatives. Lumbar puncture: Indicated when: CT is normal but clinical manifestations are suspicious of subarachnoid hemorrhage; There are no contraindications to puncture such as increased intracranial pressure, hydrocephalus ... When the purpose is to find red blood cells in the cerebrospinal fluid, it is usually negative if done before 2 hours from the time of bleeding. It is best to do it 12 hours after bleeding.

3. Treatment of subarachnoid hemorrhage
3.1 Principles of treatment Must ensure the patient's respiratory and circulatory function. Prevents increased intracranial pressure, prevents neurological sequelae. Addresses electrolyte disturbances and acid-base disorders. Well control blood pressure, avoid secondary cerebral vasospasm. Prevent the risk of recurrent bleeding. 3.2 Medical treatment The patient is fully rested, avoiding movements or positions that cause increased intracranial pressure. Monitor vital signs with a monitor. If the patient has respiratory disorders, it is necessary to use oxygen therapy, ventilator depending on the case. Infusion with the purpose: Increase circulation volume, raise blood pressure. Medicines to treat symptoms: Anticonvulsants, antiemetics, analgesics, drugs to regulate blood pressure, treat arrhythmias, drugs with laxative effect to avoid constipation. The diet ensures to provide enough necessary energy, eat liquid to avoid constipation.

3.3 Surgical treatment The purpose of surgical treatment is to treat the cause, prevent recurrence and prevent the risk of dangerous complications
For ruptured aneurysms:
Open surgery to find the aneurysm and clip across the neck of the bag with a metal clip. Early surgery aims to avoid complications and recurrence. In some cases, surgery is replaced by interventional methods, using catheters that go in the lumen, to plug the brain aneurysm with metal springs (coils). Cerebral vascular malformations: Surgical removal of vascular malformations or percutaneous interventions.
3.4 Measures to prevent recurrence If surgery is not performed due to contraindications, there is a higher risk of recurrence. To prevent recurrence of subarachnoid hemorrhage, it is necessary to:
Do not overwork during the recovery period. get plenty of rest, avoid psychological stress, cough Diet or medication to avoid constipation Use sedation if necessary when the patient is in an excited state Maintain stable blood pressure Subarachnoid hemorrhage It is an emergency that needs to be diagnosed and treated early. The disease carries a high risk of death and leaves many injuries, so it is essential to know and treat before bleeding occurs with regular medical examination.
Master. Dr. Ton Nu Tra My is currently a Doctor of Radiology, Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital. Dr. Tra My used to be a lecturer in the Department of Diagnostic Imaging, Hue University of Medicine and Pharmacy and had a long time working at the Department of Diagnostic Imaging, Hue University of Medicine and Pharmacy Hospital.
If you have a need for consultation and examination at the Hospitals of the National Health System, please book an appointment on the website for service.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.