This is an automatically translated article.
The article was consulted with Specialist Doctor I Le Thi Thu Hang - Dermatologist - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.Generalized erythroderma begins with red, edematous patches that spread rapidly, until the entire body skin is damaged. Initially accompanied by symptoms of systemic toxicity.
1. What is generalized red skin?
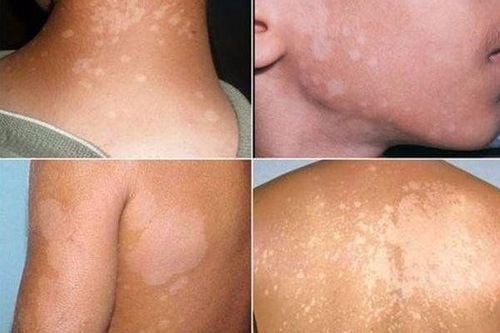
Generalized erythema is a diffuse scaly red skin condition that covers more than 90% of the body area, so it is also known as scaly generalized erythema syndrome or exfoliative dermatitis.In addition to skin lesions, the disease also has systemic manifestations. The disease progresses for a long time, severe cases can be life-threatening.
The disease occurs at any age, most often in the age group of 40-60 or older.
2. Classification of body redness
2.1 Classification by cause
Generalized erythroderma is divided into 2 groups: generalized erythroderma in adults and generalized erythroderma in infants and children.2.1.1 Generalized erythema in adults
Psoriasis: Improper treatment of psoriasis can easily lead to severe flare-ups, easily progress to pustular psoriasis or secondary generalized skin redness. Eczema (atopic dermatitis): Atopic dermatitis, if not treated appropriately, can easily lead to generalized redness. Redness of the skin, dry desquamation, possible lichenification, full thickness of the skin, especially forearms and lower legs. Generalized skin redness due to streptococcal infection: Dermatitis, skin redness, fine scales. Tinea versicolor: If the patient does not receive proper treatment or topical corticosteroid treatment. Tinea capitis can spread throughout the body. The patient has itching, scabs, diagnosed by a fresh mycological test. Some other skin diseases such as: Norwegian scabies, severe contact dermatitis, erythema multiforme, Lyell's syndrome often cause red, scaly skin all over the body.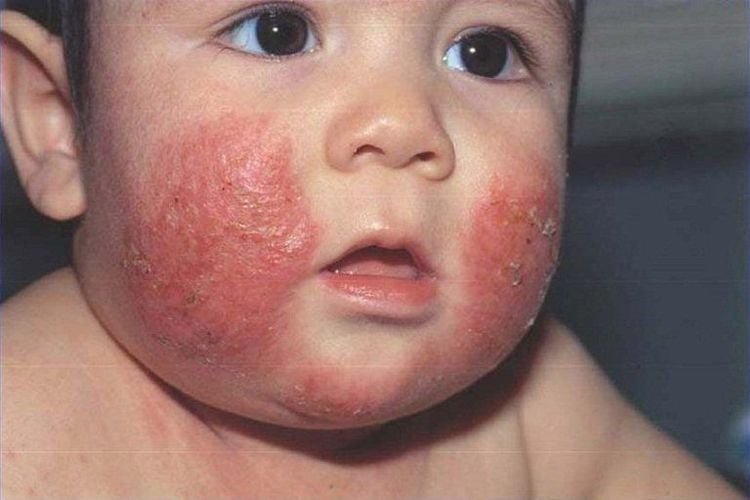
2.1.2 Redness of the skin due to drugs
Currently, systemic redness caused by drugs is common. The cause may be due to the improper use of drugs, especially antibiotics of the Beta Lactam family, Streptomycin.... Anti-epileptic drugs, anti-malarial drugs... can cause redness of the whole body, flakes and dry scales.2.1.3 Redness of the whole body due to blood diseases
Some diseases such as Hodgkin's disease: Usually causes red, scaly skin all over the body, accounting for about 25%. Fungal warts. Sezary syndrome.2.1.4 Primary generalized erythema
Regarding genetic factors, the proportion of males is higher than that of females2.1.5 Generalized erythema occurs in infants and children
Leiner's disease: The disease is mainly seen in children during the breastfeeding period from 6 to 20 weeks. There is a condition of red, scaly skin, appearing first in the oily skin, wrinkles and then spreading to the whole body. The scalp is always covered with thick patches. There may be nail lesions, enlarged lymph nodes. Children often have emaciation and diarrhea. Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome: This is a severe systemic form of staphylococcal impetigo that often occurs in young children. The patient had a fever, rapidly progressing with blisters, rapidly breaking, scabbing into large patches (rolled like cigarette paper).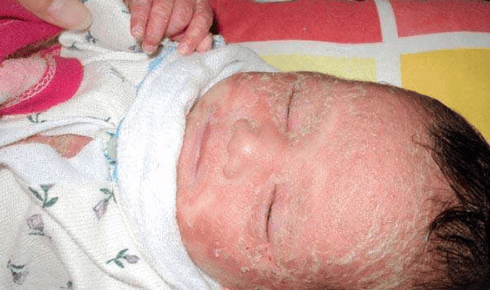
2.2 Classification according to outstanding clinical features
Redness of the skin with large psoriatic scales or small psoriatic scales. Generalized reddening of the skin, edematous vesicles (wet form), and scaling of the skin occurs secondary to this. Redness of the whole body in the form of scarlet fever. Generalized erythema papule: the disease is common in elderly men, the lesions are papules on a red background except for large skin folds.3. Clinical symptoms
3.1 Injury to skin and mucous membranes
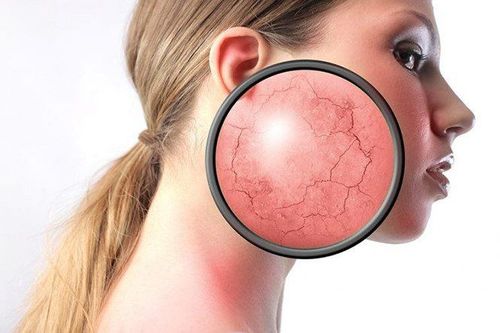
Skin lesions that are bright red or bruised. Edema may be localized to the lower extremities or to the whole body. Superinfection will have purulent scabs, making the patient worse. Increased or decreased pigmentation causes the skin to darken to form patchy patches. The skin around the eye socket may be red, inflamed, and watery. In the face can be deformed due to edema or infiltrate to remove wrinkles on the face.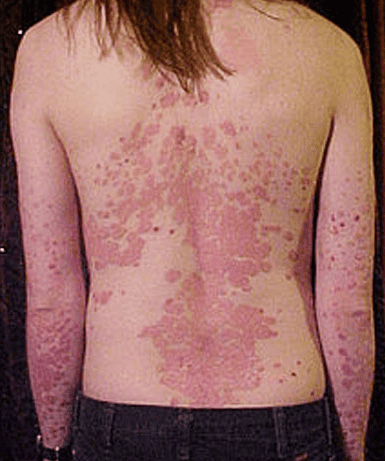
3.2 Physical symptoms
In some cases, patients only have mild itching or discomfort. In more severe cases, there may be a feeling that the skin is squeezed, restricting movement.3.3 Systemic symptoms
Patients may have a high fever or feel cold or shivery due to skin vasodilation, causing disturbances in body temperature regulation and excessive energy consumption.4. Treatment of erythroderma
4.1 General principles
Combination of symptomatic treatment and treatment to eliminate the cause of the disease. Local and systemic treatment.4.2 Specific treatment
Topical treatment: Aim to reduce skin irritation, moisturize skin and improve inflammation:Soothing, moisturizing skin: Urea 10%. Anti-keratosis, scabs: salicylic acid. Disinfectant solution, methylene blue, eosin 2%. Soak in purple medicine water bath 1/10,000. Bath in mineral spring water. Ultraviolet irradiation. Topical corticosteroids combined with antibiotics.

4.3 Systemic treatment
Anti-itch with antihistamines. Systemic corticosteroids and immunosuppressive drugs, depending on the clinical features and etiology of the disease. It is necessary to calculate the appropriate and effective initial dose to avoid drug dependence. Closely monitor the progress of the disease, when the drug has an effect, the disease decreases, the dose will be gradually reduced. Replenish water and electrolytes according to electrolytes. Use vitamin pills or eat foods rich in vitamins to improve physical health. Prevent venous occlusion, pay attention to prevent ulcers caused by lying down for a long time.5. Prevention of red skin disease
Patients should check their health at least once a year to detect the disease early, avoid any factors such as drugs and chemicals that can cause skin damage. Clean the skin well according to the doctor's instructions.When you have a skin disease, you need to go to a specialist immediately, do not automatically apply medicine even though the disease is very mild. Do not use drugs indiscriminately, including topical and systemic drugs without a doctor's prescription.
Any questions that need to be answered by a specialist doctor as well as if you have a need for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, please book an appointment on the website to be served.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.