This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Do Nguyen Thuy Doan Trang - Head of Extracorporeal Circulation Team - Cardiovascular Center - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Vasculitis is a disease that causes inflammation of the blood vessels. Vasculitis causes abnormal changes in the walls of blood vessels (thickening or thinning), leading to tissue ischemia, organ or blood vessel aneurysms, destroying blood vessels, and releasing red blood cells into tissues. Vasculitis that affects only the skin is called cutaneous vasculitis.
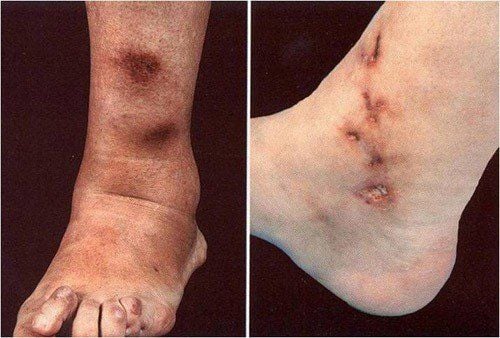
1. What is cutaneous vasculitis? Manifestations of cutaneous vasculitis?
Dermatitis vasculitis is a condition that involves inflammation of small or medium-sized blood vessels in the skin and subcutaneous tissue, not internal organs. Dermatitis vasculitis can be a skin lesion alone, or it can be a symptom of a primary (unknown) vascular lesion or secondary (triggered by an infection, drug, poison, or may be indicative of another inflammatory disorder or cancer). The ACR 1990 classification of vasculitis includes: Giant cell arteritis, Takayasu's arteritis, Wegener's granulomatosis, Churg-Strauss syndrome, Nodular arteritis, Hemorrhagic vasculitis, and hypersensitivity vasculitis.Vasculitis can affect small, medium, or large blood vessels. Vasculitis affects small blood vessels (arterioles, venules, capillaries) leading to lesions such as clumps, hemorrhagic nodules, and possibly superficial ulcers. Vasculitis affects deep, medium or large blood vessels (arteries, veins) causing cyanosis, papules, and deep ulcers on the skin. Regardless of the size of the affected blood vessels, patients may have symptoms and signs of systemic inflammation.
2. How is vasculitis diagnosed?
Diagnosis of localized cutaneous vasculitis requires careful medical history and physical examination. When taking a history, attention should be paid to determining the cause, such as some recent medication or infection. Focus should be on the examination to rule out inflammatory manifestations or vasculitis in other organs (systemic vasculitis) including: Lungs (difficulty breathing, cough, hemoptysis), kidneys (newly detected hypertension) or edema), neurological (newly appeared asymmetric weakness or paresthesia), intestines (abdominal pain, diarrhea, new bloody stools)...Urine test for red blood cells, protein and erythrocyte column. Chest x-ray to confirm pulmonary infiltrates (suggesting alveolar hemorrhage). Do a complete blood count, biochemical blood test to check for anemia, platelet count, creatinine level and quantification of substances in the acute inflammatory response.
Skin biopsy must be indicated, preferably within 24 to 48 hours after the appearance of vascular lesions. The diagnostic power depends on the depth and timing of this biopsy to obtain small and medium-sized blood vessels.
Rare vascular diseases, improper treatment can cause serious side effects, so tissue biopsy is needed to confirm the diagnosis first. Clinical examination selects the best biopsy site. Biopsies give the most positive results if taken from damaged lung parenchyma, skin, and kidney.
The diagnosis of cutaneous vasculitis is confirmed if the following lesions are detected on pathology: vascular wall is infiltrated, inflammatory cells cause destruction of blood vessel wall or intravascular and intravascular fibrin deposition. vessels (fibrinoid necrosis), extravasation of red blood cells, nuclear debris (leukopenia).

To determine the cause of vasculitis, we use a number of tests: cryoglobulins, anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA), antibodies to hepatitis B and C, complement C3, C4, weak rheumatoid factor, blood culture, serum protein electrophoresis and proteinuria. Other tests are done to determine the cause of vasculitis if clinically suspected.
3. How to treat skin vasculitis
Treatment of cutaneous vasculitis should focus on treating the underlying cause when possible (eg, hepatitis C causing cryoglobulinemia). If the cause cannot be determined and the vasculitis is localized to the skin, treatment is minimal and conservative. In some cases, only socks and antihistamines are needed. If this does not work, perform a trial with colchicine, hydroxychloroquine or dapsone, or a short course of low-dose corticosteroids.In a small number of more severe cases, stronger immunosuppressants (eg, azathioprine, methotrexate) may be used, especially if ulcerative lesions are present or prolonged corticosteroid therapy is required to control symptoms.

A system of modern and advanced medical equipment, possessing many of the best machines in the world, helping to detect many difficult and dangerous diseases in a short time, supporting the diagnosis and treatment of doctors the most effective. The hospital space is designed according to 5-star hotel standards, giving patients comfort, friendliness and peace of mind.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.