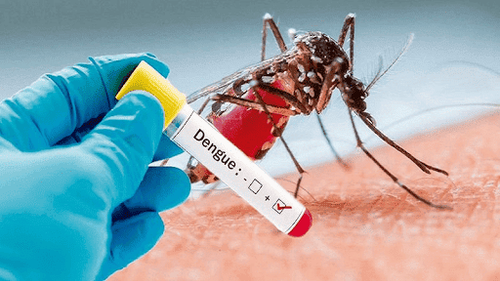
Dengue fever manifests in 3 stages of the disease, with the period from day 3 to day 7 being the most dangerous, where many complications can occur that may be life-threatening. Early recognition of the symptoms of the disease and seeking medical care at reputable healthcare facilities for examination, diagnosis, treatment, and monitoring of the dangerous progression of the disease is crucial.
1. Risk of Dengue Fever Infection
Dengue fever is an acute infectious disease caused by the Dengue virus. The disease spreads through blood, with the Aedes aegypti mosquito being the vector. This mosquito is most active at dusk and dawn.
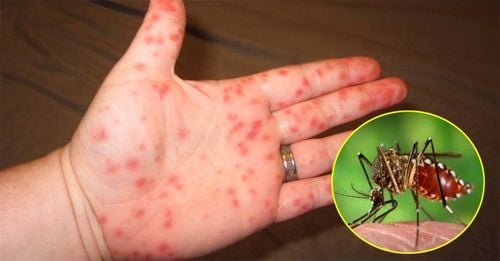
2. Dangerous Stages of Dengue Fever
Dengue fever develops in three stages:
2.1 Incubation Stage
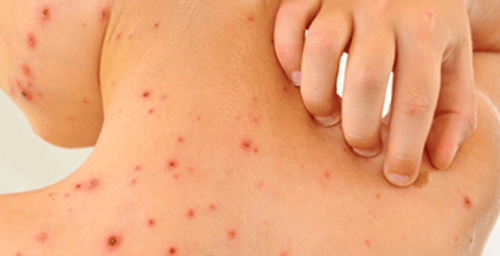
The early stage of Dengue fever may be mistaken for a common fever or viral fever. However, Dengue fever often has characteristic symptoms such as: skin hyperemia, petechial rash under the skin, and bleeding gums.
If severe, the patient may experience pain in the liver area, liver enlargement, low urine output, excessive vomiting. At this point, blood tests may show increased hematocrit and rapid platelet decrease.
2.2 Dangerous Stage
Patients with Dengue fever usually progress to the most dangerous stage after 3 - 7 days. This is the stage where proper intervention is needed to prevent harmful outcomes.
If there is significant plasma leakage, it can lead to shock with clinical symptoms such as:
- Convulsions, lethargy
- Cold extremities, pale, cold skin
- Kinking blood pressure, the difference between maximum and minimum blood pressure equal to or below 20 mmHg, blood pressure drops or is unmeasurable; low urine output...
At the same time, bleeding signs such as:
- Subcutaneous bleeding appears as scattered petechiae on the front of the lower legs, the inner arms, abdomen, thighs, and ribcage.
- Mucosal bleeding appears as nosebleeds, bleeding gums, hematuria, prolonged or early menstruation.
- Internal bleeding affects organs such as the digestive system, lungs, brain... and is considered severe and dangerous.
Some patients may show signs of ascites and pleural effusion.
In severe cases, signs of organ failure such as severe hepatitis, encephalitis, myocarditis can occur. These severe symptoms may arise in some patients who do not show clear plasma leakage or shock.
2.3 Recovery Stage
This stage lasts 48-72 hours.
The patient’s fever subsides, overall health improves, appetite increases, vital signs stabilize, and urine output increases.
3. Notes on Dengue Fever Treatment
For mild Dengue fever, patients can be treated at home as prescribed by a doctor. However, between days 3 - 7, patients, especially children, need close monitoring to detect early shock symptoms due to blood loss.
Particularly, from the 3rd day of illness (from the onset of fever), if any symptoms such as restlessness, lethargy, lethargy, pain in the liver area, excessive vomiting, low urine output, or internal bleeding appear, the patient must be urgently taken to the hospital.
Dengue fever is transmitted by the Aedes aegypti mosquito, so mothers with Dengue fever can still breastfeed their babies.
If the fever is high, only use Paracetamol for fever reduction, 10-15mg/kg/dose every 4-6 hours. Avoid using aspirin or ibuprofen as they may cause more severe bleeding.
Dengue fever in children is usually more severe than in adults. Children with Dengue fever are more prone to shock and recurrent shock than adults.
For children, if the fever subsides by the 4th day without any other symptoms, the disease is improving but still needs monitoring. If warning signs such as lethargy, lethargy, liver pain, excessive vomiting, low urine output, mucosal bleeding appear, the child must be immediately taken to the hospital for a check-up.
Dengue fever treatment mainly involves symptom management, and most of it can be outpatient care, such as fever reduction and oral fluid replacement. It is recommended to drink oral rehydration salts, boiled water, fruit juices, diluted rice water, coconut water, orange juice, milk, etc.
4. Dengue Fever Prevention Measures

Dengue fever is a mosquito-borne disease, and there is currently no vaccine or specific treatment. The most effective prevention method is mosquito control, eliminating larvae and preventing mosquito bites.
- Clean the home thoroughly, especially areas prone to dampness.
- Properly spray mosquito repellent.
- Use mosquito nets while sleeping, wear long clothes to prevent mosquito bites, even during the day.
- Use mosquito repellent cream both indoors and outdoors.
When suffering from Dengue fever, rest, eat a balanced diet, easy-to-digest foods, and supplement with vitamins to strengthen the body, drink plenty of water, and monitor for warning signs and severe symptoms such as restlessness, lethargy, lethargy, pain in the liver area, excessive vomiting, low urine output, or internal bleeding, to take the patient to the hospital promptly.
Master. Dr. Nguyễn Thị Nhật has over 10 years of experience in nephrology and infectious diseases, examining and managing patients with kidney diseases and infectious diseases. She is currently a Specialist in Infectious Diseases at the Internal Medicine Department of Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.