This is an automatically translated article.
Alcohol withdrawal syndrome is a collection of psychomotor and psychomotor symptoms that occur in alcoholics. Alcohol withdrawal syndrome occurs after stopping drinking with many degrees from mild as tremor, headache to severe such as hallucinations, delirium. Treatment of alcohol delirium requires sedation.
1. What is alcohol withdrawal syndrome?
Alcohol is a CNS depressant through increasing the inhibitory effects of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and inhibiting the stimulant effects of glutamate. In alcoholics, only when alcohol is continuously present in the blood can homeostasis be maintained. Abruptly stopping drinking with alcohol leads to a state of euphoria in the brain because the mechanisms previously inhibited by alcohol are no longer inhibited.
Alcohol withdrawal syndrome is a collection of symptoms caused by brain excitement that occurs in alcoholics when there is a sudden reduction in alcohol intake or cessation of alcohol consumption with mild symptoms such as insomnia, headache and tremor. to serious complications such as seizures and delirium that can be life-threatening.
Symptoms of alcohol withdrawal usually appear within 6 to 24 hours of a sudden decrease or cessation of alcohol consumption, even if blood alcohol levels remain.
2. Symptoms of alcohol withdrawal syndrome
Symptoms of alcohol withdrawal syndrome are proportional to the amount of alcohol consumed and the duration of alcohol consumption. Levels of symptoms include:
Hyperarousal-hyperesthesia or mild alcohol withdrawal:
The most acute manifestation of sudden alcohol insufficiency, usually occurring between 6 and 12 hours later when you stop drinking, most typically in the morning when you first wake up. Symptoms are most pronounced after 24 to 48 hours and last for several days. Psychiatric symptoms: Anxiety, increased emotions, anger easily, insomnia, nightmares, forgetfulness but still awake. Neuromuscular symptoms: Headache, tremors in the limbs, cramps often in the calves, sensory disturbances, numbness in the limbs. Symptoms of autonomic disorders: Sweating, heart palpitations, pale skin. Gastrointestinal symptoms such as loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea. Seizures:
Appears between 6 and 48 hours after abrupt withdrawal from alcohol. Short-term partial or generalized convulsions. Rarely, status epilepticus. Sometimes, these seizures are indicative of the onset of alcohol withdrawal delirium. The EEG images of alcohol withdrawal seizures are similar to those of seizures, and these EEGs are very sensitive to intermittent light stimulation. Alcohol hallucinations:
Occurs between 12 and 48 hours after abrupt cessation of alcohol. Symptoms such as visual, auditory, and/or tactile hallucinations but with relatively normal maintenance of other sensory functions.

Người nghiện rượu có thể xuất hiện ảo giác do rượu sau khi ngưng rượu đột ngột
Alcoholic delirium:
Alcoholic delirium, also known as delirium, is a severe, life-threatening alcohol withdrawal syndrome.
Appears between 48 and 96 hours after abrupt cessation of alcohol. Consciousness disorders: Confusion, delirium, agitation. Hallucinations, paranoia, complete insomnia. Severe tremors, rapid heart rate, increased blood pressure, fever, sweating, dehydration. Symptoms often increase when the alcoholic is alone or in dimly lit conditions such as in the evening and decrease in the morning. The CIWA-Ar 10-symptom assessment of alcohol withdrawal is a tool that can be used to quantify the severity of alcohol withdrawal syndrome, and to monitor and select medication for the patient. A CIWA-Ar score ≤ 8 is mild alcohol withdrawal syndrome, a CIWA-Ar score of 9 to 15 is moderate alcohol withdrawal syndrome, and a CIWA-Ar score > 15 points is severe alcohol withdrawal syndrome, a high risk convulsions and delirium.
Diagnosis of alcohol withdrawal syndrome: Diagnosis of alcohol withdrawal syndrome is mainly clinical, but it is necessary to rule out other causes that present with similar symptoms.
Diagnosis of alcohol withdrawal syndrome according to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) is as follows:
A. Significantly reduce alcohol intake or stop drinking suddenly while drinking heavily for a long time.
B. At least 2 of the following symptoms occur within a few hours to a few days of sudden reduction or cessation of alcohol intake.
Increases autonomic nervous system activity. Trembling hands and feet Insomnia Nausea, vomiting Excessive anxiety. Changes in mental status: Easily angered, agitated, delirious, Visual hallucinations, hallucinations, or delusions. Seizures (partial or general) epileptic.
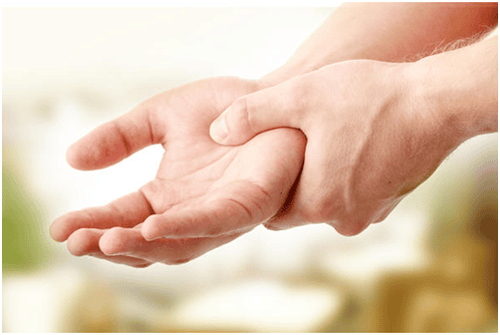
Người nghiện rượu sau khi ngưng uống rượu đột ngột có thể bị run tay chân
C. The above symptoms cause marked impairment in work, social functions or other important areas.
D. The above symptoms are not caused by diseases (such as meningitis, cerebral hemorrhage, liver failure, metabolic disorders, drug overdose,...) and other mental disorders.
Management of delirium:
Alcohol withdrawal syndrome is treated depending on the severity of symptoms. Most patients have mild to moderate symptoms that can be treated as outpatients. If the patient is in a state of alcohol-induced delirium, an emergency room visit is needed. Treatment of delirium is an emergency. If not treated promptly and properly, the death rate of delirium is up to 22-33%.
Management measures include:
Put the patient in a quiet, well-lit, safe place with limited mechanical control. Rehydrate by mouth at least 3 liters per day or by intravenous fluids. Nutritional supplementation with intravenous glucose. Correct water and electrolyte disturbances, pay attention to blood magnesium and calcium levels. Thiamine (Vitamin B1) deficiency, found in 80% of alcoholics, can cause peripheral neuropathy, cardiomyopathy, Wernicke encephalopathy. Therefore, it is imperative to supplement vitamin B1 to prevent neurological complications. Vitamin B1 is given intravenously for the first few days, then maintained orally. Supplement with other nutrients and vitamins to improve overall condition. Treat psychotic symptoms with benzodiazepines such as diazepam and lorazepam. These are safe and effective medications to prevent and treat seizures and delirium; is the drug of choice for the treatment of agitation. All patients with alcoholic delirium or convulsions require intravenous benzodiazepines to ensure rapid absorption and onset of action. Haloperidol, beta-blockers, clonidine, and phenytoin can be used as an adjunct but should not be used routinely. Alcohol withdrawal is a lifelong journey, and patients may face relapses and temptations of alcohol after withdrawal, so ongoing treatment is essential. Delirium is one of the states that occurs during alcohol withdrawal. Once you overcome this state and resist the temptation of alcohol, you can overcome the addiction easily. The more you try to quit smoking, the higher your chances of success.
Follow the website: Vinmec.com to update many other useful information.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference sources: bvdkquangnam.vn, maihuong.gov.vn