This is an automatically translated article.
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) disease is the leading infectious disease causing deafness, congenital blindness and mental retardation. Although it is an infectious disease, there is currently no document (both nationally and internationally) that says Cytomegalovirus causes pandemics.
1. Cytomegalovirus overview
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) is a type of virus belonging to the Herpes group, which gets its name from a cell infected with a swollen virus. This virus contains double-stranded, linear DNA, with a size of about 235 kb. The viral genome is divided into two regions: a long region (UL), and a short region. The long region contains two genes encoding two proteins that play a key role in antiviral therapy, including ganciclovir. The product from UL54 is the enzyme DNA polymerase and is the target of several antiviral agents indicated in the treatment of symptomatic congenital CMV infection. The product from UL97 is a phosphotransferase that is required for the phosphorylation of ganciclovir to convert the drug to its active form in vivo. Humoral immunity against CMV focuses mainly on two envelope proteins: glycoprotein B and glycoprotein H. Most human cells are susceptible to CMV infection, especially fibroblasts, epithelial cells, and endothelial cells. tissues, macrophages, and muscle cells. The exact incubation period is controversial, but is thought to be around 1-2 months.
MORE:
General overview of cytomegalovirus - Part 1 General overview of cytomegalovirus - Part 2
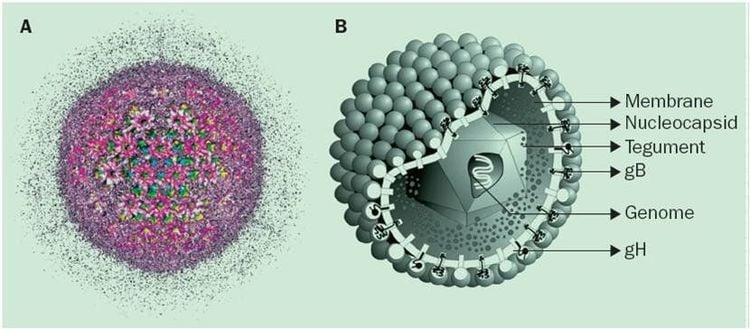
Virus Cytomegalo có thời gian ủ bệnh dài từ 1 - 2 tháng
2. Features of Cytomegalovirus disease
2.1. Case definition
Clinical cases:
Up to 95% of cases have no clinical signs. Clinical symptoms include fever, muscle weakness, fatigue, swelling of peripheral lymph nodes, visceral lymph nodes, hepatosplenomegaly, accompanied by skin lesions. About 80-100% of cases have skin manifestations such as red papules, petechiae, petechiae, urticaria, and hard erythema. Children with congenital cytomegalovirus infection often have jaundice, anemia, thrombocytopenia, hepatosplenomegaly, pruritus papules, subcutaneous nodules, and chorioretinitis. If the fetus is infected with CMV, the growth will be retarded in the uterus. Cases are identified when CMV or specific antibodies to CMV are found in the specimen.
2.2. Differential diagnosis
Mononucleosis. Toxoplasmosis. Viral hepatitis. Lymphoma.
2.3. Test
Tests to help confirm the diagnosis of CMV infection include: isolation of CMV virus, finding antibodies - CMV antigens, PCR testing for CMV-DNA or direct observation by electron microscopy.
Virus isolation:
Specimen: throat rinse, urine. Inoculation of the specimen into the cells and observing the cell changes after 1-2 weeks will give the image of bulging cells containing many inclusions in the cell nucleus. Due to the slow destruction of cells (1-2 weeks), the disadvantage of this method is the long reading time. Virus isolation combined with seroconversion is the most superior method for the primary diagnosis of CMV infection in normal people. Serological diagnosis:
Neutralization, immunofluorescence testing for antibodies is useful in diagnosing congenital but asymptomatic infections. Specific anti-CMV antibodies include IgM, IgA, and IgG. Antibodies present in breast milk will not prevent mother-to-child transmission and limit the severity of the disease. Patients infected with CMV will carry positive IgG antibodies for life. MORE: Cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection during pregnancy
Các xét nghiệm chẩn đoán giúp xác định được tình trạng nhiễm CMV
3. Epidemiological characteristics
Cytomegalovirus disease can be found anywhere in the world. According to some documents, there are about 80 - 100% of the population of Africa; 60 - 70% of the population of the United States and Western Europe; 90-100% of children and adults in developing countries and low-income countries test positive for viral serodiagnosis. In the United States, about 0.5-1.5% of infants are infected with CMV. Currently, there are no studies on the distribution of time of CMV infection. In Vietnam, there are no studies on the prevalence of CMV infection.
4. Infectious source and mode of transmission
Cytomegalovirus reservoirs are symptomatic infected people and asymptomatic patients. There is no document that says CMV can exist in the wild. The incubation period of the virus is about 4 - 8 weeks. Cytomegalo virus is transmitted during the full-fledged period, the period of remission.
Oral and respiratory tracts are the most prominent routes of viral infection. In addition, the virus can also be transmitted from person to person through saliva, urine, semen, milk, vaginal secretions. Blood transfusion, organ transplantation of infected patients, sexual contact with infected people are also transmission routes that need special attention.
Phương thức lây truyền chính của vi rút cytomegalo là qua đường hô hấp
5. Measures to prevent diseases caused by Cytomegalovirus
Preventive measures: Having sex with an infected person must use a condom.
The anti-epidemic measure is to isolate the sick. The live CMV vaccine is currently being studied in clinical trials in human volunteers.
Treatment principles: use antiviral drugs
Intravenous drugs: Ganciclovir, Cidofovir, Foscarnet Oral drugs: Valacyclovir, Acyclovir. Cytomegalovirus (CMV) is a herpes virus that causes blindness, congenital deafness, and mental retardation. Therefore, each person needs to know information to prevent and avoid transmission, affecting the health of the community.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.