This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Tran Cong Trinh - Radiologist - Radiology Department - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital. The doctor has extensive experience in the field of diagnostic imaging.Angina is a temporary chest pain that causes discomfort due to reduced blood flow to the heart muscle. Angina is not a heart attack, but it is a sign of an increased risk of heart attack. Angina may be stable (more severe with physical activity, lasting five minutes or less and relieved by rest) or unstable (occurring only during rest, longer and symptoms may be more severe.
1. What is angina?
Angina is a temporary, uncomfortable chest pain caused by reduced blood flow to the heart muscle. Due to reduced blood flow, not enough oxygen reaches the heart muscle resulting in chest pain. Coronary artery disease can lead to narrowing of the coronary arteries that carry blood and oxygen to the heart muscle, which is one of the most common causes of angina.Although angina is not a heart attack , it does signal a high risk of having a heart attack . You need medical help right away if you experience chest pain or discomfort.
There are two main types of angina, stable and unstable. Stable angina, which is the most common angina, is common during physical activity and usually lasts for a short time (about five minutes or less) if physical activity has ended. Unstable angina is less common and usually occurs during rest. Unstable angina usually lasts longer and symptoms can be more severe.
Symptoms of angina you may experience, including:
Chest pain or discomfort, such as tightness in the chest Discomfort in the jaw, neck, arms, upper abdomen, shoulders or back Fatigue Sweating Nausea Dizziness There are many risk factors associated with angina, such as high blood pressure, diabetes, obesity, family history, tobacco use, stress, and age.

Bệnh nhân đau thắt ngực có thể kèm triệu chứng buồn nôn
2. CT scan, MRI and different forms of assessment in angina assessment
To diagnose the cause and evaluate angina, the following tests may be performed:Electrocardiogram (ECG): This test records the electrical activity of the heart, used to diagnose abnormalities of the heart as arrhythmia or indicating ischemia (lack of oxygen and blood) to the heart. Cardiac activity assessment without images: This heart monitoring test is used to help evaluate how well the heart is working. During a stress test, you'll usually be asked to do physical exercises, like walking on a treadmill. ECG is recorded during exercise. An ECG is used by your doctor to assess whether your heart is getting to the right heart rate and if there are any changes that indicate decreased blood flow to your heart. If you are unable to exercise, medications that have a similar effect on the heart's response to exercise can be used. Blood tests: Blood tests can identify certain enzymes like troponin that leak into your bloodstream after your heart has had severe angina or a heart attack. Blood tests can also identify elevated cholesterol, LDL, and triglycerides that put you at higher risk of coronary heart disease and thus angina. In addition, the following imaging tests may be done:
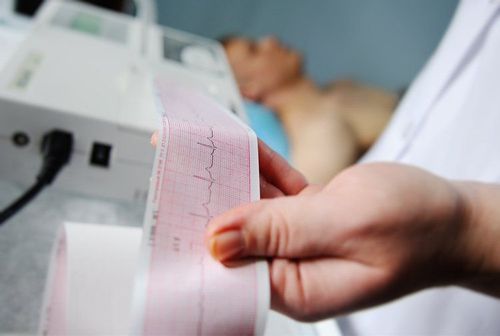
Chest X-ray: This noninvasive imaging test helps the doctor rule out other causes of chest pain such as pneumonia. Chest CT: A chest CT is a more sensitive test than a chest X-ray that can identify other causes of chest pain such as aortic disease or blood clots in the blood vessels of the lungs. This imaging test combines special X-ray equipment with sophisticated computers to create multiple images of the chest and heart. Coronary computed tomography (CT) scan: This test evaluates the coronary arteries (blood vessels that supply blood and oxygen to the heart) to determine how narrow the arteries are due to plaque without the need for a catheter invade through the arteries into the heart. Contrast material is injected through a small line in an arm vein, similar to that used to draw blood.

Chụp CT ngực cho phép xác định các nguyên nhân khác của đau ngực
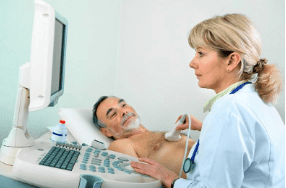
Bệnh nhân đau thắt ngực được chỉ định siêu âm tim để chẩn đoán bệnh
3. Treatment of angina
Your doctor will recommend healthy lifestyle choices like maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced low-fat diet, stopping tobacco products, and finding ways to reduce stress.In addition, you may also be treated with certain drugs such as:
Medicines such as aspirin, statins, beta blockers, calcium channel blockers or nitrates. Angioplasty and vascular stenting: In applicable cases, after appropriate testing, the physician may perform angioplasty and stenting. This procedure is done to open up blockages in a coronary artery and improve blood flow to the heart. Coronary artery bypass surgery (CABG): This surgery increases blood flow to the heart by using a vein or artery from elsewhere in the body to redirect blood flow around an area of narrowing or blockage in the heart. coronary arteries of the heart. To diagnose and evaluate angina, your doctor may perform an electrocardiogram (ECG), which evaluates your heart's activity without imaging or blood tests to help diagnose your condition.
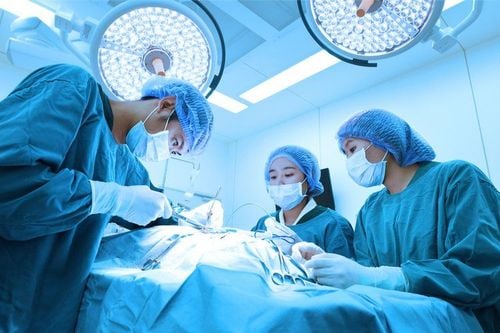
Phẫu thuật bắc cầu động mạch vành giúp điều trị đau thắt ngực
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference article source: radiologyinfo.org