This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by Master, Doctor Mai Vien Phuong - Department of Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Crohn's disease, also known as regional inflammatory bowel disease, is often more difficult to diagnose than other inflammatory bowel diseases. This is because Crohn's is not limited to any area of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract; it occurs anywhere from the mouth to the anus and has a much wider variety of symptoms.
1. General Symptoms of Crohn's Disease
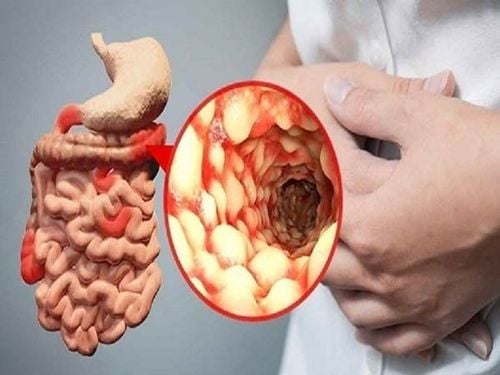
Each different site of Crohn's disease has its own symptoms. Some common signs and symptoms include:Abdominal pain Diarrhea Weight loss Lack of energy Pain usually begins within an hour of eating and is most often concentrated around the navel, right lower abdomen or both. Mild abdominal swelling or bloating is also common in Crohn's disease and may be related to food choices.
1.1 Crohn's disease of the colon Symptoms of Crohn's disease of the colon, known as Crohn's colitis, manifest differently depending on where the disease is located in the colon.
If the disease is located on the right side of the colon, cramps and diarrhea will appear. If it is on the left side or involves most of the colon, there is blood in the stool along with other symptoms.
If the disease is located in the rectum, the symptoms will be similar to ulcerative colitis. Symptoms may also include bloody diarrhea or a feeling of little or no bowel movement.
1.2 Crohn's disease of the small intestine People with Crohn's disease of the small intestine, known as Crohn's of the small intestine, often experience cramping, diarrhea, and weight loss. The foci may be in the upper part of the small intestine, called the jejunum, or in the lower part, called the ileum.
Occasionally, a person with small bowel Crohn's will become constipated. This may be because parts of the intestines can become scarred and narrowed, blocking the flow of food that is being digested and absorbed in the digestive tract. nausea and vomiting.
1.3 Crohn's disease of the ileum and colon Crohn's disease of the ileum affects both the colon and the ileum. If you have Crohn's of both the ileum and colon, you may experience symptoms related to small bowel inflammation or Crohn's colitis, or symptoms of both. This is because Crohn's of the ileum can flare up when the disease in the colon goes into remission, or vice versa.
1.4 Crohn's disease of the stomach and duodenum The duodenum is the first part of the small intestine closest to the stomach. Many people with Crohn's disease of the stomach and duodenum, known as gastroduodenal Crohn's disease, will have no symptoms.
Weight loss is another common symptom. This is because people with Crohn's stomach pain may avoid eating or consume less food to prevent pain and other symptoms.
In some cases, due to scarring, this type of Crohn's causes a narrowing of the area between the stomach and duodenum. If this happens, you will usually experience a decreased appetite, a feeling of bloating in the upper abdomen, nausea, and vomiting.
1.4 Crohn's of the appendix, esophagus and mouth Crohn's of the appendix, esophagus, and mouth are rare diseases.
Crohn's disease of the appendix can look like appendicitis or not have any symptoms.
Crohn's of the esophagus can cause pain behind the sternum when swallowing. If the esophagus is narrowed due to scarring, you may have difficulty swallowing or food may get stuck on its way down. Contact your doctor immediately if you have these symptoms.
Signs and symptoms of oral Crohn's often include large and painful sores in the mouth. If you have this symptom, contact your doctor.
2. Diagnosis of Crohn's
Your doctor may use several types of tests to make a diagnosis:Blood tests can help your doctor look for certain signs of potential problems, such as anemia and inflammation. Stool tests can help your doctor detect blood in your digestive tract. Your doctor may order an endoscopy to get a better picture of the inside of your upper digestive tract. Your doctor may order a colonoscopy to examine the large intestine. Imaging tests like CT scans and MRI scans Your doctor will likely take tissue samples or biopsies during your colonoscopy or colonoscopy to get a closer look at your intestinal tissue. When the doctor has finished reviewing all the necessary tests and ruling out the reasons, will he or she conclude that you have Crohn's disease?
In addition, the doctor may order these tests again and again to look for diseased tissue and determine how the disease is progressing.

3. Prevention of Crohn's Disease
Dietary changes in Crohn's disease play an important role in helping you screen for Crohn's disease and prolonging the time between flare-ups. So, soon after being diagnosed with Crohn's, your doctor will likely recommend making an appointment with a dietitian to help you understand how foods may affect your symptoms and dietary changes. What diet might help you?Crohn's disease is usually classified into five types, each with its own signs and symptoms. Many of these types have overlapping symptom clusters. For these reasons, it's important to keep a close eye on what you're experiencing and to share it with your doctor.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.