This is an automatically translated article.
Childhood Crohn's disease is an inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that can cause any part of the digestive tract from the mouth to the anus to become red, swollen, and inflamed. It is a chronic condition that lasts for a while or goes into remission and then comes back again.1. What is Crohn's disease?
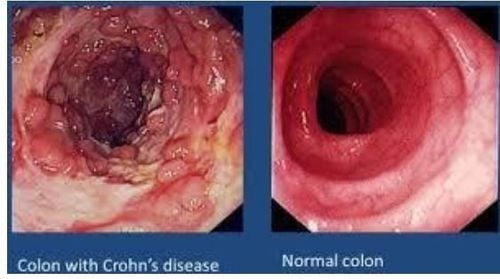
Crohn's disease is a chronic inflammation or ulceration of the gastrointestinal tract, also known as the intestines/colon. It is one of the inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD).Crohn's disease usually affects the near end of the small intestine, called the ileum. However, the disease can also occur in any part of the large intestine, stomach or esophagus, and in some cases even in the mouth.
Crohn's disease can occur at any age, but is most common in people between the ages of 15 and 30. The disease can stunt general growth, weaken bones, and delay puberty.
The mechanism of Crohn's disease is to disrupt the normal function of the gastrointestinal tract, causing the intestinal tissues to become:
Swelling, thickening, or scar tissue formation, leading to a blockage inside the intestinal lumen; Development of ulcers in the deep layers of the intestinal wall; Loss of the ability to absorb nutrients from food (malabsorption), especially in the ileum, where vitamin B12 and bile acids are absorbed; Formation of abnormal fistulas from one part of the intestine to another, or from the intestine to other nearby tissues.
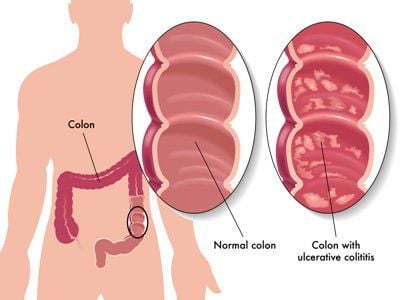
Bệnh Crohn là tình trạng viêm hoặc loét ống tiêu hóa mãn tính, hay còn gọi là ruột/đại tràng
2. Causes of Crohn's Disease in Children
The cause of Crohn's disease in children and adolescents is still unknown. It's more likely to be due to an inherited condition that causes abnormal immune system reactions in the digestive tract.People with family members with Crohn's disease, or other IBD inflammatory bowel diseases, are more likely to develop the disease.
3. Symptoms of Crohn's Disease in Children
Symptoms of Crohn's disease in children depend on the part of the intestine affected and the severity. In general, the typical symptoms are:Frequent diarrhea; Sometimes there is blood in the stool; Rectal bleeding; Weight loss; Fever; Stomachache; A feeling of heaviness, stiffness, or fullness in the lower right abdomen; Fatigue, weakness; Mouth Sores; Failure to develop normally as peers, delayed puberty (in children). Children and adolescents with Crohn's disease often experience periods of severe symptoms followed by clinical remission. A period of no symptoms, called remission, can last several weeks or years. Taking anti-inflammatory drugs or adjusting the diet will help the disease go into remission, but the symptoms can still return at any time and unpredictably.
4. Complications of Crohn's Disease
Thiếu máu là một trong số những biến chứng có thể gặp phải của bệnh Crohn
Arthritis; Gallstones ; Kidney stones ; Inflammation (swelling) of the eyes and mouth; Liver failure ; skin rash or sores; Anemia.
5. Diagnosis of Crohn's Disease in Children
The doctor will review the patient and family medical history. Various tests are done to diagnose Crohn's disease in children, including:5.1 Endoscopy (colon or sigmoid colon) The doctor inserts a thin, lighted endoscope into the rectum. lighting and cameras. Images of the inside of the rectum and colon will be monitored through an external computer monitor. A small tissue sample may be removed for testing or a biopsy.
5.2 Blood tests Your doctor will look for signs of anemia, or a high white blood cell count. This result shows that a part of the body is inflamed or infected. Other tests will also be done to detect and identify signs of inflammation.
5.3 Contrast X-ray Your doctor will use X-rays to examine the upper or lower part of your digestive tract. Contrast contains a metal substance (barium) that coats the lining of the small and large intestines. The white images on the X-rays help the doctor see for abnormalities.
Bác sĩ sẽ tìm kiếm các dấu hiệu của tình trạng thiếu máu, hoặc số lượng bạch cầu cao để kiểm tra phần nào đó trong cơ thể có bị viêm hay nhiễm trùng không
6. Treatment of Crohn's Disease
Treatment for Crohn's disease depends on the severity and the location affected. Sometimes the disease can also go into remission on its own. Therefore, it is not possible to determine how effective a particular course of treatment is. When Crohn's disease is active, treatment is aimed at controlling inflammation, correcting nutritional deficiencies, and relieving symptoms, such as pain, diarrhea, and fever.6.1 Medication In general, medication is the first step in the treatment of Crohn's disease in children and adolescents. Some commonly prescribed drugs are:
Anti-inflammatory drugs; Antibiotics ; Antidepressants; Immunosuppressive drugs (including corticosteroids). However, drugs can weaken the body's ability to fight infections, so health professionals recommend that children receive all vaccines before starting treatment.
6.2. Protein biologic therapy Biological measures are also used to treat Crohn's. This drug is prepared from proteins in the human immune system. The proteins are then genetically engineered and processed for therapeutic use.
Biologics are usually given by injection or by IV infusion. This therapy is designed to interfere with and suppress inflammatory processes
6.3. Nutrition Patients with nutritional deficiencies need to regularly supplement with calcium or vitamin D, drink plenty of water and improve the quality of their daily menu. Some research studies suggest that the diet should be replaced entirely with liquids. Proper nutrition therapy will give the intestines a chance to heal and recover quickly.
6.4. Surgery In cases where medication cannot control Crohn's disease, causing the bowel to perforate, block, leak, or bleed non-stop, a surgical removal of part of the bowel may be required. However, the disease still has a risk of recurrence in the area near the previous inflammation.
Overall, a healthy lifestyle is important for the management of Crohn's disease in children and adolescents. Patients should exercise regularly and adhere to a balanced diet to lead a healthy and active life. With proper treatment and control, most children with Crohn's disease can still go to school, as well as participate in their usual sports and activities.
Pediatrics department at Vinmec International General Hospital is the address for receiving and examining diseases that infants and young children are susceptible to: viral fever, bacterial fever, otitis media, pneumonia in children, .... With modern equipment, sterile space, minimizing the impact as well as the risk of disease spread. Along with that is the dedication from the doctors with professional experience with pediatric patients, making the examination no longer a concern of the parents.
Articles refer to sources: Webmd.com, Kidshealth.org
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
SEE ALSO:Diagnosis and treatment of Crohn's disease in children Why are breastfed babies prone to intussusception? Gastrointestinal diseases are common in children