This is an automatically translated article.
The article is written by Master, Doctor Mai Vien Phuong - Gastroenterologist - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.
It has been documented that covid-19 patients with gastrointestinal symptoms show a higher rate of liver damage than patients without gastrointestinal symptoms.
1. Overview
Coronavirus belongs to the family Coronaviridae, subfamily Orthocoronavirinae, order Nidovirales. Around the world, coronaviruses are the cause of intestinal, neurological and liver diseases in humans, other animals and mammals. On the basis of genomics and phylogenetic analysis, the Coronavirus subfamily has four genera named Alphacoronavirus, Betacoronavirus, Gammacoronavirus and Deltacoronavirus.
Coronavirus caused severe acute respiratory distress syndrome (SARS-CoV) in 2003 and Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) in 2012. New coronavirus 2019 (covid-19) belongs to the Betacoronavirus genus . It is an enveloped virus with a positive-sense, single-stranded RNA genome. Covid-19 has affected more than 65.8 million people with 1.5 million deaths globally.
2. Covid-19 detection process
In early December 2019, the first recorded pneumonia case of unknown origin in Wuhan city, China was confirmed by high-throughput sequencing analysis, a new Betacoronavirus now named is SARS-CoV-2. The sudden worldwide outbreak of this virus has been declared a national pandemic and health emergency by the World Health Organization (WHO). During previous SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV outbreaks, bats were considered natural hosts and potential reservoirs. Various studies have demonstrated that bats are reservoirs of SARS-CoV-2, however, pangolin species are also considered as natural reservoirs of SARS-CoV-2.
Symptoms of covid-19 illness vary from mild respiratory symptoms to acute respiratory distress syndrome with multiple organ failure and death, mainly in elderly patients with certain comorbidities. WHO has released guidelines for timely, effective and safe supportive management of covid-19 patients, which show that clinical syndromes associated with SARS-CoV-2 include uncomplicated disease, mild to severe pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome, sepsis and sepsis shock. However, gastrointestinal symptoms and some extrapulmonary signs such as liver damage are also associated with covid-19.
3. Liver damage in covid-19 patients
Disturbed alanine transaminase (ALT), aspartate transaminase (AST) levels and hyperbilirubinemia have been seen in 14%-53% of covid-19 patients. A recent study of 1100 patients reported that 18% of patients with severe and 56% of severe covid-19 had elevated serum AST levels. Increased ALT levels were observed in 20% of non-severe patients and 28% with severe covid-19 infections. Furthermore, it has been documented that covid-19 patients with gastrointestinal symptoms show a higher incidence of liver injury compared with patients without gastrointestinal symptoms. Correspondingly, the incidence of chronic liver disease (CLD) is high in patients with gastrointestinal symptoms of covid-19.
Incidence of coronavirus 2019 patients with variable manifestations of signs of liver damage:
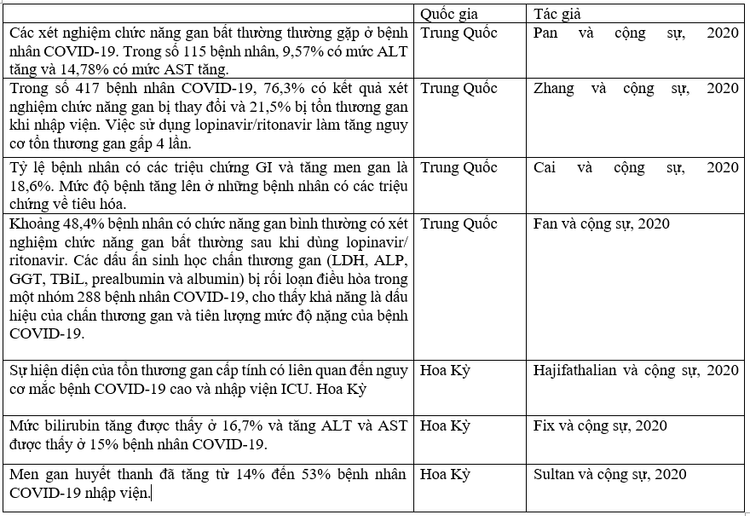
(Note: ALP: Alkaline Phosphatase; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; COVID-19: Coronavirus disease 2019; GGT: Gamma-glutamyl transferase; GI: Gastrointestinal; ICU: Intensive care unit. LDH: Lactate dehydrogenase; TBiL: Total Bilirubin).
4. Liver cancer patients are at high risk of contracting COVID-19
Liver cancer is the fourth most common cause of cancer death worldwide (the most common type is hepatocellular carcinoma - HCC). HCC patients have underlying CLD, including alcoholic liver damage, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), and chronic hepatitis B or C virus infection. It has been reported that cancer patients are at high risk of contracting covid-19. A study at three hospitals in Wuhan reported 1276 confirmed cases of covid-19, of which 28 patients had different types of cancer and two of them had HCC.
NAFLD, also known as metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD), is very common globally. One study reported that NAFLD patients had increased ALT levels after being infected with covid-19. A study from China found that NAFLD patients had an increased risk of contracting covid-19 compared with patients without the disease. However, more research is needed to understand the mechanism of liver damage caused by NAFLD and covid-19. It has been observed that the use of immunosuppressive drugs in post-liver transplant patients makes them more susceptible to SARS-CoV-2 infection. In addition, the use of these drugs has been found to enhance the cytokine storm in covid-19.
5. Liver damage related to COVID-19
Covid-199-associated liver injury manifested by entry of SARS-CoV-2 into the liver, which may progress during covid-19 treatment in patients with or without pre-existing liver disease . SARS-CoV-2-associated liver injury can result from a variety of factors, including direct cellular effects of the virus on biliary/hepatic cells, immune-mediated injury, hypoxia. , sepsis, and drugs (eg, acetaminophen, ritonavir/lopinavir, interferon, Chinese herbs, and antibacterial agents) used in the treatment of covid-19. However, there is no evidence that patients with chronic hepatitis are at risk for covid-19, unless there are other comorbidities (cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and hypertension).
ACE receptor 2 (ACE2) is involved in entry of SARS-CoV-2 and is highly expressed (approximately 80%) in the alveolar cells of the lung, intestine, and kidney. Expression of the ACE2 receptor has also been observed in cardiomyocytes, proximal nephron tubule cells, absorptive enterocytes of the ileum and colon, bladder ureteral cells, and oral mucosal epithelium. - nose - nasopharynx. It has been reported that ACE2 cell surface receptors are highly expressed in bile duct and liver cells, which indicates the ability of SARS-CoV-2 to reproduce in the liver.
6. Covid-19 related to liver injury and global clinical picture
Abnormal levels of liver injury markers such as AST and ALT or abnormal liver function tests (LFTs) in covid-19 patients add to the burden of disease for clinicians as well as scientists study on treatment regimens and determine the association of covid-19 with related liver diseases. Data documenting liver failure in covid-19 patients shows varying degrees of liver damage markers globally.
In this context, preliminary data are reported by Cai et al from Shenzhen, China from January 11 to February 21, 2020 and followed up to March 7, 2020. a report from a local hospital showed that, 318 of 417 covid-19 patients (76.3%) had abnormal LFT values and 90 of 417 (21.5%) had liver damage on admission. .
The prevalence of liver injury in Asia was further evaluated by Vespa et al in a cohort of 292 covid-19 patients up to 30 March 2020. Compared with Cai et al., an injury model Cholestatic liver disease with elevated alkaline phosphatase (ALP) levels > 150 U/L was observed in 9.6% of the selected population. Another study of cholestatic liver injury conducted from January 20 to 31, 2020 at Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center reported abnormal liver functions when ALT and AST levels, gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT), ALP, and total bilirubin were increased. Thus, literature reports describe data regarding predictive markers of covid-19 and associated liver injury, but the underlying cause of liver injury associated with worse outcomes remains elusive. start.
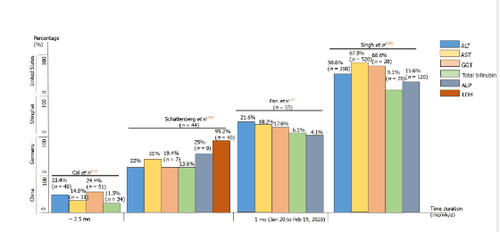
This figure only shows data published in peer-reviewed journals. ALP: Alkaline Phosphatase; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; GGT: Gamma-glutamyl transferase; LDH: Lactate dehydrogenase.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: Ahmad A, Ishtiaq SM, Khan JA, Aslam R, Ali S, Arshad MI. COVID-19 and comorbidities of hepatic diseases in a global perspective. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(13): 1296-1310 [PMID: 33833483 DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i13.1296]