This is an automatically translated article.
Chronic colitis is common in adults, the elderly account for the majority. The question many people are interested in is whether chronic colitis is dangerous? Please refer to the article below to be able to answer the above question.
1. What is chronic colitis?
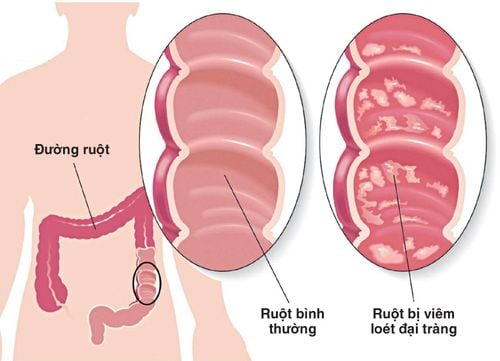
Inflammation of the colon for a long time leads to chronic causing chronic colitis. Lesions are usually mild, localized, or diffuse to the colonic mucosa.
In Vietnam, chronic colitis is a common disease of the gastrointestinal tract, about 20% of the population has chronic colitis, this rate is constantly increasing.
2. Causes of chronic colitis
Cause of disseminated colitis
Due to bacterial infection Dysentery, bacilli: Shiga, Flexner, ... Salmonella Escherichia coli, streptococcus, staphylococcus and some other bacteria Typhoid Due to amoeba parasites: accounting for most Some causative factors are still controversial such as: hairworm, Lamblia, Chilomastix mesnili, Balantidium coli, Trichomonas intestinalis Due to mercury, arsenic, lead, gold, arsenic poisoning. Food poisoning. Possible cause unknown Causes of localized colitis
Crohn's disease of the colon, cecalitis, sigmoid colitis. Unscientific diet Disorders of bacteria in the intestinal tract.

Chế độ ăn uống không khoa học có thể gây viêm đại tràng mãn tính
3. Symptoms of chronic colitis
The most common symptom of chronic colitis is abdominal pain. Characteristics: dull pain in the lower part of the navel (lower abdomen, lower abdomen), possibly abdominal pain along the colonic frame in a certain position.
Abdominal pain often occurs after eating, may be sad to have a bowel movement, after defecation the pain will go away. In chronic colitis, the abdomen is full of gas and pain, therefore, a lot of bowel movements and after defecation will be felt. less pain. In many cases, abdominal pain is worse at night, especially when it is cold.
Digestive disorders also frequently occur such as bitter mouth, loss of appetite, prolonged indigestion; broken, unformed stools, defecation many times, sometimes solid stools causing constipation. The abdomen is slightly distended, the patient will feel tight and uncomfortable.
4. Consequences of chronic colitis
The older the patient, the more times the disease recurs, the higher the risk of dangerous complications. Some consequences of chronic colitis:
Massive bleeding: The inflammation recurs many times into the chronic, so the damaged colonic mucosa will not be restored, it will be very weak, serious inflammation. Therefore, when using stimulants such as alcohol, ... or eating unhygienic foods or using antibiotics excessively, ... will cause toxic colon or massive bleeding. Colonic perforation: After repeated episodes of inflammation, antibiotic treatment is required to destroy beneficial intestinal bacteria, and the villi are weak and bare. Therefore, old or recurrent inflammatory lesions penetrate deep into the thin layer of the colon wall, continue to grow deep and at some point will cause colonic perforation. If not treated promptly, it is very dangerous and can be life-threatening. Acute dilatation of the colon: Digestive function of the colon is impaired due to chronic colitis, not only in certain lesions but also the entire structure is dilated, leading to ulceration and perforation of the colon. very dangerous. Acute colonic dilatation complications can cause patients to appear severe abdominal pain, fall into a coma, and if not treated promptly, the mortality rate will be very high. Colon cancer: is a very dangerous complication, the rate of this complication in our country is quite large. When ulcerative colitis persists and recurs continuously, putting mucosal epithelial cells at risk of metaplasia, dysplasia, benign cells turn into malignant cells, and then develop into cancer. Colon. This process takes about 8 years.
5. Diagnosis and treatment of chronic colitis
Diagnosis
Clinical:
Pressure is felt in the sigmoid colon or cecum, the brain is yoke, the percussion is still clear. Abdomen is slightly distended or normal, no pain or tenderness. Blood, nose or pus can be seen following the finger to visit the rectum, rule out some tumors Some cases of fatigue and weakness. Subclinical:
Stool test Specimen: blood, pus, mucus, soluble albumin Soluble albumin: has high diagnostic value, reflecting inflammation of the colonic mucosa. Endoscopy Conventional sigmoidoscopy or flexible colonoscopy can be performed. On the wall of the colonic mucosa can see blood, pus The mucosa of the colon is red, congested, easy to bleed or has obvious ulcers. Through endoscopy, it is possible to do a biopsy of the colonic mucosa or take samples directly from the ulcer to look for bacteria, and other parasites to determine the cause of the disease. Colon X-ray This method is rarely used because of its low accuracy. X-ray can show that the contraction of the colon is disturbed, the movement in the colon is increased; disk stack images; colonic margins straight or serrated, lanceolate; The diameter of the colon is narrowed, transverse grooves are lost; Colonic surfaces unknown, bread-shaped intestines; In case of severe colitis, the radiographic manifestations are more pronounced: blurred edges, double contour images, striated mucosa and especially honeycomb pseudo-polyposis.
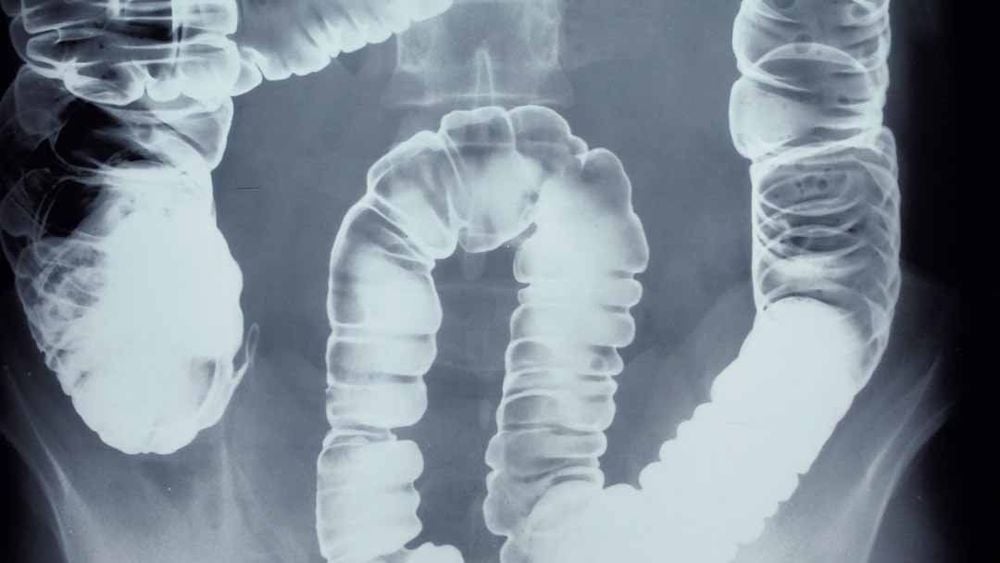
X Quang khung đại tràng có thể giúp bác sĩ chẩn đoán viêm đại tràng mãn tính
Treatment
To effectively treat chronic colitis, the cause must first be determined, on that basis, it will be based on a regimen for effective treatment (medical treatment), if due to polyps will be treated surgically (removal).
Treatment of chronic colitis should ensure that it is a combination of medical and comprehensive treatment, changing lifestyle, eating and working habits accordingly.
Treatment of causes: Salmonella, Shigella, other parasites or other autoimmune causes,...
Treatment of symptoms
Anti-diarrheal: kaolin, vegetable charcoal. Anti-constipation: paraffin oil. Pain relief, anti-colic colonic: atropine, belladonna, barbitiric, papaverin. Abstain from foods high in cellulose, fermented foods Increase movement and exercise, reduce anxiety and stress. In order not to get chronic colitis, first not to get inflammatory bowel disease, especially acute enteritis. Therefore, it is necessary to ensure a reasonable diet, ensure food hygiene and safety such as:
Cook cooked food and drink boiling water, do not drink unpasteurized fresh cow's milk. Eat plenty of vegetables, fruits, and fiber every day. When having diarrhea, it is necessary to avoid substances containing a lot of cellulose so that the intestinal wall does not "rub". You can eat pureed fruit such as: bananas, apples, watermelons... Limit spicy, hot, greasy foods Avoid prolonged use of antibiotics, which increases the risk of bleeding. Active treatment for pulmonary tuberculosis. Body mobility. Chronic colitis can have very dangerous consequences. If you find yourself having any unusual symptoms, please go to the medical facility as soon as possible to be examined and treated promptly by a doctor.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.