This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Tong Diu Huong - Radiologist - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.A brain aneurysm is a bulge in a blood vessel in the brain that leads to a blood vessel breaking easily, causing bleeding into the brain. This disease progresses very quickly and is life-threatening. However, in the absence of rupture complications, this pathology is difficult to detect and is often discovered incidentally when the patient undergoes computed tomography scan due to other medical examinations.
1. What is a brain aneurysm?
A cerebral aneurysm is a weakened and abnormally enlarged brain artery that can rupture and bleed.Brain aneurysms usually occur in an artery located in the front part of the brain, which is the blood vessel that supplies oxygen-rich blood to brain tissue, however any brain artery can develop into an aneurysm.
Normally, a healthy artery wall is made up of three layers, but in an aneurysm, the wall of the bulging blood vessel is thin and weak because there is no muscle layer and only two layers remain.
Most brain aneurysms (90%) appear without any symptoms and are small (less than 10 mm). Smaller aneurysms may have a lower risk of rupture.
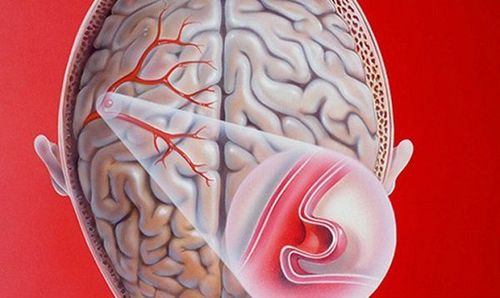
Phình động mạch não gây ra nhiều biến chứng nguy hiểm
2. Cone-beam computed tomography in the diagnosis of cerebral aneurysms
2.1 Before the procedureThe patient will be asked about his medical history, signs of cerebral aneurysm or allergic condition that the patient has, especially anesthetics and anesthetics. And the patient also needs to fast and fast for at least 6 hours before.
2.2 Procedure
The patient will lie on the table and the nurse will set up an intravenous line in the patient's arm. However, for children or people who cannot control themselves, the doctor may use pre-anesthetic drugs before the procedure.
First, the patient's head will be fixed firmly to avoid deviation. The doctor begins to disinfect and numb the place where the needle is inserted. The most common puncture site is the femoral artery, however, in case this is not possible, the doctor can use another location such as the brachial artery or axillary artery...
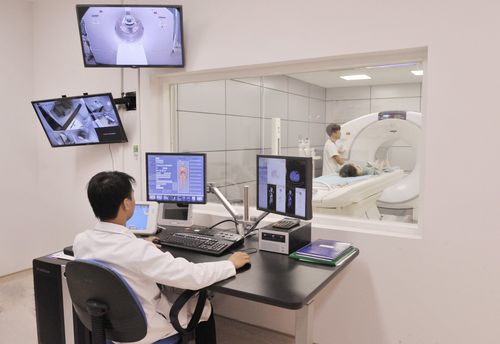
After the needle is inserted and Insert the catheter into the artery, the doctor will push the catheter into the internal carotid artery. When in place, the doctor injects about 15-18 ml of contrast agent and conducts a cone-beam computed tomography to create an image of the blood vessels in the brain.
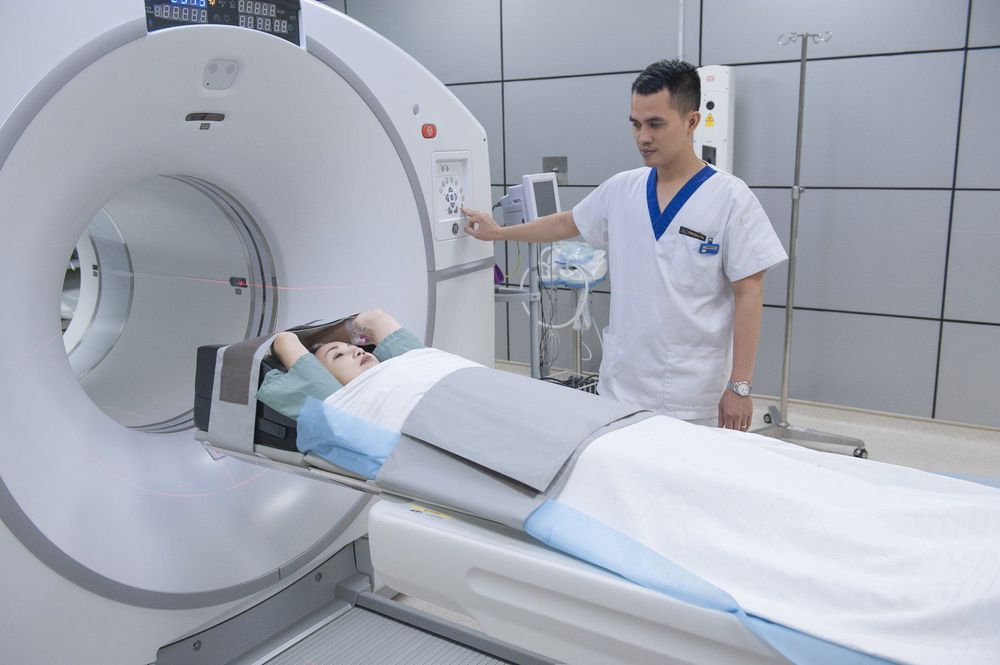
Chụp cắt lớp vi tính chẩn đoán phình động mạch não
Vinmec International General Hospital has applied modern examination techniques to improve the quality of medical examination and treatment for all customers. Accordingly, the doctors who carry out the procedures are all well-trained doctors with high expertise, thus giving accurate results, making a significant contribution to the identification of the disease and the stage of the disease. offer the optimal treatment regimen for customers.
Master. Doctor. Tong Diu Huong has more than 10 years of experience in the field of specialized imaging in diseases on images Ultrasound, X-ray, multi-slice CT, Magnetic resonance in diseases of the nervous system, digestive system , urology, cardiology, musculoskeletal... Besides, there are interventional imaging techniques, fine needle aspiration cells under the guidance of ultrasound and computed tomography.