This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Vu Thi Hau - Radiologist - Department of Diagnostic Imaging and Nuclear Medicine - Vinmec Times City International General Hospital.Small bowel tumor is a rare disease and difficult to detect and diagnose in the early stages. Small bowel CT scan is a modern diagnostic technique that allows finding and detecting small bowel tumor lesions.
1. Overview of small bowel tumors
Among tumor diseases in the digestive tract, small bowel tumor is a rare disease, difficult to detect because the disease has no obvious clinical symptoms until the disease causes complications.Small bowel tumors have nearly 40 different histopathological types. Based on the cell origin, small bowel tumors are divided into 3 groups: epithelial, mesenchymal, and lymphoma.
Like other tumor diseases, small bowel tumors are divided into 2 types: benign and malignant.
Benign tumors include: lipomas (usually occurring in the ileum), leiomyomas, angiomas, polyps (Peutz-Jeghers syndrome). Malignant neoplasms include: adenocarcinoma, lymphoma and sarcoma. Diagnosis of small bowel tumors is difficult due to the long small intestine and the overlapping loops. Currently, small bowel computed tomography is considered a modern imaging technique that allows the best assessment of all lesions in the small intestine, as well as suggestive diagnosis, detection and classification of small bowel tumors.
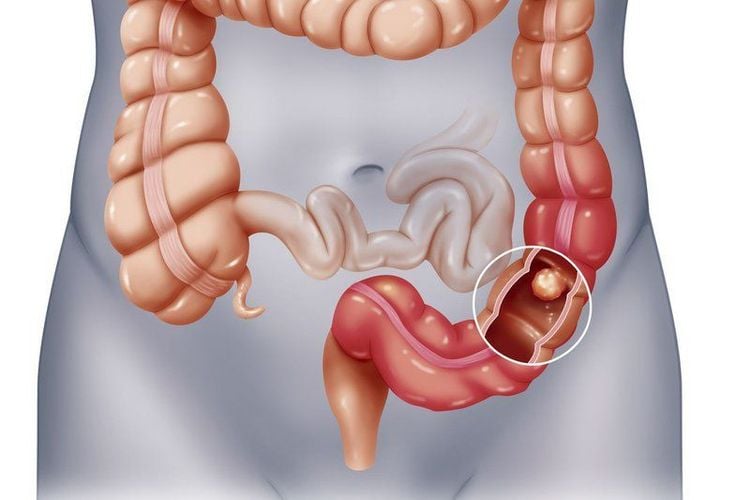
U ruột non là căn bệnh hiếm gặp và khó phát hiện
2. Small intestine CT scan technique
In cases where gastrointestinal endoscopy does not help to detect small bowel lesions, CT scan of the small intestine is indicated to look for intestinal lesions in cases of intestinal obstruction and gastrointestinal bleeding of unknown etiology.Small bowel computed tomography has the following advantages:
Allows survey of the entire length of the small intestine and the thickness of the intestinal wall, from lesions in the mucosa, submucosa to adjacent structures intra-abdominal as mesentery. Allows processing and reconstruction of intestinal structures in planes or three-dimensional space with high resolution and contrast. Allows assessment and staging of small bowel tumors. However, the disadvantage of this technique is that it is difficult to detect the disease at an early stage. To do this, it is necessary to use contrast medium to stretch the intestinal lumen and help show the structures more clearly, thereby allowing assessment and detection of lesions. When the intestinal lumen is not tight enough, it will affect the evaluation results of the characteristics, size, location and morphology of tumor lesions, especially small tumors and located at the site of the collapsed bowel.
Quy trình chụp CT ruột non
3. Computerized tomography X-ray images of small bowel tumors
Features of computed tomographic images of small bowel tumors allow the detection, diagnosis and classification of small bowel tumors.3.1 Morphology of the lesion
Based on the correlation between the lesion and the intestinal wall, there are 3 basic morphological forms of small bowel tumors, which are:Polyps growing into the intestinal lumen: Neuroendocrine tumors. Intestinal wall thickening: Common lesions are adenocarcinoma, lymphoma. Lesions growing outside the wall: The most common lesion is small bowel mesenchymal tumor.
3.2 Tumor absorbing properties
Each type of tumor has different drug absorption and depending on the time of investigation, the drug absorption of small bowel tumors is also different. Some studies have shown that the extent of tumor enhancement helps to suggest the diagnostic classification of small bowel tumors:Moderate to strong: Small bowel mesenchymal tumors and neuroendocrine tumors (which are rich in vessels). Poor treatment: adenocarcinoma and lymphadenopathy (poor vascular tumor).
Dưới hình ảnh X-quang, có thể phát hiện các loại u ruột non thường gặp
3.3 Other accompanying signs
Besides the morphological characteristics of the lesions and the drug-responsive nature of the tumor, recognition of other accompanying signs also helps to limit the scope of classification and diagnosis of small bowel tumors. The signs are:Enlarged lymph nodes Metastatic lymph node morphology: rich or poor vessel metastasis morphology, metastatic lymph node location (peritoneal metastasis).
4. Some X-ray features of common small bowel tumors
Lipoma: Lipoma is a common type of lipoma in the ileum. On imaging, lipoma has a homogeneous mass density, well-defined borderline and no drug absorption after injection. Adenoma: Adenoma is a benign tumor of the small intestine with clear contours with the intestinal wall and homogeneous absorption. Adenocarcinoma: Adenocarcinoma is a common malignancy in the small intestine, with focal thickened intestinal segments, irregular border. An adenocarcinoma is a poorly vascularized tumor, therefore, the drug absorption is moderate and heterogeneous. Small bowel mesenchymal tumor: On imaging, small bowel mesenchymal tumor is a solitary tumor, which is rich in vessels, so it has strong drug absorption. Lymphoma: Lymphoma is a common small bowel tumor. The imaging features of lymphoma are diverse because the tumor has many different groups. In which, the infiltrative form (most common) has diffuse and asymmetrical thickening of the intestinal wall, the border is not clear, the drug absorption is poor and homogeneous, the density is equal to or lower than that of muscle. Neuroendocrine tumors: On imaging, depending on the size, neuroendocrine tumors have different manifestations such as small nodules on the intestinal wall, polyps in the mucosa or submucosa and very strong drug absorption (in the arterial phase). ). To detect neuroendocrine tumors, the lumen must be sufficiently distended. Neuroendocrine tumors may also present as focal intestinal wall thickening.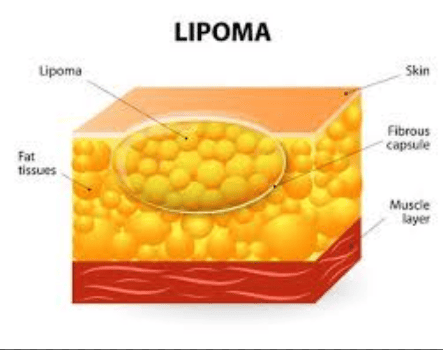
Dưới hình ảnh X-quang, u mỡ Lipoma có mật độ khối đậm độ mỡ đồng nhất, đường bờ giới hạn rõ và không bắt thuốc sau khi tiêm.
At Vinmec International General Hospital, CT scan of the small intestine is performed by a team of highly qualified and experienced doctors, with advanced equipment and machines, helping to give results quickly. fast and accurate.
Master. Doctor. Vu Thi Hau has many years of experience in the field of diagnostic imaging including magnetic resonance, CT and ultrasound. Graduated from Hanoi Medical University in 2014 with a BSNT and trained in France for 1 year. Currently engaged in the field of diagnosis of neurological, head and neck, ear - bone, musculoskeletal, digestive and urological diseases.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact the nationwide Vinmec Health System Hotline, or register online HERE.