This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Tong Van Hoan - Emergency Medicine Doctor - Emergency Department - Vinmec Danang International Hospital.Pulmonary embolism (PE) and deep venous thrombosis (DVT), collectively known as venous thromboembolism (VTE), are one of the three leading causes of cardiovascular death. large, after myocardial infarction and stroke. The mortality rate due to pulmonary embolism is 15% in 3 months after being diagnosed with myocardial infarction.. In which, the rate of patients with severe pulmonary embolism accounts for a low rate but the mortality rate is the highest. Thrombolysis and anticoagulation are the cornerstone of treatment, which has been shown to reduce mortality and reduce the risk of re-hospitalization in patients with severe pulmonary embolism.
The rate of pulmonary embolism increases, especially in critically ill patients, in intensive care patients, in immobile patients or in comorbidities... The use of thrombolytics in these patients is very common. Complications, in which compartment syndrome is a complication, although rare, there is a risk of death because when patients with surgical indications always have concomitant drug-related coagulation disorders, this syndrome often occurs. occurs in the extremities involved in establishing an intravenous line.
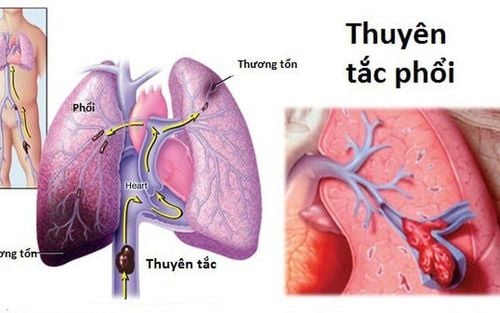
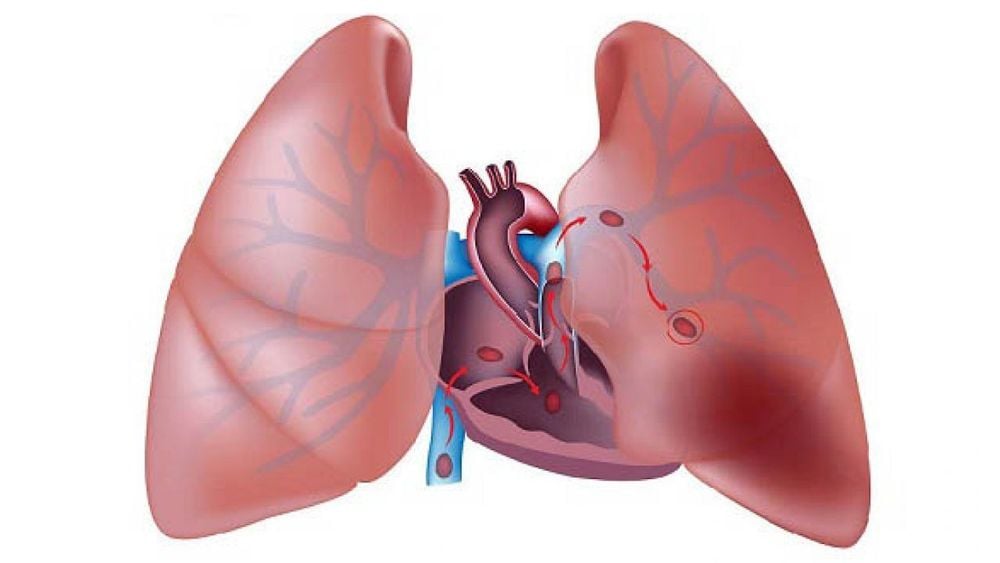
1. What is a pulmonary embolism?
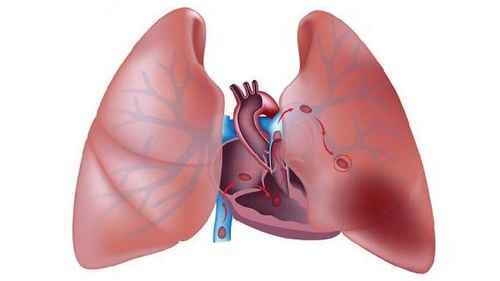
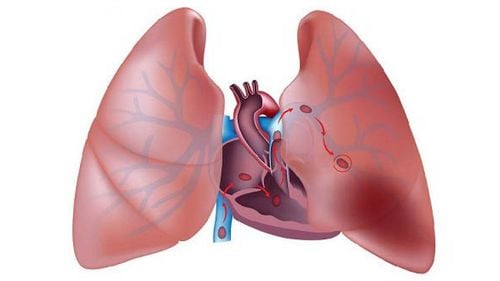
Pulmonary embolism is a pulmonary embolism usually caused by a blood clot from the deep veins of the lower extremities. A thrombus that has ruptured and is free-floating in a blood vessel can travel to another area of the body and block a blood vessel there, possibly with one or more thrombus.Normally, all the veins in the body carry blood into the larger vein, which then carries blood to the right heart and further into the pulmonary artery. If there is a thrombus in the venous system, the thrombus will travel from the veins to the right heart and then from the right heart into the main pulmonary artery and may become lodged there or continue to travel into one of the lungs.
When a thrombus lodges in the pulmonary artery, it blocks blood flow to the lungs to receive oxygen. If there is not enough blood to receive oxygen and move it to the left heart, oxygen levels in the body drop dangerously and can cause damage to all organs in the body, including the brain and kidneys. and heart.
In addition, due to obstruction in the lungs increases the pressure on the right heart. The right heart can be enlarged and contracted more heavily, even compressing, affecting the left heart. If the left heart cannot pump enough blood, blood pressure also drops. All of these effects can lead to death suddenly or shortly after a pulmonary embolism has occurred without treatment.
Pulmonary embolism is a common and fatal disease with a mortality rate of about 30% if left untreated. However, mortality can be significantly reduced through early diagnosis and treatment.
2. Thrombolytic therapy in the treatment of pulmonary embolism
Treatment for pulmonary embolism aims to dissolve the blood clot, prevent the clot from growing larger, and prevent new clots from forming. The first step in the treatment of a pulmonary embolism is to administer shock and provide oxygen. Anticoagulants such as heparin and warfarin are used to prevent blood clots from forming. Currently, fibrinolytic therapy is becoming more popular in the treatment of pulmonary embolism.Treatment with fibrinolytic therapy depends on the individual patient background and the physician's assessment of the risks versus benefits. The fibrinolytic drug is infused into the patient's body through a peripheral venous catheter. The FDA recommended infusion dose for alteplase is 100 mg continuously over 2 hours and other anticoagulants should be avoided during that time.
3. Compression of the cavity after fibrinolysis
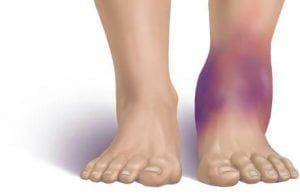
Compartment syndrome is an increase in soft tissue pressure in the closed cavity, leading to tissue ischemia. The main cause of compartment syndrome is fracture, trauma. In addition, there are other causes such as burns, intravenous infusion, bleeding, drug use, etc. Muscle groups and fascia structures of the limb are located in separate compartments. When the interstitial pressure in the compartments exceeds the capillary perfusion pressure, the circulatory system will be disturbed leading to compartment syndrome.Compression syndrome is thought to be a rare complication of fibrinolytic therapy. Tissue ischemia cannot be reversed without decompression. It can lead to skin necrosis and to volkman spasticity occurring in the extremities. Myoglobin is released as a result of cell destruction causing kidney dysfunction, which can even be fatal.
The most common treatment for compartment syndrome is to open the fascia of the muscle compartments. However, opening the fascia that creates an open wound in a patient taking thrombolytics carries a potential risk of death from coagulopathy.
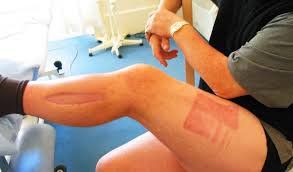
In summary, pulmonary embolism is 1 in 3 causes of cardiovascular death. Compartment syndrome is a rare complication that can occur in the treatment of pulmonary embolism with fibrinolytic therapy. When complications occur, it is necessary to immediately remove the infusion line, raise the limb, apply heat to accelerate the reabsorption of fluid, closely monitor the edema, and coordinate with the surgical specialist to consider surgical indications.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.