This is an automatically translated article.
Pulmonary artery obstruction is one of the dangerous and life-threatening blood vessel blockages. With timely intervention, treatment can be successful, but there are also many cases of dangerous complications.
1. What is pulmonary embolism?
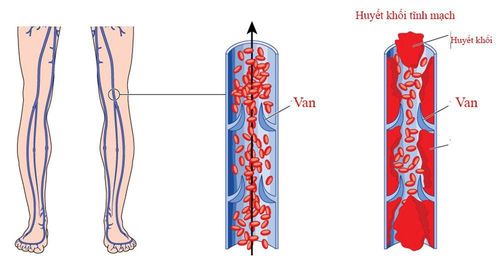
Pulmonary embolism is a blockage of an artery in the lungs, mainly caused by a blood clot (thrombus). This blockage can occur in the central artery of the lung or an artery near the edge of the lung. The clot causing the blockage can be large or small, and there can be one or more clots. Depending on these characteristics, pulmonary embolism can be severe or mild, determining the severity of the disease.
In addition, causes of pulmonary embolism include other factors such as:
Fat drops of broken bone marrow Using unclean needles, containing foreign bodies A small piece of tumor ruptured from a mass large tumor such as cancer Amniotic fluid embolism (in pregnant women) Large air bubbles in the veins.
2. Treatment of pulmonary embolism
Chụp X-quang có thể được sử dụng trong chẩn đoán thuyên tắc động mạch phổi
Pulmonary embolism is diagnosed based on the symptoms of the disease and the results of tests such as: X-ray, chest CT scan, CT lung scan, electrocardiogram, leg Doppler ultrasound , blood test, echocardiogram.
As mentioned, most cases of pulmonary embolism are caused by blood clots. To treat the disease, doctors will prescribe blood-thinning drugs and use thrombolytic therapies to prevent blood clotting.
In addition, the patient will have a blood test to determine which drug is right for him.
In case of severe pulmonary embolism, the patient will be indicated to perform surgery to place a mesh-shaped thrombofiltration device into the vena cava to prevent blood clots from entering the lungs.
3. Complications of pulmonary embolism
Pulmonary embolism can lead to complications such as:
Shock: blood clots affect the cardiac circulation, which can cause the heart to stop beating Cardiac circulation is affected for a long time, leading to an increased burden on the heart, for a long time. date the patient may have heart failure Recurrent pulmonary embolism: an embolism occurs again. In this case, the patient needs to use anticoagulation to prevent treatment complications: Complications from anticoagulant treatment such as bleeding elsewhere in the body (eg, stomach ulcers.. .) Increased blood pressure in the pulmonary vessels (pulmonary hypertension) in a patient with repeated pulmonary embolism.
4. Prognosis of pulmonary embolism

Trường hợp thuyên tắc mạch phổi được phát hiện sớm và điều trị kịp thời thì tiên lượng được đánh giá là tốt, bệnh nhân có thể hồi phục hoàn toàn
The prognosis of pulmonary embolism depends on the disease state, the time of initiation of treatment, and the patient's health.
In case pulmonary embolism is detected early and treated promptly, the prognosis is assessed as good, the patient can recover completely.
If the patient has serious comorbidities before the pulmonary embolism, the prognosis will be worse, the treatment is more difficult, and it can be life-threatening.
The most likely time for complications or danger is the first few hours after an embolism occurs or within the first six weeks after the first pulmonary embolism.
Currently, at Vinmec International General Hospital, fibrinolysis is being applied for emergency treatment of patients with pulmonary embolism. With modern imaging equipment, CT perfusion results are available within 7 minutes and performed routinely. The technique is performed by a team of qualified, experienced doctors and modern equipment and professional services.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.