This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with Specialist Doctor II Cao Thi Thanh - Pediatrician - Pediatrics - Neonatology - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.1. Hand, foot and mouth complications usually appear after how many days?
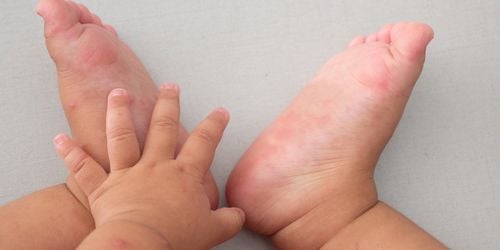
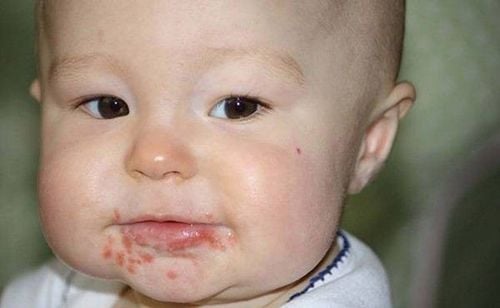
Hand, foot and mouth disease often occurs year-round in most localities. Around the time of the change of seasons, the weather changes from cold to hot, which is the time when the disease outbreaks strongly. The current hand, foot and mouth disease tends to increase in two periods, mainly from March to May and from September to December every year.Children with hand, foot and mouth disease when showing high fever and vomiting a lot can easily lead to complications. Hand, foot and mouth complications include neurological, cardiovascular and respiratory complications, usually appearing as early as day 2 to day 5 of the disease (in the full-blown phase). The dangerous complications of hand, foot and mouth disease are encephalitis - meningitis, myocarditis, acute pulmonary edema, the risk of death if not detected early and treated promptly. In the absence of complications, most children can fully recover 3 to 5 days after the full stage.
2. Complications of hand, foot and mouth disease
2.1. Neurological complications of hand, foot and mouth neurological complications include: encephalitis, brain stem inflammation, meningitis, encephalitis, with the following manifestations:Myoclonic tremor (startling): Convulsions short 1-2 seconds, mainly on the arms and legs, usually occurs when the baby is falling asleep or when the baby is lying on his back; Restlessness, drowsy, jittery, shaky limbs, unsteady gait, backward gaze; nystagmus; Increased muscle tone; Weakness, paralysis of limbs (acute flaccid paralysis); Cranial nerve palsy; Coma is a serious complication, often accompanied by respiratory failure, circulatory failure. 2.2. Cardiovascular and respiratory complications Cardiovascular and respiratory complications of hand, foot and mouth disease are: myocarditis, acute pulmonary edema, hypertension, heart failure and cardiovascular collapse. The telltale signs include:
Rapid pulse (over 150 beats/min); Slow capillary filling time (over 2 seconds); Manifestations of vasomotor disorders, skin with purple veins, sweating, cold extremities, may be localized in only one body area (hands or feet,...); Hand, foot and mouth complications in the early stages, high blood pressure (systolic blood pressure ≥ 110 mmHg (for children under 1 year old), ≥ 115 mmHg (for children aged 1-2 years), ≥ 120 mmHg (for children over 2 years old) The following stage: No pulse and blood pressure can be measured; Shortness of breath: The patient has rapid, shallow breathing, wheezing, chest indrawing, laryngeal stridor, irregular; Acute pulmonary edema : The baby has pink foam, difficulty breathing, pale skin, many moist rales in the lungs, blood in the endotracheal tube or pink foam 2.3. Complications in pregnancy Some evidence shows that hand, foot and mouth disease in 3 There is a risk of miscarriage in the first month of pregnancy, although the incidence is very rare. However, pregnant women should still take precautions by limiting close contact with people who are pregnant. Hand, foot and mouth disease can overcome the disease to give birth, and babies born with the disease usually show only mild symptoms.
Trắc nghiệm: các chỉ số cần chú ý về sự phát triển thể chất của trẻ
Chiều cao, cân nặng của bé ở từng giai đoạn nên là bao nhiêu là bình thường, bao nhiêu là bất thường? Cùng ThS.BS Ma Văn Thấm điểm lại xem bạn đã nắm được các chỉ số phát triển thể chất của bé chưa nhé!The following content is prepared under supervision of Thạc sĩ, Bác sĩ y khoa, Ma Văn Thấm , Nhi , Phòng khám Đa khoa Quốc tế Vinmec Dương Đông(Phú Quốc)
3. Recognizing hand, foot and mouth complications to take the child to the hospital

Startled and confused (usually when starting to fall asleep); Sleep a lot, lethargy; Trembling extremities, unsteady walking, weakness in arms and legs. 3.2. The child has had serious complications If the child has the following symptoms, they should be hospitalized urgently and closely monitored:
Tired breathing; Crying; Fluffy skin, cold extremities; Rapid pulse; High Blood Pressure.
4. What to do with hand foot mouth?
There is no specific treatment for hand, foot and mouth disease, the main treatment is to deal with symptoms. For symptoms of fever and pain, fever and pain relievers containing acetaminophen or ibuprofen can be used. It is important to increase rehydration to avoid dehydration.Children with hand, foot and mouth disease are easy to spread the virus to people around, so it is recommended that children stay out of school for about 10 days, limit contact with healthy children when sharing a house because the disease is easily spread between families. young. Currently, to prevent hand, foot and mouth disease caused by enterovirus 71 (the main cause of hand, foot and mouth complications), it is necessary to ensure hygiene when feeding, playing and living children.
If you have unusual symptoms, you should be examined and consulted with a specialist.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: Department of Preventive Medicine - Ministry of Health