This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Vu Tan Phuc - Gastroenterologist - Department of Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Phu Quoc International General HospitalThe worldwide prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is on the rise. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease can affect both adults and children and can lead to more complex and dangerous conditions.
1. Overview
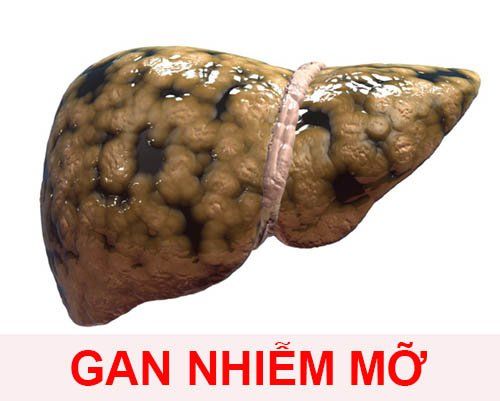
Currently, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is often a chronic disease, often seen in patients with obesity and weight gain. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease occurs when the fatty deposits in the liver reach 5% - 10% of the weight of the liver even when the patient drinks little or no alcohol. It is a fairly common disease and in mild cases it may not cause any signs or symptoms. However, in more severe cases, it can lead to inflammation and scarring in the liver tissue.Non-alcoholic fatty liver can be classified into 3 types, ranging from harmless to potentially life-threatening, including:
Pure nonalcoholic fatty liver: this is the mildest type. It is a condition in which fat accumulates in the liver but does not damage the liver, so the patient can still live and function normally. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH disease): in this type, fatty deposits can cause inflammation in the liver that leads to damage to liver organs, scarring, and reduced liver function. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with cirrhosis. From hepatitis will lead to severe scarring and liver failure (the liver can no longer function).
2. Non-alcoholic fatty liver symptoms
Simple fatty liver often has no symptoms or symptoms are not clear, some cases have symptoms similar to other diseases: fatigue, weakness, loss of appetite... In more severe stages such as cirrhosis, the Symptoms will become more obvious, such as jaundice, weight loss, nausea and pain in the right upper abdomen.About 10-25% of people with NASH will progress to scarring or cirrhosis of the liver. Symptoms of the disease include: weakness, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea, tarry stools, abdominal swelling in the liver and pain sensation, yellowing of the skin and eyes; confusion, difficulty concentrating, memory loss and hallucinations, itching and dilation of blood vessels under the skin, easy bleeding and bruising on the skin, red palms...
3. Risk of complications
Nonalcoholic fatty liver often contributes to an increased risk of cancer including: hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), colorectal cancer in men and breast cancer in women.Many recent studies show that at least nearly 50% of cases of degenerative liver cirrhosis occur in patients who already have obesity or type 2 diabetes. On the other hand, primary liver cancer (HCC) also occurs in patients with cirrhosis due to NASH disease with a risk of 8% to 15%. In most cases of cirrhosis, the fatty deposition of the liver has been degraded along with the inflammatory process and is called degenerative cirrhosis.
4. Treatment measures
Because the progression of NAFLD is slow, there is no effective therapy to date. However, the treatment regimen for fatty liver usually adheres to the following steps: losing weight if there is obesity, reducing cholesterol, triglyceride and high blood sugar levels will be quite helpful in the treatment of fatty liver.If the patient only has fatty liver, does not have NASH disease, and does not have cirrhosis, it is necessary to have a healthy diet and be physically active, not needing drug treatment. For patients with NAFLD liver disease, overweight, and obesity, a 7-10% weight loss is the treatment goal. Weight loss can reduce high blood transaminases and improve liver histology. For every 1% weight loss, the transaminase rate will decrease by 8%. Patients should consider eliminating high-fructose foods and processed foods that promote NAFLD. Instead, increase the amount of vegetables and fruits in the diet (every day should eat at least 300g of green vegetables, 200g of fresh ripe fruit). Prioritize choosing vegetable oil (except coconut oil) and limit animal fat (except fish fat). Patients should consider choosing an exercise depending on their preferences and regularly practice to increase health, improve fitness and lose weight. People should intend to periodically examine the liver for diagnosis, monitoring and appropriate treatment if there are symptoms of disease onset. For patients without the above conditions, but at high risk of disease progression (diabetes, metabolic syndrome, persistent elevation of liver enzymes, high necrotizing inflammation) may be treated with drugs to prevent progressive disease. Certain hypoglycemic or lipid-lowering medications are also quite helpful during NASH treatment. Weight loss through exercise and diet combined with insulin sensitizers can help restore a fatty liver to normal. Other therapies would be beneficial in slowing the progression of inflammation and fibrosis.
Besides, to determine the extent of damage in the liver parenchyma due to non-alcoholic fatty liver, patients can conduct ultrasound diagnosis of liver tissue elastography. Advantages of this ultrasound technique include:
Allows assessment of tissue stiffness. Allows assessment of the nature of the damaged tissue. Increase the specificity of the diagnosis, helping to narrow the indication for biopsy without missing the lesion. Liver elastography helps to evaluate cirrhosis non-invasively, with high accuracy, easy to perform.. If you have abnormal symptoms, you should be examined and consulted with a specialist.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.