This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Nguyen Thi Bich Nhi - Ophthalmologist - General Surgery Department - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital. The doctor has 10 years of experience in the field of ophthalmology.Reduced vision mainly occurs when the eye has a refractive error, disease, or injury. If not treated promptly, it can cause blurred vision, even blindness, greatly affecting learning and living.
1. What is a vision problem?
The eye is the most sensitive sensory organ. In fact, the brain spends more time processing visual information than other senses. It has a very important function of observation, so when vision is significantly impaired, you need to find a way to restore it, avoiding affecting daily activities and life.The most common form of vision impairment is refractive error (farsightedness, nearsightedness and astigmatism). Refractive error occurs when the cornea changes curvature, making the image of objects not focused on the retina, causing poor vision. Refractive errors can be corrected using glasses, contact lenses, or refractive surgery such as LASIK.
In addition, the eye is also functionally impaired, which occurs in diseases such as retinal detachment, macular degeneration, cataracts and glaucoma leading to blurred or no vision. The goals of treatment for these conditions are usually to restore vision, limit the severity of the disease, and preserve remaining vision.
2. Myopia
Myopia is the result of images of objects being brought forward rather than on the retina. This causes distant objects to appear blurry. Children with myopia are characterized by close vision when reading, and must sit at the top of the class to see words. It occurs in equal proportions between men and women. The increased prevalence of myopia in children has been attributed by researchers to excessive use of handheld devices and computers. Children with nearsightedness often progress to more severe if not treated and change appropriate habits.
Trẻ bị cận thị đặc trưng với các biểu hiện nhìn gần khi đọc sách
3. Farsightedness
Farsightedness is a condition in which the image of objects is focused behind the retina, making nearby objects blurry. Farsightedness is common in adults, when the size of the eyeball has matured. Because before that, the length of the eye was always changing, lasting nearly 1⁄3 between birth and 5 years of age.4. Astigmatism
Astigmatism is often associated with nearsightedness or farsightedness. It occurs when the cornea is no longer curved like it was originally, causing the eye to lack a focus point. People with astigmatism have unstable vision, sometimes seeing clearly, other times seeing blurry. Astigmatism is usually present from birth, most people have it but it takes a long time to be discovered. In addition, the degree of astigmatism also changed little over time.
Loạn thị thường xuất hiện từ khi sinh ra
5. Presbyopia
Presbyopia usually begins around age 40. It occurs when the eye loses its ability to focus at near or far. When reading a book at a moderate distance, reading for a while, then blurred vision. That's why most older people need to rely on glasses to read. Bifocals allow the wearer to see both near and far objects clearly.6. Retinal detachment
The retina helps light rays form images in the brain by converting light signals into nerve impulses. It's like a smooth wallpaper inside the eyeball. Areas of the cornea that are thin or damaged can form small holes that allow fluid in the eye to seep behind the retina, causing retinal detachment.Retinal detachment is painless but it can lead to many serious complications if not treated promptly:
Moderate or severe myopia Anterior eye surgery or trauma Anterior retinal detachment Thins the walls of the retina more.
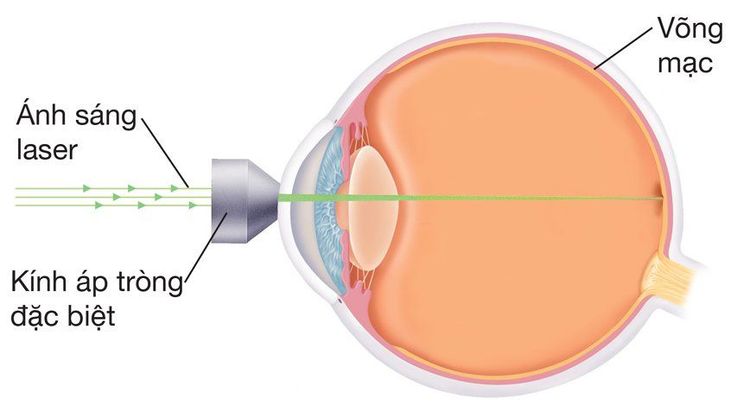
Bong võng mạc có thể điều trị bằng lazer
7. Color Blindness
Color blindness occurs mainly due to disturbances in light-sensitive cells, which are cones and rods. In which, cones receive strong light stimulation and rod cells receive low light stimulation.Color blindness occurs when these two types of cells are deficient or dysfunctional. The disease is more common in men than women, accounting for 8% of all men. Children are at risk of color blindness inherited from their families. There are very few people who are completely color blind, that is, only see gray when observing all things around.
8. Goosebumps
Night blindness - difficulty seeing in low light - occurs when rod photoreceptors are reduced. The following factors increase the risk of night blindness:Liver dysfunction Vitamin A deficiency Hereditary diseases of the retina, such as retinitis pigmentosa Cataracts.
Thiếu vitamin A làm tăng nguy cơ mắc bệnh quáng gà
9. Eye fatigue
Eye fatigue occurs when the eye has to work continuously for a long time or has a refractive error that has not been examined to determine the disease. Usually, it usually appears when you drive, watch movies or read books, use the computer.Familiar symptoms of eye strain include:
Headache Forehead pain Eye fatigue Eye strain Eye fatigue quickly disappears if the eyes are given a chance to rest or refraction problems are resolved. If you wear prescription glasses, recurring eye strain could be a sign that you need to readjust your glasses. You should give your eyes a break every hour to help reduce eye strain, especially when working at a computer.
10. Cataract
The lens acts as a lens, helping to display images of objects in the retina. It accounts for 1/3 of a person's visual capacity. Cataracts occur when the lens changes from clear to opaque. This prevents light from entering the eye or restricts it, making things appear blurry. It's even worse when seen at night.Cataracts are the leading cause of blindness, accounting for more than 20 million cases worldwide. Cataract surgery is the most frequently performed surgery in the United States, with approximately 3 million cases per year. The surgery is performed by implanting a clear artificial lens to replace the cloudy lens. Most of the cases after surgery restore their vision.

Đục thủy tinh thể có thể là nguyên nhân gây mù
11. Conjunctivitis
The conjunctiva can become inflamed for many reasons. Most cases of conjunctivitis are predictable, and the inflammation usually clears up after a few days. Although infectious conjunctivitis can be very contagious, it is rarely serious and usually does not cause permanent vision damage if detected and treated promptly.There are several forms of infectious conjunctivitis:
Bacterial conjunctivitis usually infects both eyes and produces a lot of pus and mucus. It is treated with antibiotic eye drops. Viral conjunctivitis usually begins in one eye, causing watery eyes. The other eye followed after a few days. Like the common cold, this infection clears up without treatment. Neonatal conjunctivitis is a rare form of acute conjunctivitis in neonates. The infection is passed from mother to baby during birth. It needs to be treated immediately to prevent permanent eye damage or blindness. Children can also get infections in places other than the eyes, such as the lungs.
12. Glaucoma
More than 2 million American adults have Glaucoma each year, making it one of the leading causes of irreversible vision loss. Glaucoma includes:Chronic open-angle glaucoma (COAG), which accounts for 90% of all cases in the US, usually presents in middle age and appears to be partly genetic. Angle-closure glaucoma can be chronic or acute. Chronic is a slow progression of the disease, but can turn into an acute episode suddenly. With acute, the patient presents with sudden pain and blurred vision, and requires immediate medical attention. Secondary glaucoma is associated with eye disease or eye injury, steroid drug use.
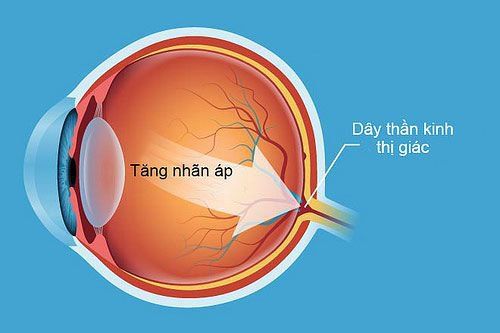
Tăng nhãn áp là bệnh lý thường gặp ở mắt
13. Macular Degeneration
Macular degeneration is the leading cause of vision loss in the US, with millions of older adults showing signs of the disorder. Because symptoms usually don't appear in people younger than 55, the disorder is more accurately called age-related macular degeneration (AMD).AMD affects central vision, detailed vision, essential when you drive, read, and work that requires close vision to sewing. The manifestation of AMD is that when you look at an image, you cannot see the center of the image but only the surrounding area (peripheral vision is preserved). AMD disorder occurs in two forms, dry and wet. The wet form is rare and requires immediate medical attention. If AMD is treated late, it can lead to loss of central vision.
14. Strabismus, Strabismus
In the eye, there are six eye muscles that help it rotate in all directions. The eyes do not look straight ahead when the eyes are balanced because there is an imbalance of eye muscles, strong muscles will pull the eyeballs towards themselves more than weak muscles. If the eye is turned inward, it is called an esotropia, and if the eye is turned outward, it is called an exotropia. There are many treatments for strabismus depending on the cause, mainly eye muscle surgery, or some people needing glasses.
Mắt lác có thể điều trị bằng phương pháp phẫu thuật
15. Amblyopia
Double vision occurs when two eyes look at different images. In infants and young children, the brain will not tolerate double vision and will shut off vision in the weaker eye. This loss of vision while the eye is still healthy is called Amblyopia. Treatment of amblyopia in children by strengthening weaker eye activity.Not all cases of strabismus develop into amblyopia and all cases of amblyopia are caused by strabismus. For example, infants with severe congenital cataracts in one eye will develop amblyopia, unless surgically replaces the cloudy lens. Amblyopia can also be caused by other eye problems such as:
Ptosis (drooping eyelids). Severe refractive error in one eye: If an infant has one eye with farsightedness, farsightedness, or astigmatism that is much more severe than in the other eye, amblyopia may develop. If you are experiencing vision problems, go to a medical facility immediately to be examined and treated by a doctor as soon as possible. Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital has vision-related service packages such as:
Refractive error screening package Cataract surgery consultation and examination package Ortho-K package.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.