This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor II Tran Van Trong - Specialist in Pediatric Surgery, Plastic Surgery - Aesthetics - Department of General Surgery - Vinmec Danang International Hospital.1. Overview of thoracic deformities
It is caused by a defect in the formation of the sternum, bone, and costal cartilages.Because it rarely affects the patient's life function and progresses slowly over time, most children come to the clinic and are diagnosed when they are adults or adults.
Definitive diagnosis is based on clinical examination, routine chest X-ray, chest CT.
Indications for treatment are mostly due to aesthetic factors, rarely due to respiratory-circulatory function problems. The main treatment technique is plastic surgery. The results of surgery, despite many advances in recent years, are still limited.
2. Classification of common thoracic deformities
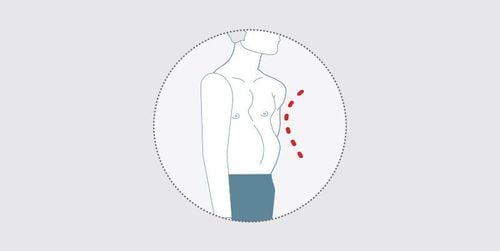
Concave breast disease Chicken breast breast Open breastbone.Trắc nghiệm: Nhận biết sớm dấu hiệu chậm phát triển thể chất và trí tuệ ở trẻ
Nếu 6 tuổi không biết đếm số, 7 tuổi vẫn chưa phân biệt được giữa thực tế và tưởng tượng thì có thể bé chậm phát triển thể chất và trí tuệ hơn so với bạn bè cùng lứa. Bạn đã nhận biết được các dấu hiệu bất thường sớm này chưa? Cùng làm nhanh bài trắc nghiệm sau để trang bị thêm kiến thức cho mình nhé!
The following content is prepared under supervision of Thạc sĩ, Bác sĩ y khoa, Ma Văn Thấm , Nhi , Phòng khám Đa khoa Quốc tế Vinmec Dương Đông(Phú Quốc)
3. Diagnosis and principles of treatment of various types of thoracic deformities
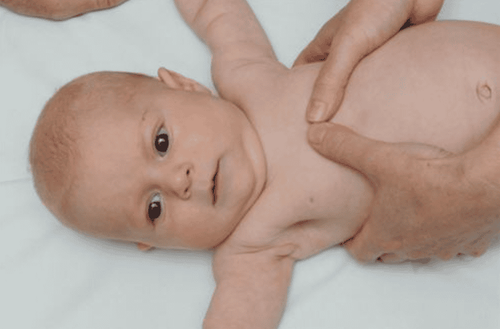
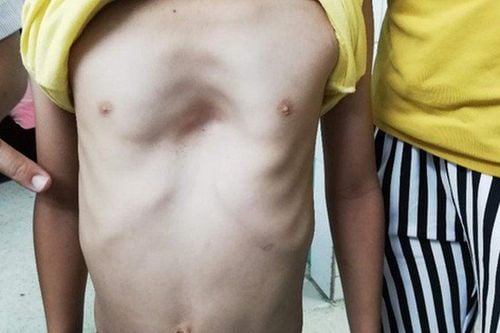
3.1. Concave chest disease The specific disease name is concave chest, concave chest or funnel chest. This is the most common chest wall deformity (90%), with an incidence of about 1/300 to 1/400 of new-borns, male/female ratio about 3/1.* Clinical manifestations:
+ Functional symptoms – whole body:
Usually there is nothing typical, patients and families often know they have anomalies since childhood but come to the clinic late. When that child is older, due to more chest concave expression and inferiority complex in daily life. Some symptoms may appear in patients with very severe thoracic cavity, during early adolescence (when the skeletal system develops rapidly and the child participates in strenuous physical activities), such as: cough, shortness of breath, prolonged chest pain, tachypnea, tachycardia, rapid fatigue on exertion,... + Symptoms in the thorax:
Anterior chest wall concave inward, symmetrical or asymmetrical . The deepest point is usually just above the sternum. This sign is most important in the diagnosis. In addition, the rib cage is flatter than usual. The mandibular region and the 1st and 2nd ribs showed no abnormal mass. The region of 2/3 below the sternum and along with the rib cartilage attached along the sides, curves to the back. The sternum usually curves forward. The abdomen above the navel is often enlarged, giving the sign of a bloated belly. In severe malformations, the apex can be displaced to the left thorax, sometimes with an abnormal heart murmur. * Subclinical manifestations:
X-ray of the thorax straight, inclined: to evaluate the posterior concave state of the sternum on the slant film, through which it is possible to calculate the low thoracic index.\ CT thoracic scanner: to measure only severe number, Haller concave index, or concave index: the ratio of the width of the ribcage (A) to the distance between the anterior aspect of the spine and the posterior surface of the sternum at its most concave (C). Normal A/C is about 2.56 at any age. Severe depression when the severity index is > 3.25 Pulmonary function measurement: low value, can see a decrease in vital capacity and maximal tidal volume in severe cases. Echocardiography: sometimes with combined cardiopulmonary injury (mitral regurgitation, atrial perforation). Electrocardiogram: can show right rectilinear, ST-T depression, right bundle branch block. * Indications for thoracotomy treatment:
Clinically, severe chest concavity and Haller index > 3.25 are important factors for indications for surgery. Age of surgery: The most suitable age for surgery is children over 3 years old because at this stage the operation is convenient for anesthesia, surgeons, and children: Children > 6 years old have good long-term results after surgery. than. * Treatment methods:
+ Conservative treatment: historical, not currently in use. Such as: exercise, physical therapy.
+ Filled with artificial material injected under the skin anteriorly with concave sternum.
+ Plastic surgery treatment:
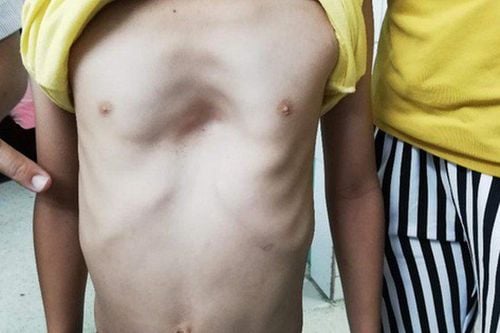
Small techniques: Brown technique (releases the attachments of the diaphragm and associated organizations on the back under the sternum). Shaping large straight muscles for young children. Major interventions on the chest wall: popularly applied in the past 20-30 years, now almost abandoned. Currently, the minimal intervention method (Nuss) is the most popular method today. 3.2. Chicken Breasts Chicken breasts are much rarer than concave breasts. The entire anterior thorax consists of the costal cartilages and the sternum protrudes anteriorly like a chicken breast. There is a possibility of major and recent minimally invasive surgical treatment.
Carefully differentiate from sternal ridges, severe congenital heart disease, or severe bronchial disease.
3.3. Sternal regurgitation is a disease of a partial defect in the sternum, usually in the sternum region. The disease is rarer than the above diseases. The sternal defect may be slightly recessed and through which the heart or major blood vessels pulsating under the skin can be palpated. Should have surgery to reconstruct the sternum.
4. Rare types of thoracic malformation
Poland syndrome. Heart outside the chest. Cantrell's Pentateuch. Marfan syndrome. Noonan syndrome. Congenital thoracic atrophy. Thoracic vertebrae dysplasia.Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.